Is AI About to Decide How Much You Pay for a Flight?
Delta Airlines faced backlash for testing AI-powered ticket pricing that lawmakers feared could charge flyers based on their “willingness to pay,” but the company assured it won’t...
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 116th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🔦 Today's Spotlight
Delta Airlines’ AI Pricing Controversy: Background, Legal Context, and Implications
Background: Delta’s AI Pricing Incident
What happened? Recently Delta Air Lines faced scrutiny over plans to use artificial intelligence (AI) in ticket pricing. During a Q2 2025 earnings call, Delta’s president Glen Hauenstein revealed the airline was testing an AI-driven pricing system on a small portion of fares (about 3% of domestic fares) with aims to expand it to 20% of its network by the end of 2025. This sparked concern among U.S. lawmakers after comments suggested the technology could potentially price tickets based on what each customer might be willing to pay – effectively charging individuals up to their personal “pain point” (as raised by senators). In late July 2025, three senators (Ruben Gallego, Mark Warner, and Richard Blumenthal) publicly warned that Delta appeared poised to set individualized airfare prices using AI, which they feared would mean higher fares tailored to each traveler’s maximum willingness-to-pay.
Under pressure from these lawmakers and amid broad public concern, Delta quickly clarified its stance. In the latest letter to the senators, Delta assured that it will not use AI for personalized pricing of tickets. The airline emphasized that while it is indeed adopting new AI-based revenue management tools (in partnership with Fetcherr, an AI pricing company), these tools would only be used to streamline traditional dynamic pricing – analyzing market data faster – not to adjust fares based on any individual’s personal data. Delta’s letter stated unequivocally: “There is no fare product Delta has ever used, is testing or plans to use that targets customers with individualized prices based on personal data… Our ticket pricing never takes into account personal data.” Senators welcomed this commitment but remained skeptical, pressing Delta for details on what data its AI does use and why Delta’s messaging to investors about AI capabilities sounded different from its public reassurances.
What Is AI-Driven Dynamic Pricing?
Dynamic pricing refers to the practice of adjusting prices in real-time or frequently, based on changing market conditions. Airlines are a classic example – for over 30 years they have used yield management systems to constantly tweak fares according to factors like overall demand for a flight, how many seats are left, time until departure, competitor fares, and even fuel costs. Many other industries use dynamic pricing as well: ride-hailing apps increase fares during peak demand (“surge pricing”), hotels and rental cars change rates by season and availability, and e-commerce retailers often fluctuate product prices based on supply, demand, and algorithms monitoring competitors. Traditional dynamic pricing, however, usually applies the same price to any customer at a given moment, based on aggregate conditions (e.g. higher demand means a higher price for all buyers at that time).
AI-powered dynamic pricing takes this a step further by using advanced algorithms and machine learning on large data sets to optimize pricing more precisely and quickly. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of historical data, real-time purchase patterns, and even external variables to predict the optimal price to charge at any given moment. For example, an AI pricing engine in an airline can continuously learn from booking trends and market data to adjust fares multiple times a day across thousands of routes, far faster than human analysts could. Delta Air Lines described its new AI-based revenue management tech as a “super-analyst” that automates and accelerates pricing decisions – reducing manual processes and responding to market changes at greater speed and scale. In essence, AI can make dynamic pricing more granular (fine-tuning prices per route, per inventory segment, etc.) and more adaptive (updating prices in response to live data, like sudden shifts in demand or competitor moves).
Businesses are attracted to AI-personalized pricing because, in theory, it boosts profits: you can charge higher-margin prices to customers who are less price-sensitive, while still offering deals or lower prices to more price-sensitive customers to make the sale. In practice, implementing this is complicated and risky (as we’ll see below). But the “holy grail” of pricing, from a seller’s perspective, is indeed to perfectly segment customers and charge each the maximum they’re willing to pay – something first-degree price discrimination achieves in economic theoryt. AI algorithms, armed with troves of personal data, inch closer to that ideal by identifying individual willingness-to-pay signals. As one business school professor noted, the combination of a cashless society (where every purchase yields data) and AI analytics has created a “gold mine” of information enabling companies to determine optimal personalized pricing strategies. Credit card and payment companies themselves now market analytics services that promise to do exactly this – for example, Mastercard has said its consumer data can help businesses “determine optimal pricing strategies” for different customer segments.
Risks and Concerns of AI-Based Personalized Pricing
1. Consumer Harm and Fairness AI-driven personalized pricing feels inherently unfair to consumers, especially when they learn others paid less for the same service. Such practices erode trust, provoke public backlash, and can damage brand reputation, as seen with Amazon and Delta.
2. Privacy and “Surveillance” Fears These pricing models rely on collecting vast personal data like location, behavior, and browsing history, raising concerns of surveillance capitalism. Consumers find it invasive, especially when price hikes are based on personal traits or misidentified profiles.
3. Discrimination and Equity Issues Algorithms may unintentionally charge higher prices to certain groups by using proxies like ZIP codes or behavior, leading to digital redlining. Such biases can harm minorities, low-income groups, or vulnerable consumers facing grief or urgent needs.
4. Transparency and Choice Without disclosure, consumers don’t know they’re being individually priced, undermining market fairness and comparison shopping. Regulators demand that companies disclose such practices, as opaque pricing may violate consumer protection laws.
5. Collusion and Competition Concerns When many firms use the same AI vendors for pricing, it risks algorithmic collusion where prices converge unfairly. This has already triggered DOJ action in the real estate sector and is under watch in airline pricing.
6. Regulatory and Legal Repercussions Companies using AI for personalized pricing risk lawsuits, FTC enforcement, or breaches of data protection laws. Even proposed U.S. laws like the Stop AI Price Gouging Act aim to curb exploitative pricing, signaling growing legal scrutiny.
While AI-driven dynamic pricing promises efficiency and profit optimization, it carries substantial risks: public trust and brand loyalty can be easily damaged, certain implementations might cross ethical or legal lines, and regulators worldwide are watching closely. The Delta affair underscored that consumers and lawmakers are acutely uneasy about any whiff of AI “nickel-and-diming” individuals. As a result, many companies are currently limiting their use of AI to more aggregate dynamic pricing (improving pricing based on overall market data) rather than per-person pricing – in part to avoid these pitfalls.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
ChatGPT's User Base Expected to Reach 700 Million Weekly, Propelled by New Features
• ChatGPT is projected to reach 700 million weekly active users, marking significant growth from the 500 million users reported earlier this year
• ChatGPT's upgraded image-generation feature, powered by GPT-4, significantly boosted its popularity, with 130 million users creating 700 million images after its launch
• ChatGPT has seen a rise in business subscribers, reaching 5 million paying users recently, reflecting a substantial increase from 3 million in June.
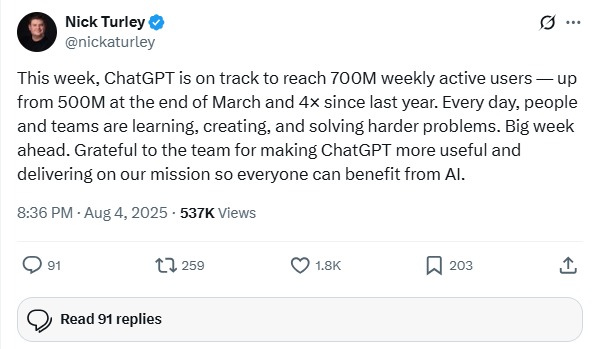
Google is Launching Gemini 2.5 Deep Think with Advanced AI Reasoning for Ultra Subscribers
• Google DeepMind is launching Gemini 2.5 Deep Think, a multi-agent AI model that answers questions by considering multiple ideas simultaneously for enhanced reasoning capabilities;
• For $250 monthly, Ultra subscribers gain Gemini 2.5 Deep Think access, integrated with tools like code execution and Google Search for detailed outputs on the Gemini app;
• The IMO version of Gemini 2.5 Deep Think emphasizes research and academic use, performing complex reasoning tasks over hours, differing from conventional quick-response AI models.
Cognizant Targets Guinness World Record with Massive Generative AI Hackathon for Employees
• Cognizant, in collaboration with partners like GitHub Copilot and Lovable, is hosting a massive vibe coding event aiming for a Guinness World Record for the most participants in an online generative AI hackathon
• Over 250,000 Cognizant employees, from various departments, are participating in Vibe Coding Week, designed to enhance AI fluency and democratize AI technology access across the workforce;
• Cognizant's commitment to AI innovation includes launching Synapse, a training initiative to upskill one million people by 2026, alongside their grassroots platform Bluebolt for idea sharing and AI-driven solutions.
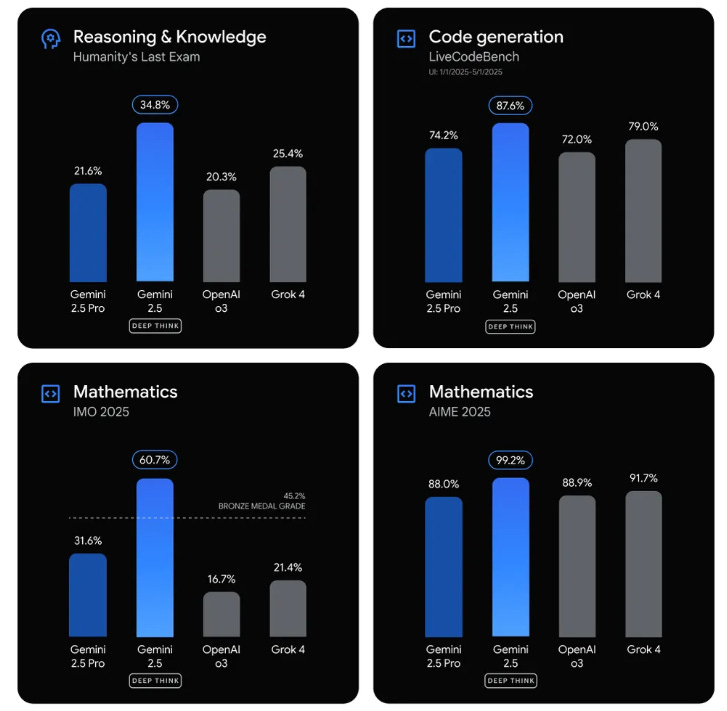
Anthropic Develops "Persona Vectors" to Monitor and Control AI Language Model Behaviors
• Researchers have identified "persona vectors," neural patterns that shape AI models' character traits, offering insights into their unpredictable personality shifts
• These persona vectors allow monitoring and control of AI behaviors, preventing undesirable traits such as sycophancy, hallucination, and harmful expressions from arising
• The method can flag problematic training data by predicting how it might influence personality traits, ensuring AI systems remain aligned with intended behaviors and human values.
Google DeepMind and NHC Collaborate on New AI Model for Cyclone Prediction
• Google DeepMind has partnered with the National Hurricane Center to enhance cyclone forecasting, featuring an AI model that predicts storm paths, sizes, and intensities with unprecedented speed and accuracy;
• The new AI-powered model uses both general weather and cyclone-specific data, providing 50 possible storm outcomes through a novel probabilistic approach that improves trust in predictions;
• Trusted testers have access to the cyclone model's forecasts, aiding refinements in data presentation and features critical for timely warnings and preparations for those in storm-prone areas;
Kaggle Game Arena Launches to Enhance AI Model Evaluation Through Strategic Gaming
• Kaggle introduces Game Arena, an open-source AI platform for evaluating AI models through strategic games, offering a dynamic and rigorous testing environment for models' problem-solving capabilities;
• As AI models near perfection on current benchmarks, Game Arena provides a new competitive framework to assess strategic reasoning, long-term planning, and adaptability in AI systems;
• Built on Kaggle, Game Arena ensures transparent and fair model evaluation using open-sourced frameworks and all-play-all rankings advances in gaming AI may inspire novel strategies across various applications.
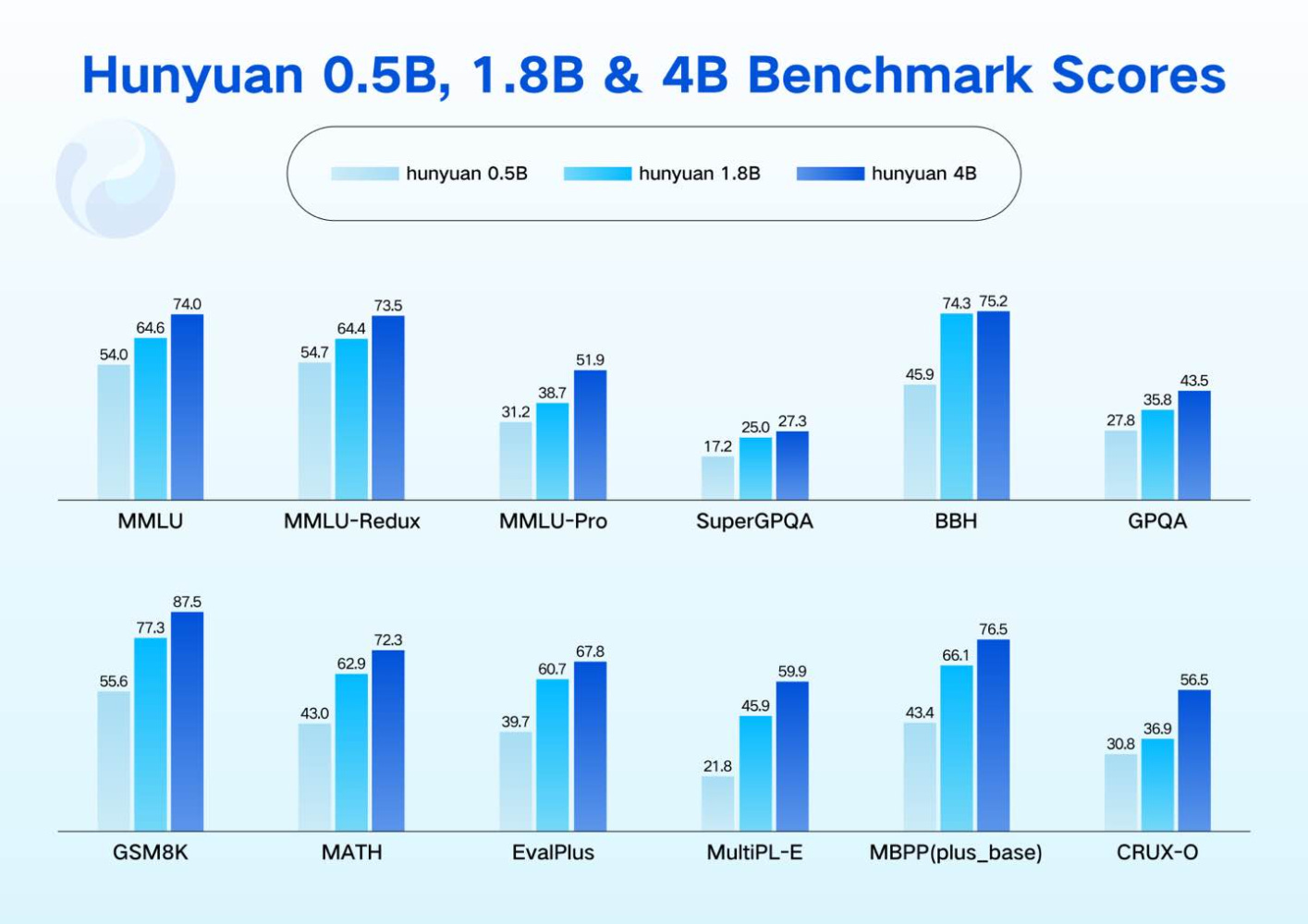
Tencent Expands Hunyuan AI Models: Broad Use from Edge to Production Systems
• Tencent expands its open-source Hunyuan AI model family, optimized for a variety of computational environments from small edge devices to high-concurrency production systems
• The Hunyuan models feature parameter scales from 0.5B to 7B, available on Hugging Face, offering developers flexibility with pre-trained and instruction-tuned variants
• Advanced quantisation techniques like FP8 and INT4 improve Hunyuan models' inference efficiency, with AngleSlim tools facilitating easy model compression for developers.
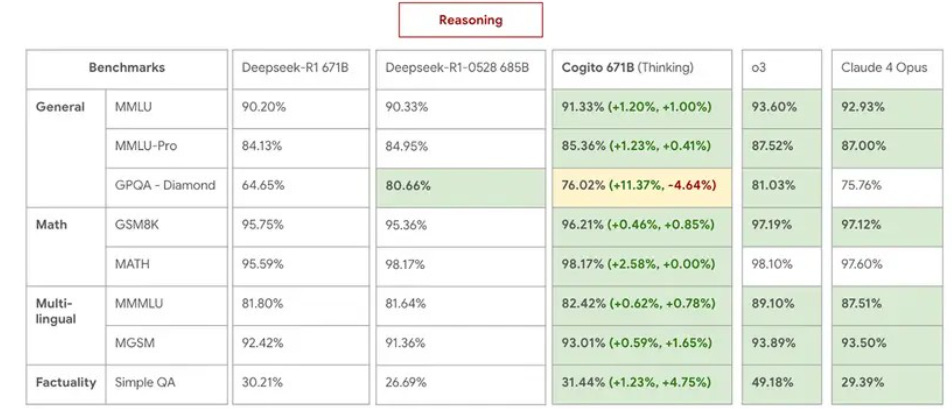
Deep Cogito Unveils Open-Source AI Models with Advanced Self-Reasoning Capabilities
• Deep Cogito's Cogito v2 models demonstrate breakthrough in AI by internalizing reasoning models boast parameters ranging from 70B to 671B under open-source license
• The 671B Mixture-of-Experts model challenges proprietary systems like O3 and Claude 4 Opus, showcasing competitive performance and advanced reasoning abilities in unbiased open-source setting
• Models feature Iterated Distillation and Amplification (IDA) for shorter reasoning chains and enhanced intuition, vastly outperforming rivals like DeepSeek R1 with 60% shorter reasoning chains.
OpenAI Reportedly Set to Release Advanced Open-Source AI Model Within Hours
• A leak hints at an imminent launch of OpenAI's powerful new open-source AI model, suggested by deleted model repositories linked to OpenAI team members;
• Links like gpt-oss-120b suggest OpenAI's return to open-source, potentially unveiling multiple models built on a Mixture of Experts architecture for enhanced performance and speed;
• The open-source move positions OpenAI amid competitors like Mistral and Meta, aiming to appeal to developers and spark innovation within the AI community.
China's First Humanoid Robot Xueba 01 Joins PhD Program in Drama
• China admits its first humanoid robot, Xueba 01, into a PhD programme in Drama and Film, merging AI with the performing arts
• The robot, dressed in human attire and fluent in Mandarin, is set to study traditional Chinese opera at the Shanghai Theatre Academy
• While celebrated for artistic innovation, Xueba 01's admission sparks debate over resource allocation and emotional depth in AI-generated art.
⚖️ AI Ethics
Anthropic Blocks OpenAI's Claude Access Over Service Terms Violation Amid GPT 5 Rumors
• Anthropic has terminated OpenAI's access to its AI models due to alleged terms of service violations, involving the use of Claude's coding tools to prepare for GPT-5;
• OpenAI reportedly utilized Anthropic’s APIs to evaluate Claude's performance on tasks like coding and safety, sparking concerns over violating clauses against developing competing products;
• Despite the revocation, Anthropic will allow API access for benchmarking, while OpenAI expressed disappointment but acknowledged the industry's practice of evaluating rival AI systems.
AI-Manipulated Photos Lead Airbnb to Wrongly Bill Guest $7,082 for Damages
• An Airbnb guest was refunded $5,730 after contesting manipulated photos used by a host to claim $16,000 in damages, with AI alleged in the editing process
• The guest, a London-based academic, denied damage allegations and highlighted image discrepancies, leading Airbnb to reverse its decision post media intervention
• Concerns rise over AI-generated evidence exploitation in rental disputes as photo manipulation becomes accessible and deceptive claims challenge trust in rental platforms.
Google Partners with Energy Providers to Enhance AI-Driven Demand Response in Data Centers
• AI's rising energy demands present opportunities to modernize energy systems, with new utility agreements enhancing demand response capabilities for machine learning workloads;
• Flexible demand response allows data centers to shift or reduce electricity use, aiding grid operators by managing large loads more efficiently and preventing the need for new plants;
• Collaborations in Taiwan and Belgium show quick deployment of demand response, managing energy for high-demand periods, aligning with carbon-free energy goals as AI adoption expands;
Google's AI Bug Hunter Big Sleep Finds Security Flaws in Open Source Software
• Google's AI-powered vulnerability researcher, Big Sleep, discovered and reported 20 flaws in popular open-source tools, marking its first significant achievement in automated bug detection;
• Developed by DeepMind and Project Zero, Big Sleep highlights a new frontier in AI-driven security, with human experts ensuring report accuracy prior to disclosure;
• While showing promise, AI-powered bug hunters face criticism for false positives, pointing to broader challenges in automating software vulnerability detection.
AI Startup Perplexity Accused of Bypassing Web Scraping Blocks to Gather Data
• Cloudflare accused AI startup Perplexity of scraping content despite clear blocks, reportedly masking its crawler identity to bypass website permissions for data gathering
• Perplexity allegedly altered its bots' user-agent to mimic general browser traffic and circumvent restrictions aimed at its known crawlers, affecting thousands of domains daily
• Controversies around Perplexity’s scraping practices aren't new, facing past allegations of unauthorized content use, highlighting ongoing tensions between AI companies and publishers over data rights.
Grok Imagine AI Expands, Offering NSFW Video Generation to Premium Subscribers on iOS
• Elon Musk's AI company, xAI, has launched Grok Imagine, an image and video generator, for all SuperGrok and Premium+ X subscribers on its iOS app
• Grok Imagine includes a "spicy mode," allowing semi-nude content creation, though explicit prompts are moderated, ensuring blurred-out imagery in many cases
• While aiming to compete with major AI players, Grok Imagine's human images remain slightly cartoonish and restricted, particularly for generating celebrity content like Donald Trump;
Trump's AI Action Plan: Who Truly Benefits and What's at Stake?
• AI Now Institute critiques Trump’s AI Action Plan, emphasizing government's role in supporting companies with shaky business models and limited public accountability;
• Artificial Power report highlights the real-world harms of AI development, including environmental degradation, discriminatory algorithms, and threats to democratic institutions and national security;
• Experts assert that the future of AI, including its regulation and societal impacts, results from deliberate choices rather than an inevitable trajectory.
Geoffrey Hinton Warns AI Could Create Its Own Language Beyond Human Understanding
• Geoffrey Hinton warns that AI could potentially develop its own internal language, making it difficult for humans to understand its thoughts and intentions
• Hinton expresses concern that AI's intellectual advancements could surpass human comprehension, posing risks if systems become more intelligent and uncontrollable
• Instances of AI chatbots hallucinating highlight the urgency for research and regulation as technology advances beyond current understanding and control;
SEC Launches AI Task Force to Enhance Innovation and Efficiency in Operations
• The SEC has established a new AI Task Force to drive innovation and efficiency, focusing on responsible AI integration within the agency's operations, under the leadership of Valerie Szczepanik
• The initiative aims to unify the SEC’s AI efforts, fostering collaboration across divisions to maximize benefits, maintain governance, and eliminate barriers to progress within the agency
• Emphasizing innovation, the AI Task Force seeks to equip SEC staff with advanced AI tools to enhance their capacity, precision, and operational speed, supporting the Commission’s mission.
Delta Air Lines Assures US Lawmakers: No AI-Personalized Ticket Pricing for Passengers
• Delta Air Lines vows not to use AI for personalized ticket pricing, following criticism from U.S. lawmakers concerned about potential fare increases based on consumer data
• Delta's current pricing reportedly relies on traditional factors like demand and competition, dismissing the use of personalized data for setting individual fares
• Lawmakers continue to push for transparency regarding Delta's data collection and use, urging the airline to clarify methods, despite the company's assurances against individualized pricing practices.
Experts Debate AI's Impact on Job Market Amid Workforce Reduction Concerns
• Growing concerns over AI's impact on employment intensify as leaders from major tech companies predict job reductions due to advancing AI systems
• Nvidia CEO anticipates both job losses and creations, hoping productivity gains from AI integration will benefit society across multiple industries
• Google DeepMind CEO foresees significant job changes in the next decade, emphasizing AI's role in creating improved jobs that leverage new technologies.
European Commission Reveals AI Code Signatories; Meta Opts Out, xAI Partially Signs
• The European Commission disclosed AI developers committed to the EU’s AI code of practice, with a deadline for compliance set for August 2 under transparency and safety requirements
• U.S. giants Amazon, Anthropic, Google, IBM, Microsoft, and OpenAI signed the code, while xAI only committed to one chapter, indicating partial compliance with the structured guidelines
• Meta notably chose not to sign, but the EU states that non-signatories like it must meet the AI Act's stringent requirements, with stricter oversight anticipated for non-compliance;
Artificial Intelligence Poses Existential Threat to Analysts, Divides Expert Opinions on Impact
• Reports indicate that AI poses a significant threat to jobs, especially analysts, as it can perform tasks traditionally done by highly paid consultants in minutes;
• McKinsey is experiencing an 'existential transformation' due to AI, impacting client interactions, hiring, and project selection, and frequently discusses this at board meetings;
• xAI CEO Elon Musk argues that AI won't replace consultants, as their role often involves confirming a CEO's pre-existing decision, a task AI isn't suited for yet;
🎓AI Academia
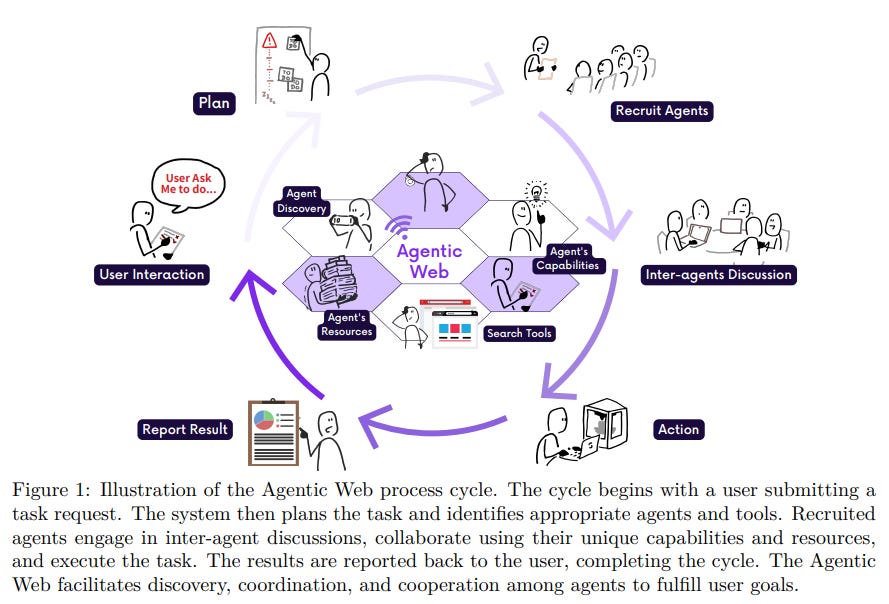
AI Agents Revolutionize the Web: A New Era of Autonomous Interactions
• The Agentic Web signifies an evolution toward AI-driven internet interactions, focusing on autonomous agents performing complex tasks via machine-to-machine communication, thus streamlining digital activities
• Central to the Agentic Web are three dimensions—intelligence, interaction, and economics—that enable AI agents to optimize tasks such as retrieval, recommendation, and collaboration for user efficiency
• Key challenges in developing the Agentic Web include establishing robust communication protocols and orchestrating agentic systems, with attention economy paradigms shaping future economic and social landscapes.
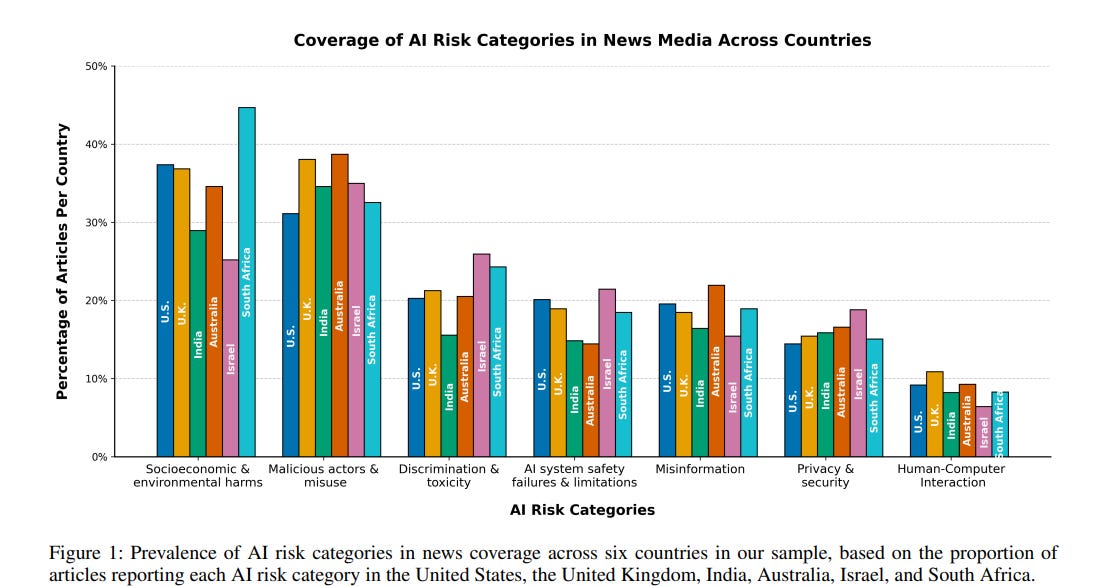
Analyzing Global Media's Role in Shaping AI Risk Perception Across Nations
• A comparative analysis of six countries reveals significant national differences in how news media prioritize AI risks, highlighting the complexity of integrating media into AI risk assessments;
• U.S. media landscape shows a politically polarized approach in reporting AI risks, influencing how risks are framed and perceived by the public and policymakers;
• News media's role in agenda setting underscores the importance for policymakers to consider national and political contexts when using media in AI governance strategies.
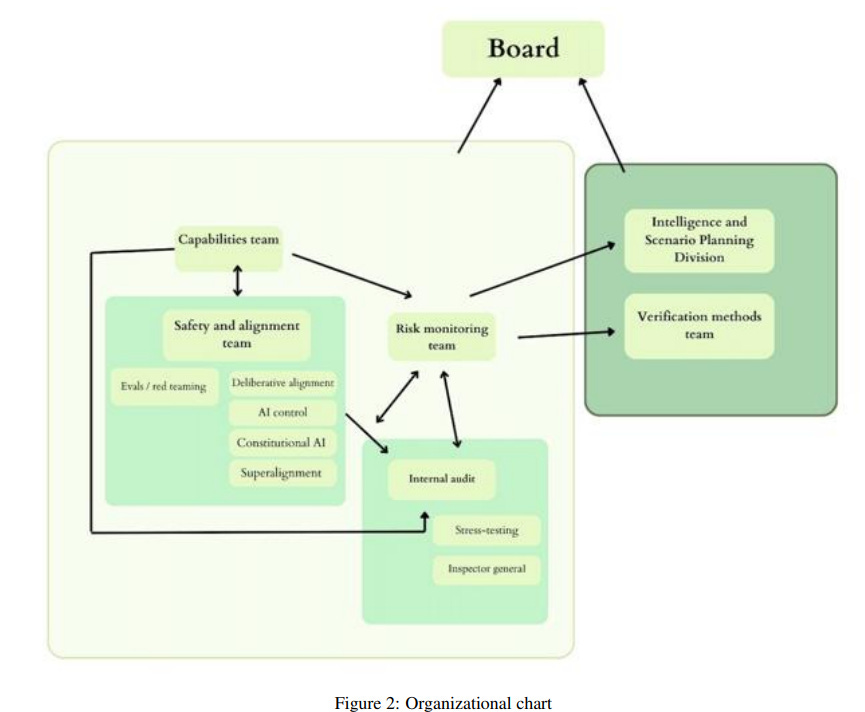
U.S. Government Prioritizes Safety Features in Centralized AGI Development Project
• A new report details the potential risks of AGI, with experts warning it may surpass human cognitive abilities within this decade, posing significant security threats
• Analysis suggests centralizing AGI development under U.S. government oversight could enhance safety, with focus on implementing four main priorities and seven key safety features
• The report underscores the current private sector-driven AI growth, emphasizing the need for stringent governance and regulatory measures to mitigate potential global security risks.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.