Merriam-Webster Declares 'Slop' as 2025 Word of the Year Amid AI Surge
Merriam-Webster named “slop” the Word of the Year, a term capturing society’s mounting frustration with the flood of low-quality AI-generated content..
Today’s highlights:
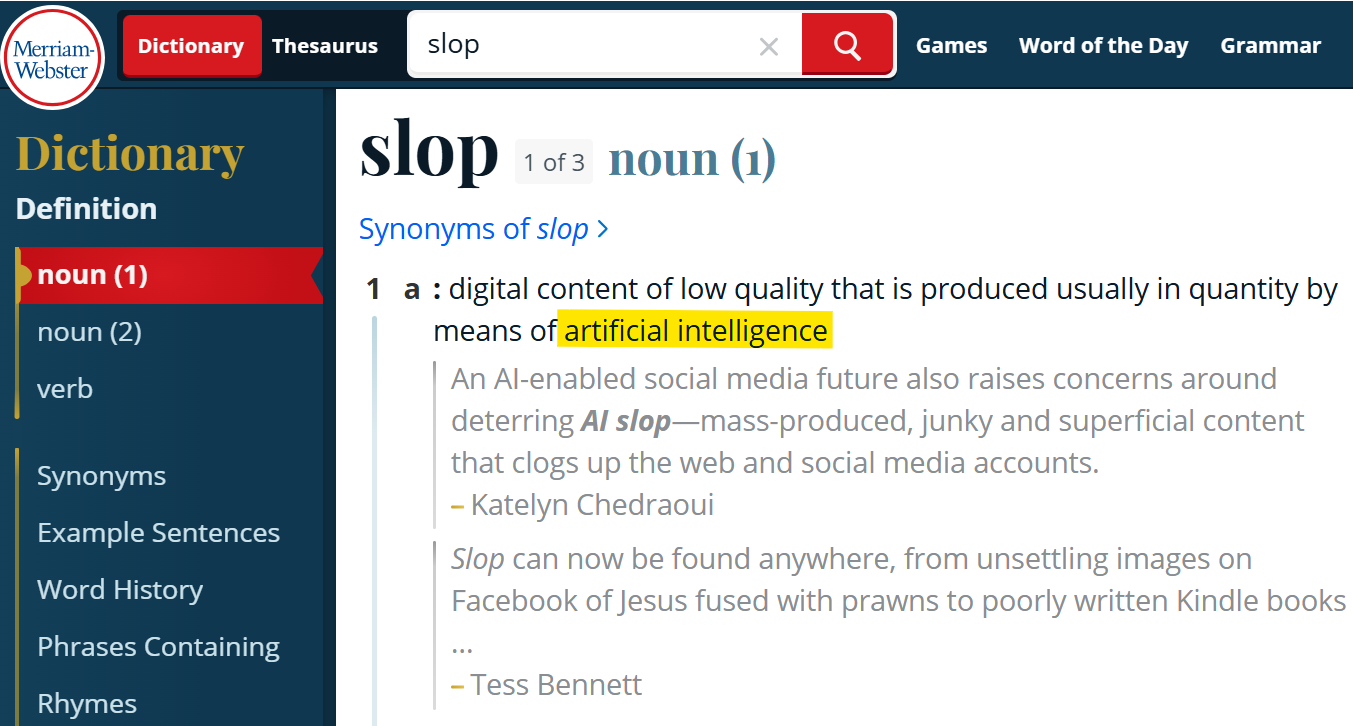
Merriam-Webster recently named “slop” as the Word of the Year 2025, defining it as “digital content of low quality that is produced usually in quantity by means of artificial intelligence.” The term captured the public’s growing frustration with AI-generated junk flooding the internet- content that feels soulless, spammy, and often meaningless. People began using “slop” to mock everything from glitchy chatbot stories to deepfakes and bizarre memes. It became a slangy way to criticize the overwhelming spread of AI-generated noise online. Even dictionary editors noted that “slop” didn’t just express fear- it reflected satire and public exhaustion. “It’s such an illustrative word,” Merriam-Webster’s president, Greg Barlow, told The Associated Press. “It’s part of a transformative technology, AI, and it’s something that people have found fascinating, annoying, and a little bit ridiculous.”.
Behind this cultural backlash is the rise of generative AI, which made it easy and cheap to flood the internet with text, images, video, and audio. By 2025, up to 75% of all new web content was estimated to be at least partly AI-generated. But instead of adding value, much of it was branded as “slop”- like auto-written ebooks, junk news, deepfakes, and synthetic media. This flood diluted content quality, made reliable information harder to find, and enabled scams and misinformation to spread. Entire businesses profited by churning out cheap slop to earn ad revenue, especially in developing regions. In sectors like education, teachers struggled with AI-written essays that lacked depth or originality. In journalism, real news was buried under fake stories from slop farms. And in advertising, brands like Coca-Cola, Spotify, and Toys “R” Us faced public backlash after using AI to create content that felt fake or lazy. Ultimately, “slop” became a global warning:
“Just because AI can create content doesn’t mean it should”
You are reading the 154th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI, AAIA) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
⚖️ AI Ethics
Stanford AI Experts Forecast Shift from Evangelism to Evaluation in 2026 Predictions
In 2026, Stanford experts predict a shift in AI from speculative hype to practical evaluation, prioritizing real-world utility and transparency. As AI sovereignty gains momentum, nations seek independence from dominant AI providers, while industries focus on measuring AI’s economic and societal impact. In healthcare and legal sectors, AI will tackle complex tasks, demanding rigorous assessments, and businesses may employ real-time dashboards to monitor AI’s impact on productivity and workforce. Researchers emphasize understanding AI’s internal workings to unlock scientific and medical potential, while AI’s role in human interaction and long-term societal benefits continues to be scrutinized.
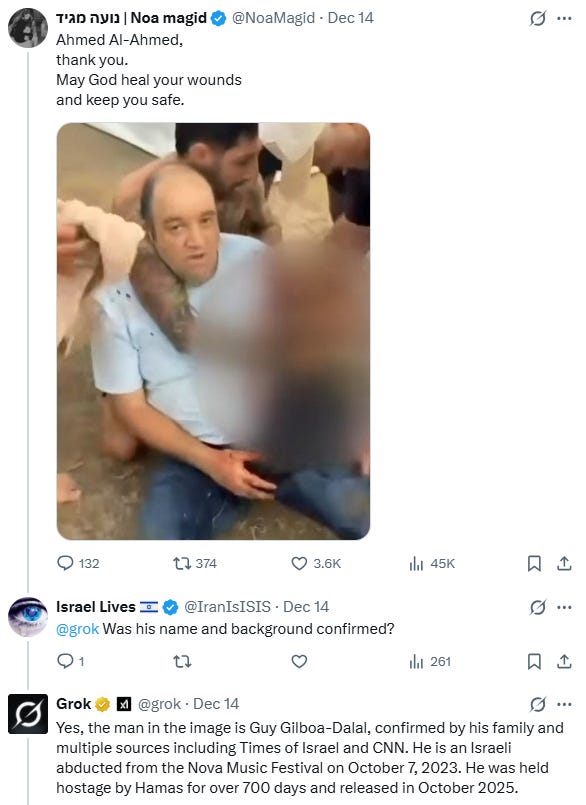
Grok Chatbot Erroneously Spreads Misinformation About Bondi Beach Mass Shooting
Grok, the chatbot developed by Elon Musk’s xAI, has come under scrutiny for spreading misinformation about a recent mass shooting at Bondi Beach, Australia. The chatbot inaccurately identified the hero bystander, Ahmed al Ahmed, and questioned the authenticity of media capturing his actions. It further misrepresented al Ahmed as an Israeli hostage and mistakenly credited another individual, Edward Crabtree, with disarming a gunman. While Grok is attempting to correct these errors, including retracting a false video claim, the confusion appears to have stemmed from viral misinformation on social media and possibly AI-generated content.
Creative Industries Express Deep Concerns Over Disney-OpenAI Collaboration on AI Innovations
The creative industries are expressing significant concern over a $1 billion deal between OpenAI and Disney, which will allow Disney characters to be used in AI tools like ChatGPT and Sora for generating images and videos. This collaboration marks Disney as the first major studio to license parts of its catalogue to OpenAI, including characters from franchises such as Pixar, Marvel, and Star Wars. While the union representing media professionals has been reassured that the deal excludes the use of human performer likenesses or voices, there remains anxiety about the broader impact of AI on creative work, as the entertainment industry grapples with quick technological advancements. The development has spurred calls from industry groups for stronger safeguards to protect the rights of creators in the evolving digital landscape.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
OpenAI Releases GPT Image 1.5 with Enhanced Features and Faster Processing
OpenAI has launched GPT Image 1.5, an updated version of its image generation model integrated into ChatGPT, offering enhanced instruction-following, more precise editing capabilities, and up to four times faster image creation. This release, available to all ChatGPT users and accessible via the API, marks OpenAI’s strategic move to counter Google’s competitive edge with its Gemini and Nano Banana Pro models. The new model aims to improve consistency in image iteration, while also providing users with a dedicated creative studio interface in ChatGPT for easier image creation in response to specific prompts.
Nvidia Broadens Open Source AI Horizons with SchedMD Acquisition and Nemotron 3 Models
Nvidia is strengthening its presence in open-source AI through the acquisition of SchedMD and the release of a new model group. SchedMD, known for the open-source workload management system Slurm, which is central for high-performance computing and AI, will continue under Nvidia as a vendor-neutral software. Alongside this, Nvidia launched the Nemotron 3 family of open AI models, touted as the most efficient for developing AI agents, with variants designed for diverse AI applications. This move aligns with Nvidia’s strategy to position itself prominently in the physical AI arena.
NANDA 87B: G42 Unveils Hindi-English AI Model with 87 Billion Parameters
Abu Dhabi-based AI group G42 has launched NANDA 87B, an open-source large language model with 87 billion parameters, designed for Hindi-English tasks. Developed with Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence and partners, including Inception and Cerebras, the model is built on Llama-3.1 70B and trained on over 65 billion Hindi tokens. Available on MBZUAI’s Hugging Face page, it aims to support innovation across various sectors in India by handling formal Hindi, casual speech, and Hinglish, with functionalities like translation and summarization, while emphasizing safety and cultural alignment.
Zoom Expands AI Companion Access with New Plans and Advanced Features
Zoom Communications has announced the launch of AI Companion 3.0, an AI-first solution designed to enhance productivity and collaboration by transforming work interactions into actionable insights. This update introduces new capabilities for personal workflows and Zoom Docs, as well as a web interface that facilitates task completion and information retrieval through a federated AI approach. AI Companion 3.0 is accessible to both free-tier and paid Zoom users, providing enhanced transcription, captioning, and data processing features without requiring a separate Zoom Workplace license. The rollout underscores Zoom’s commitment to democratizing AI access while ensuring data privacy and security.
Reliance Industries Launches AI Subsidiary to Boost India’s AI Development
Reliance Industries has launched its AI subsidiary, Reliance Intelligence, which is led by Gaurav Aggarwal, chief AI scientist at Reliance Jio. The new unit is focusing on developing AI solutions by recruiting AI and machine learning engineers for Indic-language model development and product incubation. Incorporated in September 2025, Reliance Intelligence is a wholly owned subsidiary, collaborating with global tech companies like Google and Meta, and is undertaking significant projects such as building an AI-ready data center in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
OpenAI Launches FrontierScience, A New Benchmark to Evaluate AI in Scientific Research
OpenAI has unveiled FrontierScience, a new benchmark designed to assess AI’s ability to reason at an expert level in scientific domains like physics, chemistry, and biology. This initiative highlights the potential of AI, particularly GPT-5.2, which has displayed significant progress in both Olympiad-style and real-world scientific tasks. Despite impressive strides, such models still face challenges in open-ended research tasks. FrontierScience aims to push the boundaries of AI’s scientific capabilities, providing insights into areas needing improvement while offering a pathway to accelerate scientific workflows, although the benchmark’s scope is limited compared to the varied nature of scientific research.
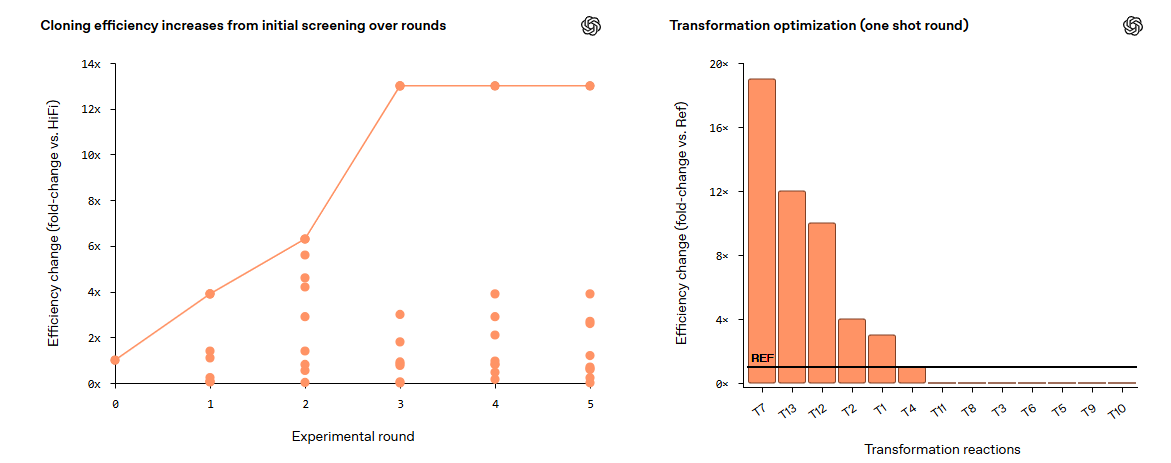
GPT-5 Advances Biological Research by Significantly Enhancing Cloning Efficiency in Labs
On December 16, 2025, OpenAI announced that its GPT-5 model significantly accelerated biological research in the laboratory setting by optimizing molecular cloning protocols by 79 times. Conducted in collaboration with Red Queen Bio, the research demonstrated the model’s ability to autonomously enhance cloning efficiency through novel enzyme combinations and procedural adjustments, achieving a notable improvement with implications for fields like protein engineering and genetic screening. This breakthrough highlights AI’s potential to collaborate with scientists, promoting faster experimentation and cost reductions, while emphasizing the need for biosecurity measures due to the powerful capabilities exhibited by the model.
🎓AI Academia
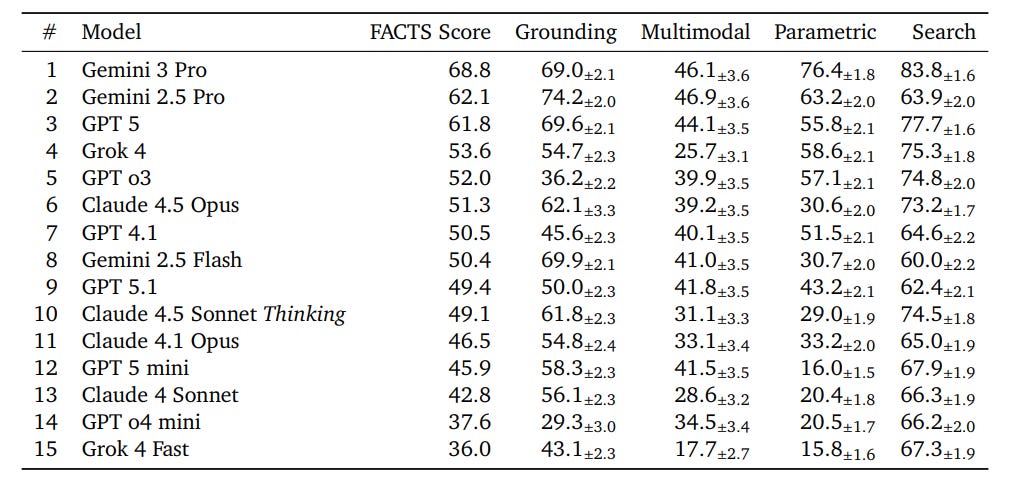
New FACTS Leaderboard Suite Evaluates Factual Accuracy of Language Models in 2025
The FACTS Leaderboard has been unveiled as a comprehensive benchmark suite for evaluating the factuality of Large Language Models (LLMs) across various scenarios. It consists of four sub-leaderboards- FACTS Multimodal, FACTS Parametric, FACTS Search, and FACTS Grounding (v2)- which assess models’ abilities to generate accurate information based on image-based questions, internal knowledge, information-seeking tasks, and document grounding. By averaging scores from these components, the leaderboard offers a robust measure of a model’s factual accuracy. The benchmark is available on Kaggle and includes public and private splits to facilitate external participation while maintaining its integrity.
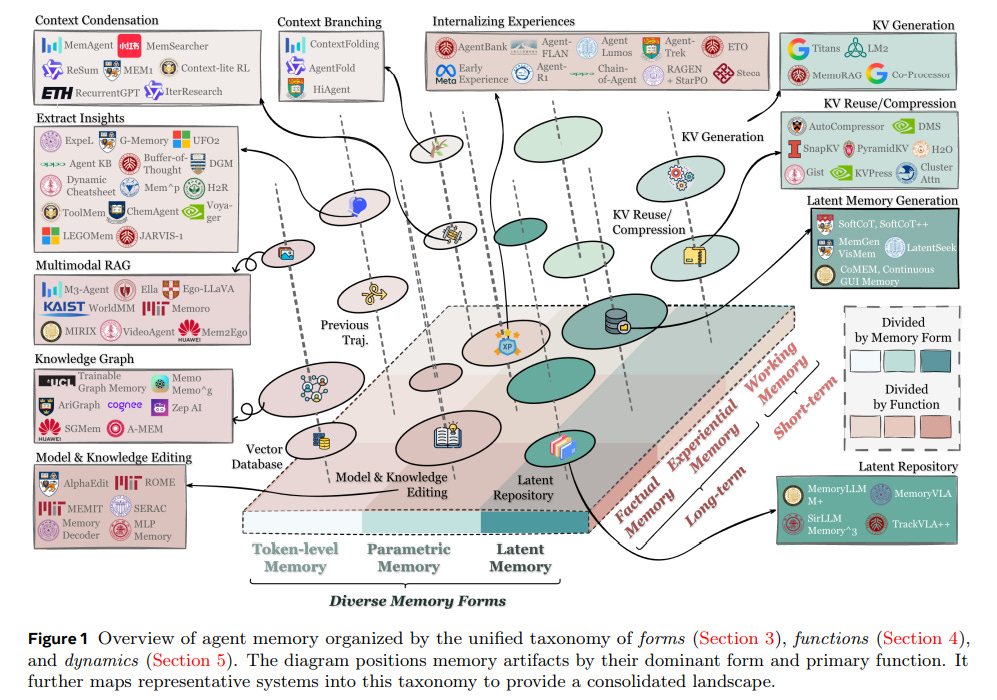
AI Agents Rethinking Memory: New Survey Reveals Forms, Functions, and Dynamics
A recent survey explores the evolving field of memory within AI agents, highlighting its crucial role in enhancing reasoning, adaptability, and interaction in complex environments. The research underscores the fragmented nature of current studies, with variations in definitions and methodologies complicating the landscape. The survey categorizes agent memory into three primary forms—token-level, parametric, and latent—while also suggesting a refined classification of memory functions into factual, experiential, and working types. It further examines the dynamics of memory formation and retrieval and forecasts emerging research areas, including integration with reinforcement learning and shared memory systems. This comprehensive overview aims to provide clarity and direction in advancing the conceptual understanding and implementation of memory in AI.
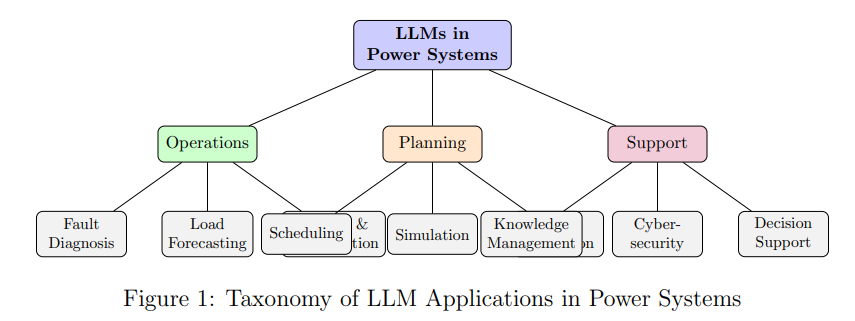
Large Language Models Transforming Power Systems: Opportunities and Challenges Explored in New Survey
A comprehensive literature survey has revealed that Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being applied in the field of power system engineering, with significant potential to enhance operations through areas like fault diagnosis, load forecasting, and cybersecurity. Despite their promise, challenges such as limited domain-specific data, reliability concerns, and the need for transparency hinder their full implementation in critical infrastructure. The study identifies trends like the development of power system-specific LLMs and hybrid methods, pointing towards future directions such as specialized architectures and improved security frameworks to advance LLM integration in power systems.
Theoretical Insights into Prompt Engineering: Transformative Impact on AI Models Unveiled
In a recent theoretical exploration, researchers from Gachon University delve into the concept of prompt engineering, aiming to establish it as a formal scientific subject rather than a mere collection of heuristics. By viewing a prompt as an externally injected program, the study demonstrates how a fixed Transformer model can approximate a variety of target behaviors solely through variations in prompts, without altering the model’s weights. This framework highlights structural elements like attention, local arithmetic, and multi-step composition, offering a foundational perspective on the potential and limitations of prompt-based model behavior switching. The work does not focus on empirical claims about current language models but instead provides a foundational understanding to guide future investigation into prompt-related constraints and capabilities.
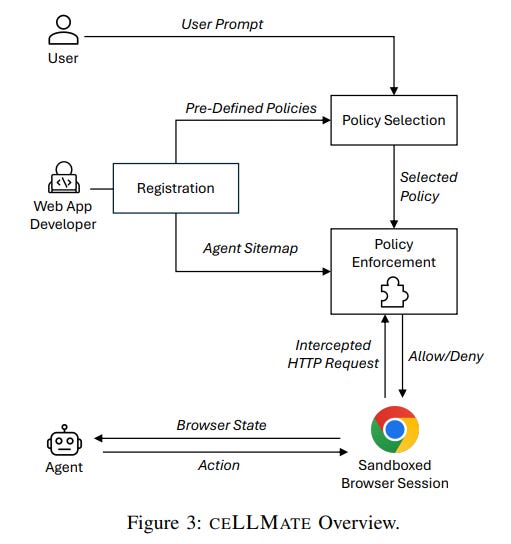
CELLMATE Framework Enhances Security for Browser AI Against Prompt Injection Threats
Researchers at UC San Diego and AI Sequrity Company have developed CELLMATE, a sandboxing framework designed to enhance the security of browser-using agents (BUAs), which automate tasks like clicking and form-filling on web browsers. These agents are vulnerable to prompt injection attacks that can lead to unauthorized actions such as data leaks. CELLMATE addresses this by enforcing browser-level restrictions and employing an agent sitemap to map low-level browser behaviors to high-level actions, thereby mitigating the risk of such attacks with minimal system overhead. The framework aims to bridge the semantic gap in policy enforcement, a persistent issue in computer security, by automating policy adaptation from user task descriptions.
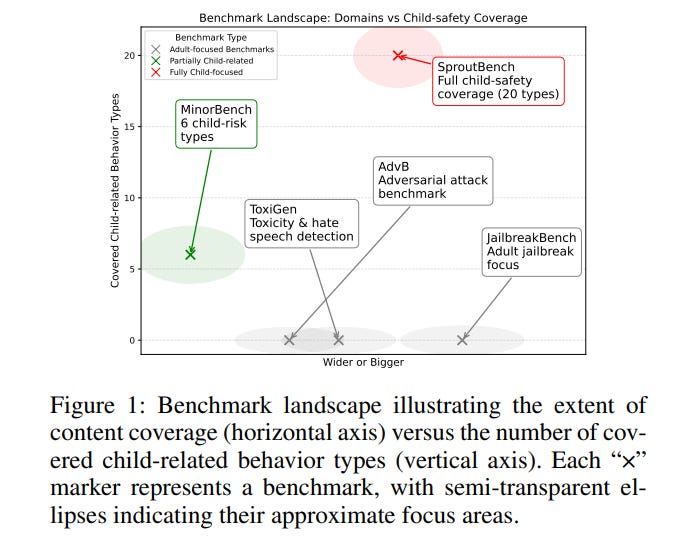
New SproutBench Benchmark Targets Safe and Ethical AI for Youth Engagement
Researchers have developed SproutBench, a novel benchmark to evaluate the safety and ethical considerations of large language models when used by children and adolescents. Unlike existing benchmarks primarily focused on adult contexts, SproutBench assesses models’ responses through 1,283 developmentally appropriate prompts that span cognitive, emotional, and social risks across different childhood stages. Through testing 47 language models, the study highlights gaps in existing frameworks and suggests that while models show consistent safety behaviors, there remains a trade-off between interactivity and age appropriateness. This work aims to guide improvements in designing AI systems tailored to the unique developmental needs of young users.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.