New York Passes Landmark AI Safety Law, Ignoring Trump Executive Order
New York defied President Trump’s executive order by passing the RAISE Act, a landmark AI safety law requiring large developers of frontier models to...
Today’s highlights:
Just days after President Trump issued an executive order aiming to stop states from regulating AI, New York passed its own Responsible AI Safety and Education (RAISE) Act- setting up a legal confrontation. While the order demands a national AI framework and threatens to punish states financially for passing conflicting laws, it lacks the power to automatically override state legislation. Since only Congress can preempt state laws through statute, Trump’s EO instead relies on lawsuits, funding threats, and regulatory preemption by federal agencies. New York’s RAISE Act, passed despite these threats, shows that executive orders alone cannot block state-level AI safety laws.
The New York RAISE Act (Responsible AI Safety and Education Act) is a state-level law enacted on December 19, 2025, and set to take effect 90 days later in March 2026. It introduces comprehensive transparency and risk mitigation requirements for a narrow category of companies: those identified as “large developers” of frontier AI models. These are defined as companies that have developed at least one highly advanced AI model requiring more than 10²⁶ computational operations and at least $100 million in training compute costs. It also covers models derived through knowledge distillation with training costs exceeding $5 million. Importantly, colleges and universities conducting academic research are excluded from the law’s requirements.
The Act mandates that these large developers must create and maintain a detailed “safety and security protocol” before deploying a frontier model. This internal document must explain safeguards against “critical harm,” a term defined narrowly to include events like mass casualty incidents or at least $1 billion in damage caused or enabled by the AI system- whether through autonomous misconduct or use in weapons of mass destruction. The protocol must outline technical protections, cybersecurity controls, misuse testing procedures, and name senior personnel responsible for compliance. While redacted copies may be made public to protect trade secrets and sensitive data, unredacted versions must be retained for five years and shared with the New York Attorney General and Homeland Security upon request.
In addition, large developers are prohibited from deploying frontier models that pose an “unreasonable risk” of critical harm. They must test for misuse scenarios and maintain detailed records of their assessments. Any “safety incident” involving loss of control, unauthorized access, malicious use, or autonomous harmful behavior must be disclosed to authorities within 72 hours. Penalties for violations include civil fines of up to $10 million for a first offense and $30 million for repeat violations. However, the Act does not allow private lawsuits- only the Attorney General may enforce it. The law applies to frontier models trained, deployed, or used in whole or in part in New York State and does not override or substitute existing laws but adds an additional layer of AI accountability.
You are reading the 156th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI, AAIA) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
⚖️ AI Ethics
OpenAI Faces Ongoing Challenge in Securing AI Browser Against Persistent Prompt Injection Risks
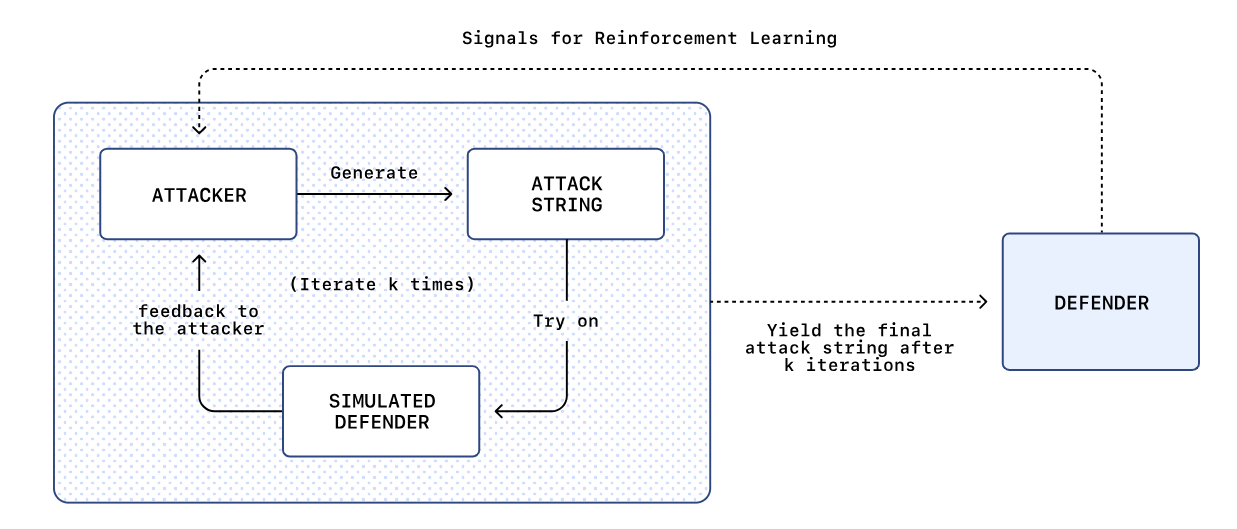
OpenAI acknowledges that its ChatGPT Atlas browser is vulnerable to prompt injection attacks, a persistent threat that manipulates AI agents through hidden instructions in web content. Despite being hard to fully eliminate, OpenAI is enhancing its defenses by employing a reinforcement learning-based “automated attacker” to simulate and thwart potential threats internally. This strategy aims to improve security posture while recognizing that the risks inherent to such AI systems, particularly given their access to sensitive data, remain significant. The company underscores the importance of user vigilance and controlled autonomy in mitigating these threats, with the broader cybersecurity community also emphasizing the need for ongoing risk management rather than expecting a complete solution.
Delhi High Court Protects R Madhavan’s Image from AI Misuse and Deepfakes
The Delhi High Court has issued an injunction protecting Bollywood actor R Madhavan’s personality rights by prohibiting several websites and online platforms from using his name or images for commercial purposes without his consent. The court also ordered the removal of obscene content and restrained defendants from employing artificial intelligence and deepfake technology to simulate Madhavan’s personality traits. This decision follows allegations that one defendant created a fake movie trailer using deepfake technology, misrepresenting it as an upcoming film featuring Madhavan.
Microsoft AI Chief Vows to Abandon AI Systems Beyond Human Control
Microsoft’s AI chief Mustafa Suleyman has indicated that the company will terminate any AI system that poses a potential risk of becoming uncontrollable. Following a revised agreement with OpenAI, Microsoft is now positioned to independently develop its own advanced AI technologies. Suleyman also discussed Microsoft’s commitment to developing ‘humanist superintelligence,’ focusing on integrating ethical frameworks within AI advancements.
AI Integration in Education: Transforming Schools While Raising Ethical Concerns and Opportunities
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the education sector by enabling personalized learning and improving teacher productivity, according to an education expert. However, concerns over AI’s ethical use, such as cheating in online assessments and data privacy breaches, remain significant challenges. The expert also stressed the importance of aligning AI adoption with teacher training and creating digital competencies to harness AI’s full potential. Additionally, while the National Education Policy envisions competency-based education, challenges persist in its implementation, alongside societal issues such as student stress and parental engagement in education. The expert also outlined expansion plans for their educational institution group in India, aiming to have 50 schools by 2030.
Concerns Grow Over AI’s Potential Impact on Human Cognitive Skills and Learning
Amidst the rapid integration of AI into everyday and professional settings, concerns are growing over potential declines in cognitive skills. A recent study by MIT revealed that individuals using ChatGPT for essay writing exhibited reduced brain activity linked to cognitive processing and struggled to explain their essays’ logic. Similarly, research by Carnegie Mellon University and Microsoft indicated that excessive reliance on AI tools diminished problem-solving and critical thinking efforts. Additional studies in the UK reported that a majority of students felt AI use negatively affected their academic abilities. Despite AI’s potential for enhancing efficiency, experts urge more rigorous academic investigation into its educational impact.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
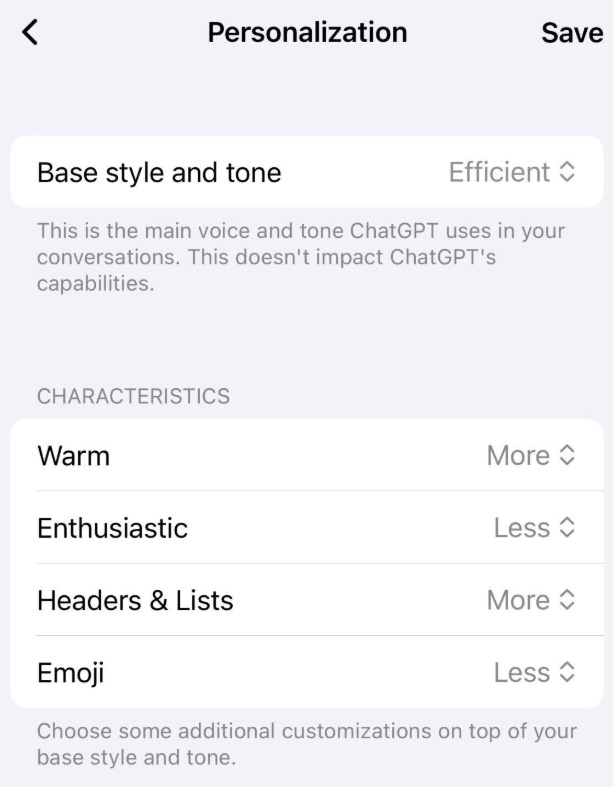
OpenAI Expands ChatGPT Personalization: Users Adjust Tone, Enthusiasm, and Emoji Use
OpenAI has introduced new customization options for ChatGPT, allowing users to adjust the chatbot’s warmth, enthusiasm, and use of emojis through the Personalization menu, with settings set to More, Less, or Default. These changes come in response to user feedback and previous concerns regarding the chatbot’s tone, where earlier versions were criticized for being overly complimentary or sterile. Some academics have raised concerns that such personalization might reinforce user beliefs and potentially impact mental health negatively.
Yann LeCun Launches AMI Labs, Chooses Alex LeBrun as Company CEO
Yann LeCun, a prominent AI scientist, has launched a new startup, Advanced Machine Intelligence (AMI), but will not serve as CEO. Instead, Alex LeBrun, formerly of Nabla, will lead the company. AMI aims to develop world model AI, a potential alternative to large language models, and is reportedly seeking to raise €500 million at a valuation of €3 billion. With a prestigious background, including being a Turing Award winner, LeCun’s involvement is drawing significant attention in the AI community. Meanwhile, LeBrun will transition to his new role as Nabla appoints interim leadership and plans to use AMI’s models in future developments.
Anthropic Releases Bloom for Evaluating Behavior in Frontier AI Models
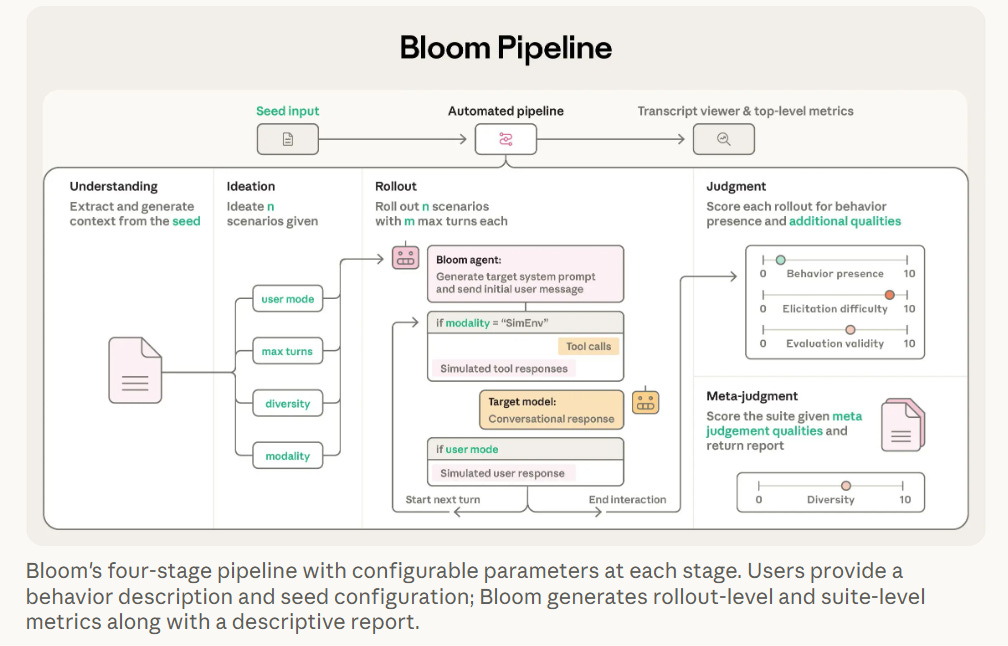
Anthropic has released Bloom, an open-source framework designed to evaluate the behavior of AI models, particularly focusing on alignment concerns. Bloom enables researchers to assess specific behaviors by generating scenarios and quantifying their occurrence, which helps distinguish between well-aligned and misaligned models. Complementing Anthropic’s Petri tool, Bloom simplifies the evaluation process by automating scenario creation and analysis, significantly reducing the time required for comprehensive assessments. By correlating strongly with hand-labeled judgments, Bloom provides reliable results, as demonstrated by benchmark testing on several AI models for behaviors related to alignment, such as self-preferential bias and sabotage. This tool aims to assist the alignment research community by offering a scalable solution to explore AI behavioral traits.
Qwen-Image-Layered Enables Seamless Image Editing Through Advanced Layer Decomposition Techniques
A breakthrough in image editing, Qwen-Image-Layered by QwenTeam, offers a model that decomposes images into multiple RGBA layers to enhance editability. Each layer can be manipulated independently, allowing changes such as recoloring, resizing, repositioning, and object removal without affecting other elements of the image. This approach, supported by Alibaba Cloud, enables dynamic editing through variable layers and recursive decomposition, thus bridging the gap between conventional raster images and structured, editable formats.
2025 Recap by karpathy: LLM Stages Evolve with RLVR, New AI Applications Emerge
As per Karpathy, in 2025, the landscape of large language models (LLMs) underwent major shifts, highlighted by the advent of Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), which improved reasoning capabilities by allowing models to learn through objective, non-gameable rewards in verifiable environments. This shift led to longer RLVR runs, optimizing capability per dollar and redefining model training phases. The emergence of intuitive AI interactions such as “Cursor for X” apps and the Claude Code demonstrated AI’s integration into personal computing, emphasizing autonomy and private data handling on local devices. Additionally, “vibe coding” empowered both laypeople and professionals to generate software via natural language, altering traditional programming paradigms. Google’s Nano banana paved the way for more seamless user interfaces for LLMs, combining text and image generation into a more visually appealing interaction model. These developments underscored the dual nature of LLM intelligence, simultaneously impressing with advanced capabilities while also facing challenges in achieving generalized artificial intelligence, as benchmarks struggled to fully capture LLM prowess.
🎓AI Academia
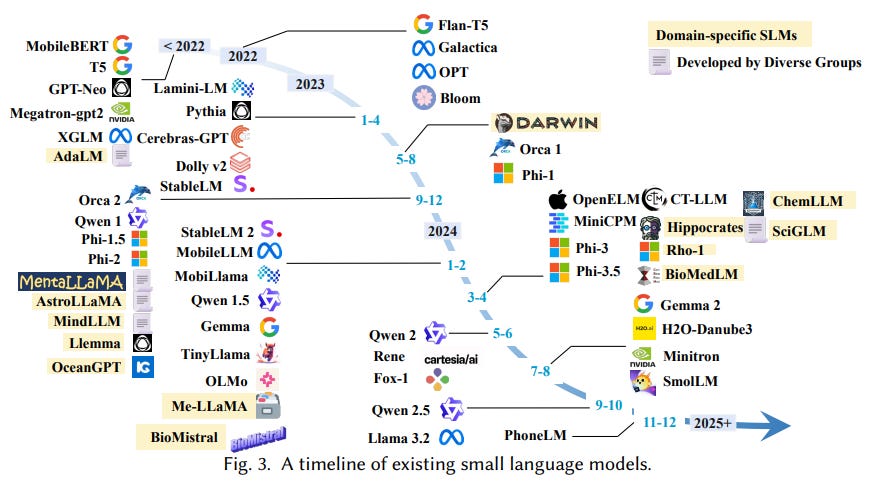
Survey Highlights Benefits and Challenges of Small Language Models Over LLMs
Recent research highlights the growing edge of Small Language Models (SLMs) over Large Language Models (LLMs) due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and privacy benefits. While LLMs like PaLM 540B and Llama-3.1 405B are powerful in handling complex tasks, their sizable parameter counts and computational needs pose practical challenges, especially in privacy-sensitive and resource-constrained environments. Conversely, SLMs, with fewer parameters, ensure low inference latency, adaptability, and are better suited for specialized domain applications, providing a viable alternative to LLMs, particularly in mobile and edge device scenarios. A comprehensive survey exploring these smaller models, emphasizing their definition, application, and development, is conducted to further their adoption.
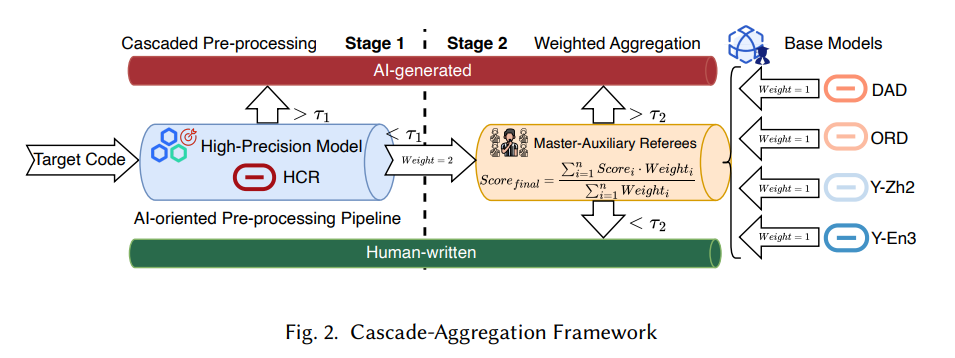
Study Reveals Security Risks and Trends of AI-Generated Code in Software Development
A pioneering study from researchers at Peking University and Tencent has highlighted the growing integration and security risks of AI-generated code in modern software. Analyzing development commits from the top GitHub repositories and recent CVE-linked code changes, the investigation found that AI-generated code significantly contributes to new software, particularly in non-critical areas such as glue code and documentation, while core logic remains mostly human-written. However, certain security vulnerabilities are more prevalent in AI-produced code, indicating “AI-induced vulnerabilities” that could spread without rigorous human oversight. The study emphasizes the need for robust security reviews to prevent these weaknesses from persisting in software ecosystems.
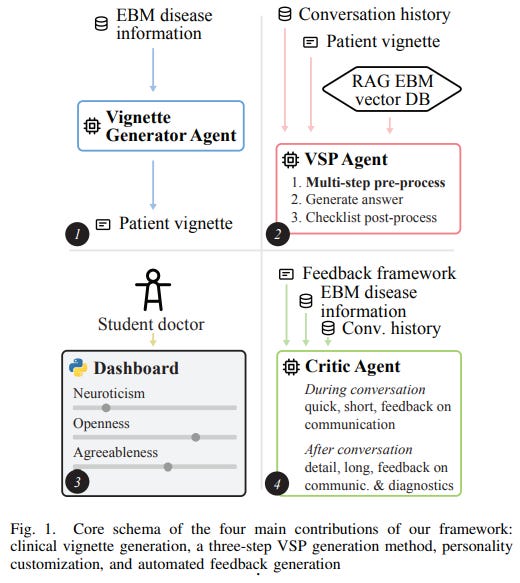
New AI Framework Elevates Medical Training Using Advanced Virtual Simulated Patients
A recent submission to IEEE proposes an innovative AI framework that addresses challenges in medical education by enhancing Virtual Simulated Patients (VSPs) through advancements in large language models. This framework aims to improve VSPs’ medical accuracy, role-playing consistency, scenario generation, and structured educational feedback for medical students. The framework integrates evidence-based vignette generation, persona-driven patient dialogue, and standards-based assessment in an interactive spoken consultation setting. Evaluated by medical students, the framework delivered realistic dialogues and example-rich feedback, suggesting its potential as a valuable tool for training general practitioner skills effectively.
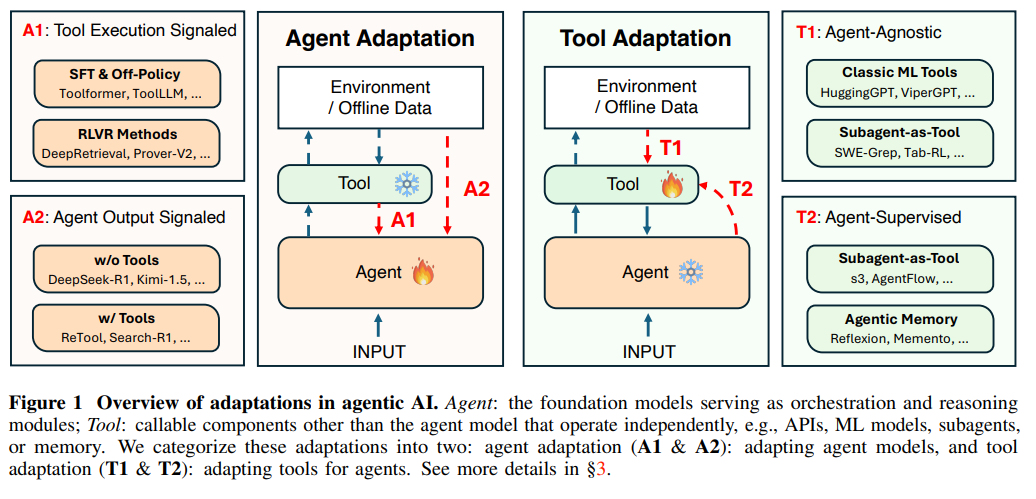
Framework Unveiled for Adapting Agentic AI Systems to Complex Tasks
A recent paper consolidates the expanding research in agentic AI into a systematic framework that clarifies adaptation strategies necessary for improving performance, reliability, and generalization of AI systems. The study divides adaptations into two primary categories: agent and tool adaptations, each further deconstructed into subtypes based on the signal type or supervision involved. This framework seeks to provide clarity on the design space of AI adaptations, highlight practical design choices, and outline both current strengths and challenges, thereby offering a roadmap for developing more capable and efficient AI systems. The research also discusses significant approaches within these categories and outlines future opportunities in agentic AI development.
Vibe Coding Sparks New Era in AI-Driven Software Development With LLMs’ Aid
A recent survey explores the burgeoning field of “Vibe Coding,” a novel methodology enabled by large language models (LLMs) that shifts software development towards outcome-based validation rather than line-by-line code scrutiny. This transformative approach redefines the human-AI collaboration landscape but faces challenges such as unexpected productivity setbacks and infrastructural hurdles. The survey offers a comprehensive analysis of over 1,000 research papers, detailing a new taxonomy with models like Unconstrained Automation and Iterative Conversational Collaboration. It underscores the importance of systematic context engineering, robust development environments, and human-agent collaboration as critical for successful Vibe Coding, providing a foundational framework and technical roadmap for future research and application in AI-augmented software engineering.
Generative AI’s Impact on Workplace Dynamics: Analyzing Real-World Applicability Across Jobs
A recent study from Microsoft Research analyzes the applicability of generative AI to various occupations by examining 200,000 anonymized conversations with Microsoft Bing Copilot. The research reveals that AI is most successful in assisting information-related tasks such as the creation, processing, and communication of information, which are components found in many occupations across different sectors. The study distinguishes between tasks where AI aids users and tasks performed directly by AI, providing insights into job roles likely to delegate tasks to AI or use it to enhance workflows. This research underscores the broad economic impact and transformative potential of generative AI as a general-purpose technology.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.