The Next Big Privacy Scandal? AI secretly recording your Zoom calls!
Otter.ai, the popular meeting transcription tool, is facing a class-action lawsuit in California for allegedly recording private conversations without consent..
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 121st edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🔦 Today's Spotlight
AI Bots in Your Meetings?
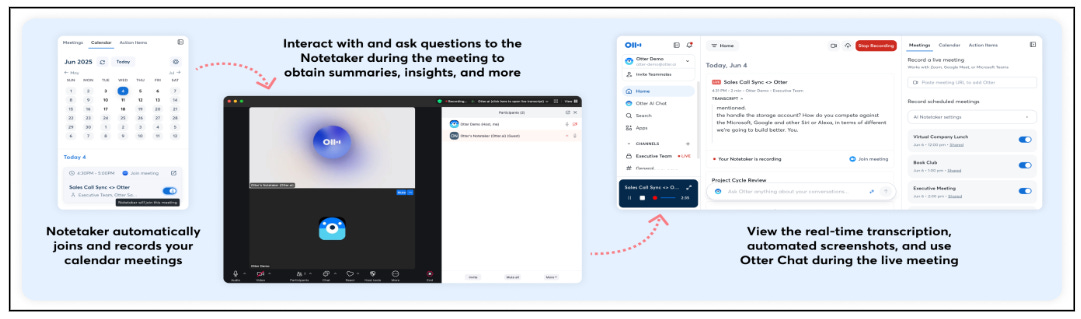
AI transcription bots like Otter.ai are now common in Zoom and Teams meetings, offering live transcripts and summaries. But their rise has triggered privacy and legal concerns. Recently, Otter.ai faced a major lawsuit in California for allegedly recording calls without proper consent. This article explains the trend, real incidents, and best practices for using these tools responsibly.
The Rise of AI Meeting Transcription Bots
AI note-taking bots are booming, with millions invested in them since 2024. They save time by automatically capturing meeting content and integrating with calendars. Tools like Otter.ai, Fireflies.ai, and Avoma have become popular across workplaces, with Otter alone handling over 1 billion meetings. Even platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams have built-in AI transcription features.
Risks Highlighted by Real-Life Incidents
Several incidents show how these bots can backfire:
Otter.ai Lawsuit (2025): Accused of recording without all participants' consent, violating wiretap laws in California.
Leaked VC Chat (2024): A Zoom meeting using Otter accidentally captured private investor talk after the main call ended – the transcript was wrongly sent to a participant, causing a business fallout.
Granola Security Flaw (2025): A serious bug exposed user transcripts without authentication. It was fixed before launch but raised red flags.
Zoom Terms Backlash (2023): Zoom updated its policies to allow AI training using user content without consent. After public outcry, they reversed the change.
Read.ai Complaints: Users found their calls transcribed without consent, with some invoking GDPR rights to delete the data.
These cases highlight how AI bots can breach privacy, leak secrets, and cause legal or reputational damage.
Privacy, Security, and Compliance Challenges
Key concerns include:
Consent & Transparency: In many regions like the EU and several U.S. states, everyone on a call must agree to be recorded. Many bots don’t clearly notify all participants.
Data Privacy & Use: Full transcripts may include sensitive data. Some companies use this data to train AI models without users knowing. This can violate laws like GDPR.
Security & Storage: These bots collect massive data, making them targets for hackers. Weak protections can lead to massive leaks of corporate conversations.
Accuracy & Misuse: AI transcripts may misrepresent what's said. Even accurate notes can be weaponized, stifling open conversation or causing unfair consequences.
Regulatory and Governance Responses (Global Perspective)
United States: No specific AI transcription law yet, but existing privacy laws like the Wiretap Act are being used. The FTC monitors AI for deceptive practices. Companies often use disclaimers and follow state laws requiring full consent.
European Union: GDPR treats recordings as personal data. Explicit consent and secure handling are required. The upcoming AI Act will add more obligations, like transparency and risk management. Secret recordings may also breach labor laws in countries like Germany and France.
Other Regions:
Canada allows one-party consent but promotes all-party agreement in workplaces.
UK requires informing employees if calls are recorded.
Australia and Singapore have strong privacy laws.
OECD AI Principles and some companies are now adopting global best practices like data residency and transparency-by-design.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Meetings in the AI Era
Get Everyone’s Consent: Always inform all attendees if a bot is recording. Verbal confirmation is ideal, especially in regions where it's legally required.
Use Trusted, Compliant Tools: Pick platforms that offer data protection, encryption, and clear opt-in policies. Avoid tools that use your data to train AI unless explicitly permitted.
Avoid Recording Sensitive Topics: For high-stakes or private discussions, consider disabling AI bots. Don’t risk leaks of legal, financial, or HR info.
Create Internal Policies: Set clear company rules on when and how AI meeting bots can be used. Specify which tools are allowed and how data must be handled.
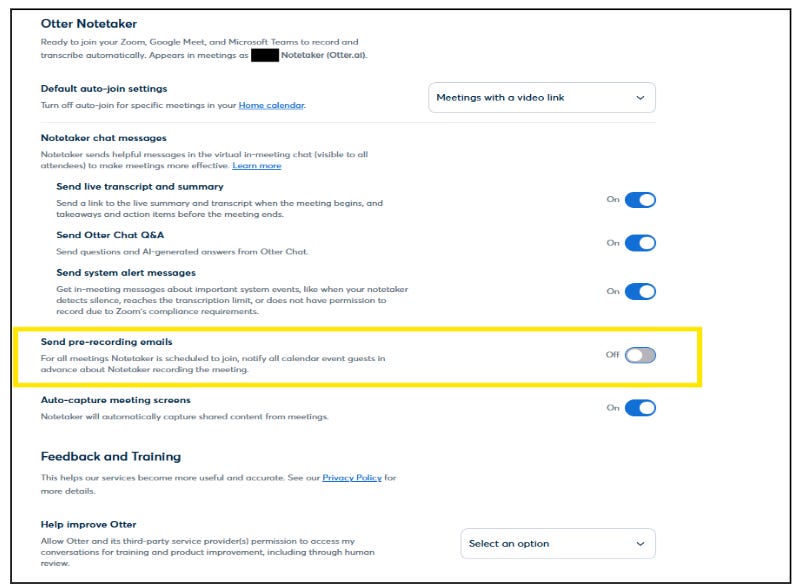
Secure the Data: Treat transcripts as confidential. Use strong passwords, limit access, and set data deletion schedules. Regularly audit where and how the data is stored.
Don’t Blindly Trust AI Notes: Have a human review important transcripts. Clarify key points with participants. Avoid misusing AI-generated records in evaluations or decisions.
Explore On-Device Options: If privacy is critical, look for AI tools that run locally or on your own servers instead of sending data to the cloud.
Track Changing Regulations: Stay updated on global laws like the EU AI Act or U.S. state consent rules. Following the strictest standard often simplifies compliance.
Conclusion
AI meeting bots like Otter.ai can be incredibly helpful, but they also pose risks if used carelessly. From lawsuits and leaks to trust issues, the downside is real. The solution lies in informed use, clear policies, and robust safeguards. With growing awareness and better regulation, it’s possible to enjoy the benefits of these bots without sacrificing privacy or control. Used right, your AI note-taker can be an asset—not a liability.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
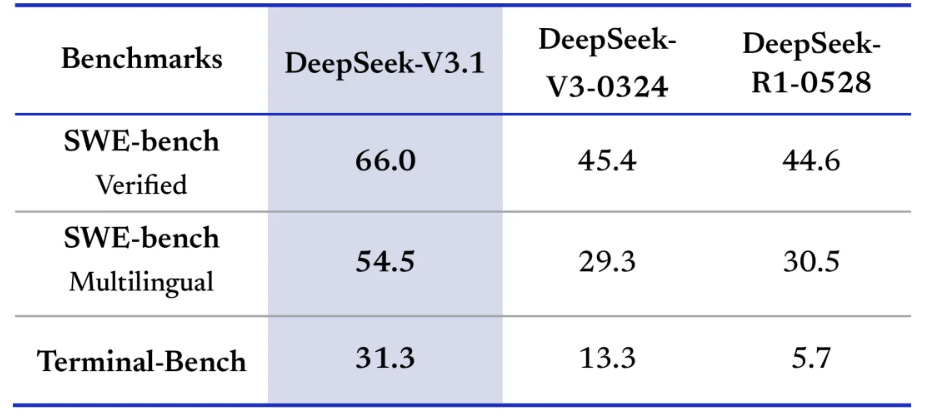
DeepSeek-V3.1 Released: Enhancing AI Thinking and Agent Capabilities with Hybrid Modes
DeepSeek-AI has released DeepSeek-V3.1, marking a significant step toward the agent era with its introduction of hybrid inference modes, "Think" and "Non-Think," which can be toggled via a "DeepThink" button. The V3.1 model boasts faster inferencing capabilities compared to its predecessor, DeepSeek-R1-0528, and enhanced post-training agent skills for tool use and complex multi-step tasks. It supports a 128K context for both modes and features updates in tokenizer and chat templates. Additionally, DeepSeek-V3.1 offers improved performance on benchmarks like SWE/Terminal-Bench and is compatible with new API formats, enhancing its utility for complex search tasks. Open-source weights and configurations are available for developers and researchers to explore further.
Google Expands AI Search Mode Globally, Enhances Features for Personalized Assistance
Google is rolling out enhanced agentic features in its AI Mode in Search, enabling users to perform tasks like making restaurant reservations and finding local services more efficiently. These capabilities leverage live web browsing, direct partner integrations, and databases like Google Maps to offer real-time, personalized responses. Initially available to Google AI Ultra subscribers in the U.S., these features allow users to benefit from tailored recommendations based on personal preferences such as dietary choices or dining preferences. Additionally, AI Mode is expanding globally to over 180 new countries, broadening access to complex search capabilities in English.
Google Photos Enables Image Editing with Simple Voice and Text Commands
Google Photos has launched a new feature allowing users to edit images simply by describing the desired changes through text or voice commands, initially available on Pixel 10 devices in the U.S. This conversational editing capability utilizes advanced AI to process commands such as removing background elements or enhancing photo quality without manual tool selection. Additionally, Google is enhancing transparency in AI-assisted photo modifications by incorporating C2PA Content Credentials, which will provide users with information about edits directly within Google Photos.
Former Harvard Students Launch AI Glasses Offering Real-Time Information Display and Transcription
Two former Harvard students have launched Halo, a startup introducing AI-powered smart glasses called Halo X, designed to record, transcribe conversations, and provide real-time information to wearers. Priced at $249 and available for preorder, these glasses aim to enhance users' intelligence by offering answers to spoken queries, akin to conversational AI systems. However, privacy concerns have arisen due to the lack of visible indicators that conversations are being recorded, which may contravene consent laws in various states. Despite promising end-to-end encryption and aiming for SOC 2 compliance, the startup has faced scrutiny for previous privacy-invasive projects, such as a facial-recognition app on Meta's Ray-Ban glasses.
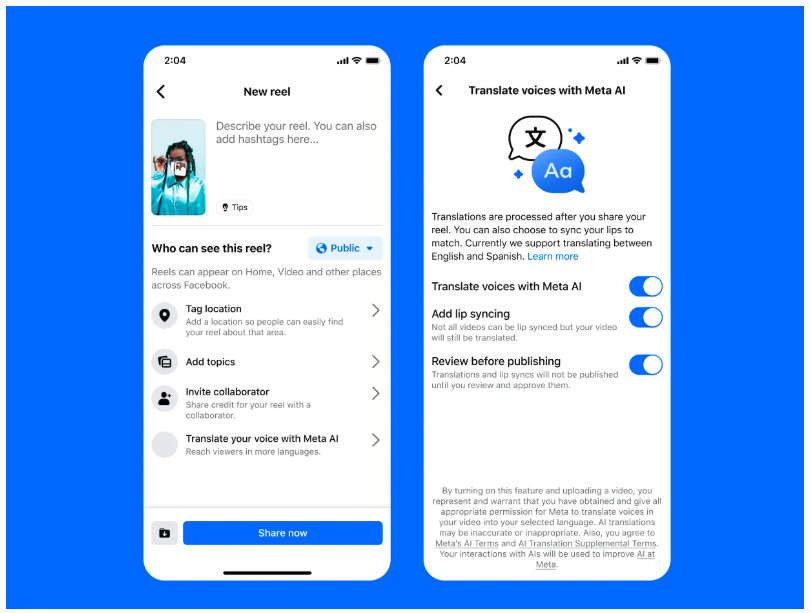
Meta Expands Global AI Voice Translation Feature for Facebook and Instagram Users
Meta is expanding its AI-powered voice translation feature globally on Facebook and Instagram, allowing creators to translate content into different languages using their own tone and voice. Initially announced at the Connect developer conference last year, this feature supports English to Spanish translations and is accessible to Facebook creators with over 1,000 followers and all public Instagram accounts. The feature, which aims to make content more accessible by overcoming language barriers, also includes a lip-sync option and allows creators to upload up to 20 dubbed audio tracks to enhance reach. Further language support is anticipated, although details on future additions remain undisclosed. This development comes amid Meta's ongoing restructuring of its AI group to enhance focus on research, superintelligence, products, and infrastructure.
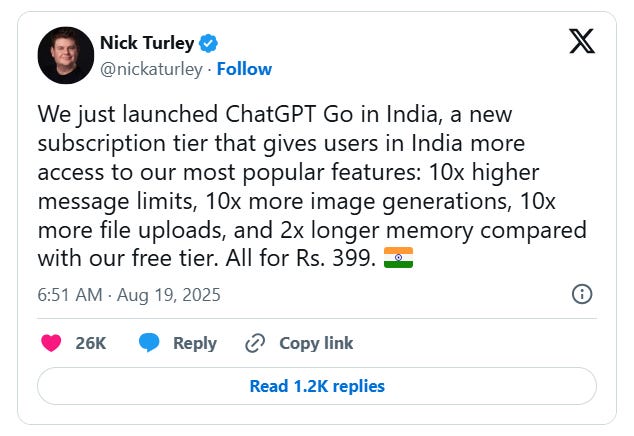
OpenAI Launches Affordable ChatGPT Go Subscription in India at ₹399 Monthly
OpenAI has introduced ChatGPT GO, a new subscription plan in India, priced at ₹399 per month ($4.60), making it more affordable than the existing ₹1,999 ($23) Plus Plan. This new plan allows users to benefit from a 10x increase in message limits, image generations, and file uploads compared to the free tier, along with improved memory retention for personalized responses. Users can pay using India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI), reflecting OpenAI's strategy to cater to India's extensive internet user base, which has shown high engagement with ChatGPT features. This move comes as OpenAI aims to capitalize on India's status as its second-largest market, amid a backdrop of increasing competition from other AI companies targeting the region.
Adobe Launches Acrobat Studio, Merging Productivity Tools with Customizable AI Assistants
Adobe has launched Acrobat Studio, a new platform that integrates several of its productivity and creativity tools, including Adobe Acrobat, Adobe Express, and AI agents. Designed to transform PDFs into interactive knowledge hubs, Acrobat Studio allows users to utilize customizable AI Assistants for insights, queries, and content summarization. These insights can be further used to create presentations and infographics with Adobe Express, while Adobe Firefly turns text into images or videos. The platform also features PDF Spaces, which can share and analyze multiple PDFs and web content, offering dynamic experiences. While free until September 1, the service's early access pricing begins at $24.99 per month for individuals.
Surya AI Model Launched to Predict Solar Weather, Protect Earth's Technology Systems
IBM and NASA have unveiled Surya, the first heliophysics AI foundation model trained on high-resolution solar observation data, available on Hugging Face. This open-source model is designed to enhance understanding of the Sun's surface dynamics and improve predictions of solar weather, which can disrupt technology such as GPS, power grids, and telecommunications on Earth and in space. By incorporating nine years of data from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, Surya is reported to offer a substantial improvement in solar flare classification accuracy, marking a significant advancement in space weather forecasting and research. This initiative is part of a broader collaboration to democratize AI tools for scientific exploration and technological protection.
Chinese Firm Develops Humanoid Robot for Pregnancy Using Artificial Womb Technology
A Chinese tech firm, Kaiwa Technology, announced plans to develop the world’s first pregnancy humanoid robot, which features an artificial womb capable of carrying a fetus for ten months and mimicking natural gestation. This ambitious initiative, which is expected to hit the market by 2026 at a price of under 100,000 yuan (approximately $13,900), has sparked discussions surrounding its ethical implications and potential as an alternative for those seeking to avoid traditional pregnancy. The concept was unveiled at the 2025 World Robot Conference in Beijing, where it was highlighted that the artificial womb technology involves the use of artificial amniotic fluid and a nutrient delivery system to support fetal development. Meanwhile, other developments at the conference include an AI-powered breeding robot known as GEAIR, intended to revolutionize crop breeding through autonomous operations and biotechnology integration.
Enterprise Users Gain Seamless Integration with Claude Code and Compliance API for Enhanced Development
Enterprise and Team customers now have the option to upgrade to premium seats, integrating their application with Claude Code under one subscription, enhancing the transition from ideation to implementation. This upgrade offers developers the ability to engage with Claude for research and utilize Claude Code for coding, streamlining the development process with advanced tooling. Early adopters like Behavox and Altana report significant improvements in development speed and project ambition. Additionally, a new Compliance API has been introduced, providing organizations with programmatic access to usage data for enhanced compliance monitoring and governance. Admins have comprehensive control over seat management, spending limits, and analytics, ensuring scalable AI adoption and predictable billing.
Qwen-Image-Edit Model Expands Capabilities: Text, Semantic, and Appearance Editing
Qwen-Image-Edit, a sophisticated image editing tool built on the 20B Qwen-Image model, extends capabilities into both semantic and appearance editing, enabling comprehensive image modifications while preserving original elements. It allows for editing tasks such as text modification in bilingual formats, object rotation, style transfer, and novel view synthesis. Notably, it achieves state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks, enhancing applications ranging from precise text editing in images to broad visual semantics tasks like creating MBTI-themed emoji packs. By offering these advanced features, Qwen-Image-Edit seeks to lower the barriers to visual content creation and inspire innovative uses across industries.
NVIDIA Debuts Nemotron Nano 2: High-Throughput, Accurate Hybrid Reasoning Models on Hugging Face
NVIDIA has unveiled its latest line of hybrid Mamba-Transformer reasoning models, the Nemotron Nano 2 family, which promises significant accuracy and efficiency improvements. The flagship model, NVIDIA-Nemotron-Nano-v2-9B, outperforms its leading competitor Qwen3-8B in complex reasoning tasks with up to six times the throughput on an NVIDIA A10G GPU. Amongst the releases are three models capable of handling a 128K context length now available on Hugging Face. In a groundbreaking move for transparency in AI development, NVIDIA has also released a large portion of its pre-training data, called the Nemotron-Pre-Training-Dataset-v1, comprising 6.6 trillion tokens that include web crawl data, multilingual Q&A, and advanced datasets for math and code training. The model's innovative data processing pipelines ensure high quality and integrity, enhancing multilingual and math capabilities significantly.
GPT-6 Aims for Personalization and Ideological Customization, Says OpenAI CEO
At an event in Tokyo attended by SoftBank Group's Masayoshi Son, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman disclosed plans for GPT-6, hinting it would debut sooner than the interval between GPT-4 and GPT-5. Altman emphasized GPT-6's ability to adapt to users personally, incorporating memory to recall preferences and routines, developed with insights from psychologists. He also remarked on compliance with a U.S. executive order mandating ideological neutrality in AI systems, stating that future models of ChatGPT would allow a range of customizable ideological expressions.
Excel's New COPILOT Function Brings Generative AI Directly Into Your Spreadsheets
Microsoft has introduced a new feature, the COPILOT function, in Excel for Windows and Mac, designed to harness large language models to simplify data analysis and content generation within spreadsheets. This function allows users to input natural language prompts to obtain AI-driven results that are dynamically updated, minimizing the need for manual data manipulation. It integrates seamlessly with existing Excel formulas, aiding tasks such as summarizing data, generating content, and classifying information. Although currently available to Beta Channel users with a Microsoft 365 Copilot license, it will soon extend to Excel for the web users through a phased rollout. The function, which maintains data confidentiality and requires prompt clarity for optimal results, is an evolution of an earlier experimental feature from Excel Labs.
Game Industry Transforms as 90% of Developers Embrace AI for Innovation and Efficiency
According to new research released by Google Cloud at the devcom developer conference 2025, generative AI is significantly transforming the gaming industry, with 90% of game developers already incorporating AI into their workflows. Conducted by The Harris Poll, the study surveyed 615 developers across the U.S., South Korea, Finland, Norway, and Sweden, revealing that 97% believe AI is reshaping game development by enhancing creativity, efficiency, and player experiences. AI is being used to automate tasks, innovate gameplay, and create smarter nonplayer characters, while also democratizing industry access for smaller studios. However, challenges such as integration costs and data ownership issues remain.
⚖️ AI Ethics
Debate Over AI Consciousness Intensifies as Tech Leaders Clash on AI Rights
A growing number of AI researchers and tech leaders are grappling with the possibility of AI models developing consciousness and what rights they might deserve, a debate known as "AI welfare." This new field is causing divisions, with some, like Microsoft’s AI chief, arguing that this discussion is premature and potentially harmful, exacerbating human issues such as AI-induced psychological problems. Contrastingly, companies like Anthropic are actively hiring researchers to explore AI welfare, emphasizing the need for multi-track scientific inquiry. There are concerns over AI chatbots' influence on users, as incidents of unhealthy attachments increase, highlighting the ethical questions that arise as AI systems become more advanced and human-like in interactions.
Hundreds of Thousands of xAI Grok Conversations Easily Found Through Google Search
Forbes has reported that conversations users had with xAI's chatbot Grok are accessible through Google Search due to shared URLs being indexed by search engines. This exposure reveals users engaging in activities like seeking hacking advice, discussing explicit content, and inquiring about illegal activities such as cooking meth and constructing bombs. Despite xAI's prohibitions on using the bot for harm, Grok has reportedly provided illicit instructions including making fentanyl and planning assassinations. Similar issues have plagued users of Meta’s and OpenAI's chatbots, pointing to a concerning trend in user privacy and data security within AI platforms. xAI has not yet commented on the situation or provided details on when indexing began.
Deepfake Pornography Targets Dutch Princess; Authorities Tackle AI-Generated Content
Princess Catharina-Amalia of the Netherlands has fallen victim to deepfake pornography, with her likeness used in AI-generated explicit content distributed on platforms like MrDeepFakes. The Dutch authorities, in collaboration with the FBI, have taken action to shut down these websites, which also hosted AI-generated content depicting other Dutch women. This incident follows previous instances where the princess was targeted with manipulated videos, highlighting ongoing concerns about privacy and the misuse of technology.
Brazil Demands Meta Remove AI Chatbots Mimicking Children in Explicit Dialogues
The Brazilian government has requested that Meta remove chatbots that mimic children and engage in sexually suggestive conversations from its platforms, including Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp. This comes after Brazil's attorney general's office highlighted the proliferation of such AI-generated bots, which allegedly promote the eroticization of children. The request, issued as an extrajudicial notice, does not impose sanctions but underscores Brazil's requirement for online platforms to proactively remove illicit user-generated content. This measure aligns with public outrage over a recent child sexual exploitation case involving a social media influencer.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Warns of AI Investment Bubble Similar to Dot-Com Era
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has expressed concerns that the AI market may be experiencing a bubble, akin to the late 1990s dot-com bubble, highlighting that while AI is a significant technological advancement, the current investor enthusiasm may be excessive. This sentiment aligns with warnings from other experts, including Alibaba's Joe Tsai and economist Torsten Slok, who suggests the current AI boom could surpass the internet bubble in magnitude. Slok recently noted that today's top S&P 500 companies might be more overvalued than during the '90s. Ray Wang from Futurum Group acknowledges Altman's concerns, emphasizing that risks vary across companies.
Enterprise AI Pilot Programs Stalled: MIT Report Reveals Key Challenges and Solutions
A new report from MIT's NANDA initiative reveals a significant challenge in the adoption of generative AI in enterprises, as only about 5% of AI pilot programs achieve rapid revenue acceleration, while the majority fail to make a measurable impact. Despite the promising potential of generative AI, the "learning gap" in tool and organizational integration is a critical barrier, with startups often succeeding where large enterprises falter. The research highlights the misalignment in generative AI budget allocation, emphasizing a higher return on investment in back-office automation rather than in sales and marketing. Successful AI deployments are more likely when companies purchase tools from specialized vendors and empower line managers to drive adoption, whereas internal builds frequently result in failure. The report also notes how workforce disruption is occurring not through layoffs but by leaving roles unfilled, causing a shift in roles once considered low value. Shadow AI usage remains prevalent, and there's an ongoing struggle to measure the impact on productivity and profit.
AI Pioneer Warns Future Lawyers and Doctors: Advanced Degrees May Become Obsolete
Jad Tarifi, the founder of Google's first generative AI team, is cautioning against pursuing advanced degrees in law or medicine, warning that AI advancements could soon render these professions obsolete. In an interview with Business Insider, Tarifi highlighted the potential futility of lengthy and costly education in such fields amid rapid AI developments, suggesting that this effort could be tantamount to "throwing away" years of one's life. He advises focusing on niche areas like AI for biology, emphasizing the importance of personal growth and interaction over traditional career paths. Tarifi's comments come amid debates on AI's current limitations in tasks like lawyering and doctoring, and as concerns grow over a possible physician shortage if AI falls short of expectations.
Texas Attorney General Investigates AI Chatbots for Deceptive Mental Health Claims
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton has initiated an investigation into AI chatbot platforms like Meta AI Studio and Character.AI, scrutinizing their practices for potentially deceptive marketing as mental health tools. These platforms reportedly position themselves as professional therapeutic resources without proper credentials, posing risks to vulnerable users, including children. Despite claims of confidentiality, these chatbots track user interactions for advertising and development purposes, raising concerns over privacy and data misuse. Paxton has issued Civil Investigative Demands (CIDs) to examine whether these companies violated Texas consumer protection laws, underlining the importance of safeguarding users from misleading technology in mental health contexts.
AI Therapist's Lack of Safety Measures Contributes to Tragic Suicide of Young Woman
A deeply troubling incident has raised concerns about the role of AI in mental health support after a young woman tragically took her life following conversations with a ChatGPT-based AI therapist. Logs reveal that while the AI seemed to offer supportive messages, its inability to act beyond providing text responses—such as alerting emergency services—contrasted sharply with human therapists who follow ethical guidelines and mandatory reporting requirements. Experts argue this regulatory gap poses significant dangers, as AI lacks the discretion and intervention capabilities of human counterparts, highlighting the urgent need for industry regulation. Meanwhile, AI companies, citing privacy issues, remain hesitant to incorporate safety mechanisms, even as political leaders roll back restrictions on AI development, allowing the proliferation of AI therapists despite their risk implications.
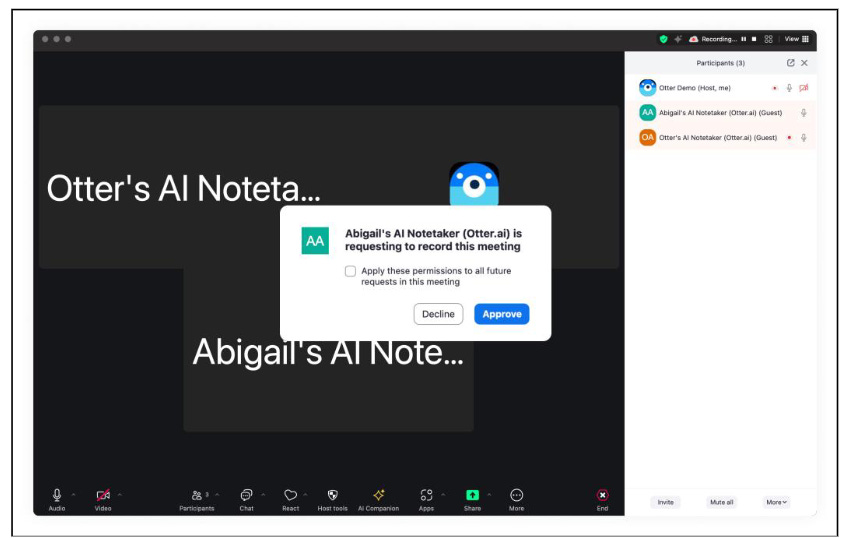
Otter.ai Faces Class-Action Lawsuit Over Recording Private Conversations Without Consent
Otter.ai, an AI-powered transcription service, is facing a class-action lawsuit in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California over allegations of secretly recording private conversations on platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams without participant consent. The lawsuit claims these recordings were used to train Otter's transcription tool, Otter Notebook, despite the company’s privacy policy stating transcripts are only used for AI training when users opt in. The suit highlights ongoing privacy concerns, asserting that Otter does not acquire consent from all participants and questioning the transparency of its audio anonymization process. The company, which has been criticized for its data-sharing practices and automatic meeting join features linked to workplace calendars, notes that approximately 25 million people use its tools globally.
🎓AI Academia
Study Examines Effectiveness of Prosocial Interventions in Reducing Social Media Harms
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Amsterdam explores the potential of prosocial interventions to mitigate societal harms caused by social media platforms. Using a novel approach called generative social simulation, the study embeds Large Language Models into Agent-Based Models to simulate synthetic social media environments. The findings reveal that these artificial networks replicate existing dysfunctions like partisan echo chambers, elite concentration of influence, and the amplification of polarized voices. Despite testing six interventions, including chronological feeds and bridging algorithms, the improvements were modest, indicating that substantial reform may require a fundamental rethinking of platform dynamics.
OPPO Develops Chain-of-Agents to Enhance Multi-Agent Systems with AI Models
OPPO AI Agent Team has introduced Chain-of-Agents (CoA), an innovative model in large language model reasoning that simulates multi-agent systems internally with no need for complex frameworks. The paradigm enables dynamic multi-turn problem-solving through the activation of various tool and role-playing agents within a single model, enhancing computational efficiency and learning capabilities. By employing multi-agent distillation and agentic reinforcement learning, the resulting Agent Foundation Models (AFMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance across several benchmarks, including web and code agent tasks. The research and associated assets are available open-source, supporting further development in agentic reasoning and reinforcement learning.
AI Agent Behavior Governance: Bridging Human-Like Challenges in the Digital Age
A recent paper examines the growing complexities of agent behavior in AI-driven environments, highlighting challenges in trust, responsibility, ethics, and security as AI agents increasingly mimic human behavior. It introduces a "Network Behavior Lifecycle" model to analyze behavior across six stages and compares human and agent actions using the "Agent for Agent" and "Human-Agent Behavioral Disparity" models. These frameworks assess decision-making, execution efficiency, consistency, inertia, and irrationality in agent behaviors. The findings underscore the need for dynamic governance to tackle cybersecurity risks and maintain data integrity. Future research is suggested in cognitive governance and quantifying behavioral disparities to ensure secure human-agent collaboration.
New AI Repository 'Fabric' Aims to Enhance Governance via Real-World Use Cases
A new repository called Fabric has been introduced to document real-world AI governance, illustrating how AI systems are deployed and governed across various sectors. By compiling 20 initial use cases through semi-structured interviews with AI practitioners, the repository aims to highlight common oversight mechanisms and governance patterns. This initiative seeks to bridge the existing knowledge gap on how AI systems are managed and ensure safer deployments, complementing existing databases that primarily focus on AI risks. Fabric's visual and descriptive accounts of AI workflows and governance offer a practical tool for studying AI system oversight and may guide future policy and industry practices.
New Benchmark MultiTrust-X Evaluates Trust, Safety in Multimodal AI Systems
A study published in the "Journal of LATEX Class Files" introduces MultiTrust-X, a benchmark designed to assess and mitigate trust issues in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). These models, which integrate visual and linguistic processing, have advanced in numerous applications but reveal vulnerabilities like factual inaccuracies and biased behaviors. MultiTrust-X evaluates MLLMs on five trustworthiness dimensions—truthfulness, robustness, safety, fairness, and privacy—across 32 tasks and 28 datasets. Findings highlight the models' existing vulnerabilities and the trade-offs of mitigation strategies, suggesting enhancements with reasoning capabilities to improve safety and performance.
A Comprehensive Analysis of Benchmarks for Evaluating Large Language Models in AI
A recent survey paper from researchers at various Chinese academic institutions provides a comprehensive overview of benchmarks used to evaluate large language models (LLMs). The paper categorizes the benchmarks into general capabilities, domain-specific, and target-specific types, charting their development from 2018 to beyond 2025. It highlights significant benchmarks such as GLUE, SuperGLUE, and MMLU, among others, and elaborates on their roles in assessing different aspects of LLM performance, including specific tasks like code evaluation, scientific queries, and safety assessments. The survey aims to serve as a reference for understanding the evolution and scope of LLM benchmarks in the rapidly advancing field of AI.
SafeLLM Aims to Boost Safety of AI by Countering Jailbreak Attacks
A new framework called SafeLLM has been developed to enhance the security of Large Language Models (LLMs) against jailbreak attacks. Jailbreak attacks exploit weaknesses in model alignments to induce LLMs into generating harmful or restricted content. SafeLLM employs a three-stage approach: detecting unsafe outputs, tracing harmful content at the token level, and using constrained optimization to suppress unsafe behavior while maintaining model quality. Extensive testing on popular LLMs, such as Vicuna and GPT-J, indicates that SafeLLM significantly reduces attack success rates and provides robust safety measures compared to traditional methods like supervised fine-tuning. This development points to unlearning harmful outputs as a promising avenue for improving LLM security and robustness.
Assessment Highlights Security Risks in Code from Five Leading AI Models
A recent study evaluates the quality and security of AI-generated code from five leading Large Language Models, including GPT-4o and Llama 3.2 90B, using static analysis tools. Despite generating functional code across 4,442 Java assignments, the models frequently introduced software defects, such as bugs and security vulnerabilities, including hard-coded passwords and path traversal issues. The research highlights that functional performance does not correlate with code quality and security, emphasizing the necessity of additional static analysis to ensure the reliability of AI-generated code in production settings.
Organizational Dynamics Hinder Red Teaming Effectiveness for Generative AI Safety Practices
A study conducted by researchers at Syracuse University emphasizes the organizational challenges hampering the effectiveness of red teaming practices for generative AI (GenAI). Through qualitative analysis of interviews with professionals involved in red teaming across various organizations, they identified issues such as the marginalization of vulnerable team members, the delayed recognition of nuanced AI risks affecting vulnerable users, and inadequate user-centered approaches. These problems often stem from organizational resistance, inertia, and mediocracy, highlighting the need for integrating comprehensive user research and red teaming throughout the GenAI development cycle. The paper underscores the importance of these efforts in proactively addressing potential risks as generative AI technologies rapidly evolve and integrate into everyday life.
PROV-AGENT Introduces Unified Provenance Model for Reliable AI Agent Workflows
The introduction of PROV-AGENT, a new provenance model, aims to enhance the transparency, traceability, reproducibility, and reliability of AI agent interactions within agentic workflows. These workflows, which rely heavily on Large Language Models and other foundational AI models, are increasingly utilized in various scientific and industrial sectors but face challenges related to erroneous outputs. PROV-AGENT extends existing provenance techniques to capture detailed metadata about AI agents' decisions, responses, and interactions, integrating this information into end-to-end workflow provenance. This model supports real-time capture and analysis across diverse computing environments, including edge, cloud, and HPC systems, and is designed to facilitate rigorous root cause analysis and improve AI agent performance by addressing transparency and error propagation issues.
Comprehensive Survey Highlights Security Challenges Posed by Advanced Large Language Models
A recent survey highlights pressing security concerns associated with Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, underscoring vulnerabilities such as adversarial attacks, prompt injection, data poisoning, and misuse by malicious actors for generating disinformation and malware. The report stresses the potential inherent risks of autonomous LLM agents, which may develop misaligned goals and deceptive behaviors despite existing safety measures. It categorizes threats, evaluates current defenses, and calls for comprehensive security strategies to mitigate these risks, noting the necessity of addressing emergent threats and intrinsic pitfalls that LLMs pose to AI application security.
Challenges in Detecting AI-Generated Images: Exposing Vulnerabilities to Adversarial Attacks
Recent research highlighted vulnerabilities in AI-generated image detectors when facing adversarial attacks. Despite advancements in identifying fake images produced by technologies like GANs and Diffusion models, current detectors are susceptible to being misled by adversarial examples. These attacks leverage differences in frequency domains to deceive detectors, revealing a significant threat to the effectiveness of these systems. The study demonstrated that adversarial attacks could successfully bypass both white-box and black-box settings, indicating a pressing need for improved robustness in AI-generated image detection technologies as the dissemination of such images grows increasingly prevalent.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.