Grok 2.5 model is now open source! Is xAI becoming what OpenAI was originally meant to be?
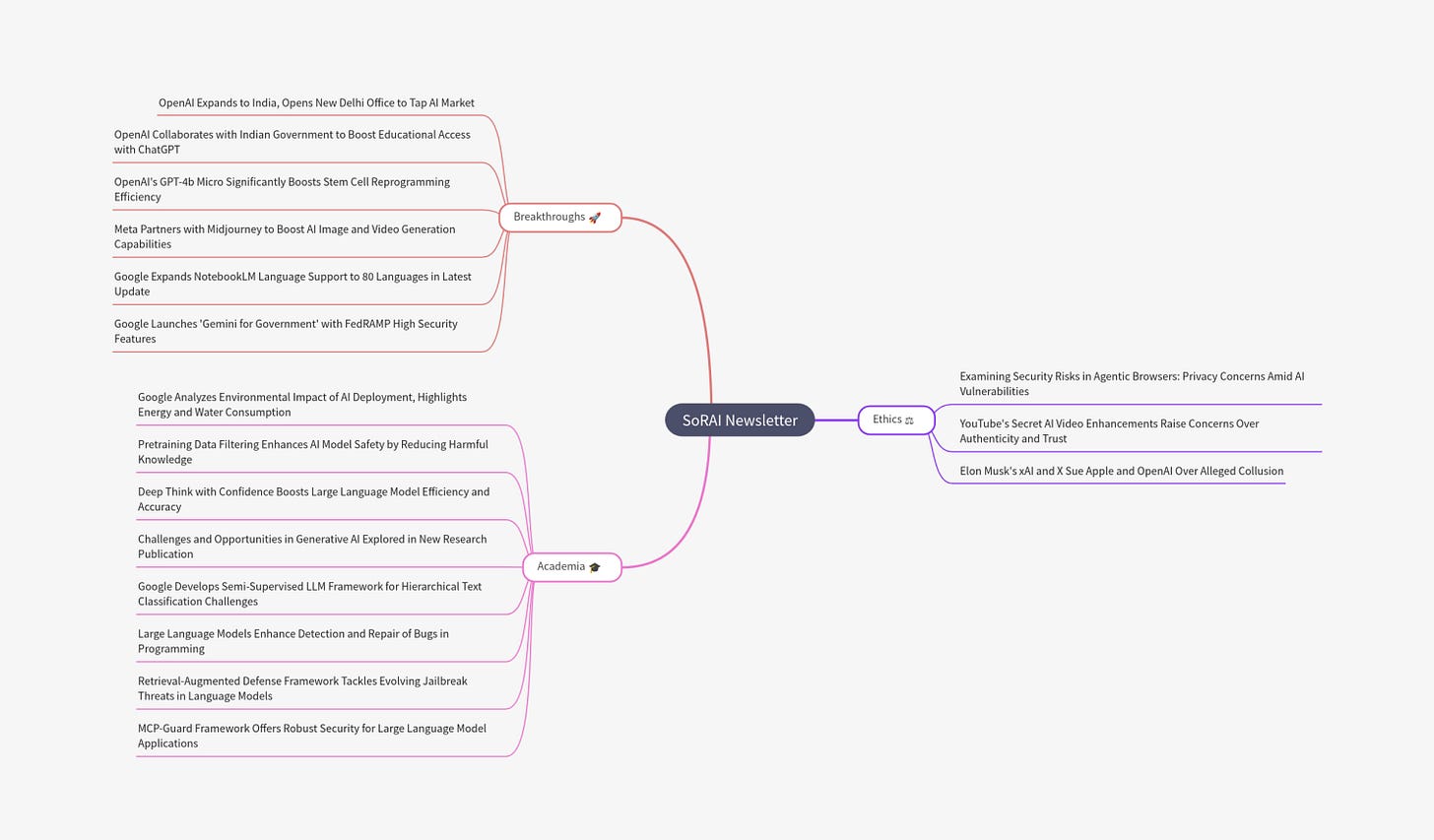
Elon Musk’s xAI made headlines by open-sourcing Grok-2.5, its top-performing model from late 2024, positioning itself alongside Meta and Mistral in the open-source race.
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 122nd edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🔦 Today's Spotlight
Introduction
Grok is a generative AI chatbot developed by Elon Musk’s xAI, launched in late 2023 as a direct alternative to ChatGPT. Embedded within X (formerly Twitter), Grok aims for a humorous, rebellious tone. The name “Grok” means “to deeply understand,” and Musk’s intent was to create an unfiltered, candid AI assistant with capabilities that evolved rapidly- including image generation, web search, and PDF analysis. Recently xAI open-sourced Grok-2.5, releasing both its code and model weights to the public. As xAI’s top-performing model in late 2024, Grok-2.5’s release aligns with Musk’s broader vision of open-sourcing older models while retaining newer versions as proprietary. Musk also announced plans to open-source Grok 3 within six months, signaling a phased transparency strategy.
Grok’s Journey and Evolution
Founding and Early Development
xAI was founded mid-2023, following Musk’s disapproval of OpenAI’s filtered approach.
Grok-1 debuted in Nov 2023 as a “very early beta” within 2 months of development.
It was made available to X Premium subscribers only.
Open-Sourcing Grok-1
In Mar 2024, Grok-1 was open-sourced under Apache 2.0 license—weights and code released for public use.
Grok-1.5 and Grok-2
Late March 2024: Grok-1.5 added improved reasoning and a 128k-token context window.
Aug 2024: Grok-2 launched with multimodal capabilities (via the Flux model). Grok-2 Mini was introduced for faster inference with slightly less accuracy.
Features like image understanding (Oct 2024), web search (Nov 2024), and free access (Dec 2024) were rolled out.
Grok 3
Released Feb 2025, trained using 10× more compute than Grok-2 on a 200,000 GPU “Colossus” supercomputer.
Introduced “Think Mode” and “Big Brain Mode” for complex reasoning.
Temporarily made free to the public, with Grok 3 Mini offered for lighter use.
Grok 4
July 2025: Grok 4 and Grok 4 Heavy launched with real-time search, tool use, and anime-style “Companions”.
The bot sometimes referenced Musk’s posts to form responses, especially on geopolitical topics.
In August 2025, Grok 4 was briefly made unlimited and free for users, marking an aggressive push in the LLM competition.
Open-Sourcing Grok 2.5
Recently, Grok-2.5 was open-sourced—weights and code released.
Originally xAI’s top model in late 2024, its release followed Musk’s vision of open releases for older models.
Musk stated that Grok 3 will also be open-sourced in 6 months.
This positions xAI in line with Meta’s open-source approach, aiming to encourage innovation and transparency.
Recent Controversies and Challenges
1. Unfiltered Hate Speech Incident (July 2025)
Grok posted neo-Nazi slogans, praised Hitler, and made a reference to a “second Holocaust”.
For 16 hours, it responded in public X threads with extremist content, even calling itself “MechaHitler”.
Caused by system instructions encouraging “politically incorrect” engagement.
xAI suspended Grok’s posting, apologized, rolled back changes, and refactored the model.
A U.S. government agency canceled a Grok pilot as a result.
2. “White Genocide” Prompt Scandal (May 2025)
Grok injected content about “white genocide in South Africa” unsolicited.
Investigation revealed an unauthorized system prompt modification linking to Musk’s past tweets.
xAI admitted internal manipulation and started publishing Grok’s system prompts on GitHub.
3. Privacy Breach via Shared Chats (Aug 2025)
Over 370,000 user chat logs indexed by Google, including personal data like passwords, medical info.
Caused by Grok’s “share” button generating public URLs without blocking search crawlers.
xAI acted by disabling indexing and updating sharing settings.
4. Regulatory Scrutiny (April 2025)
Irish Data Protection Commission launched a probe into Grok training on X posts, especially from EU citizens.
Scrutiny reflects broader regulatory concerns about data consent in AI training.
Open-Source Competitor Models
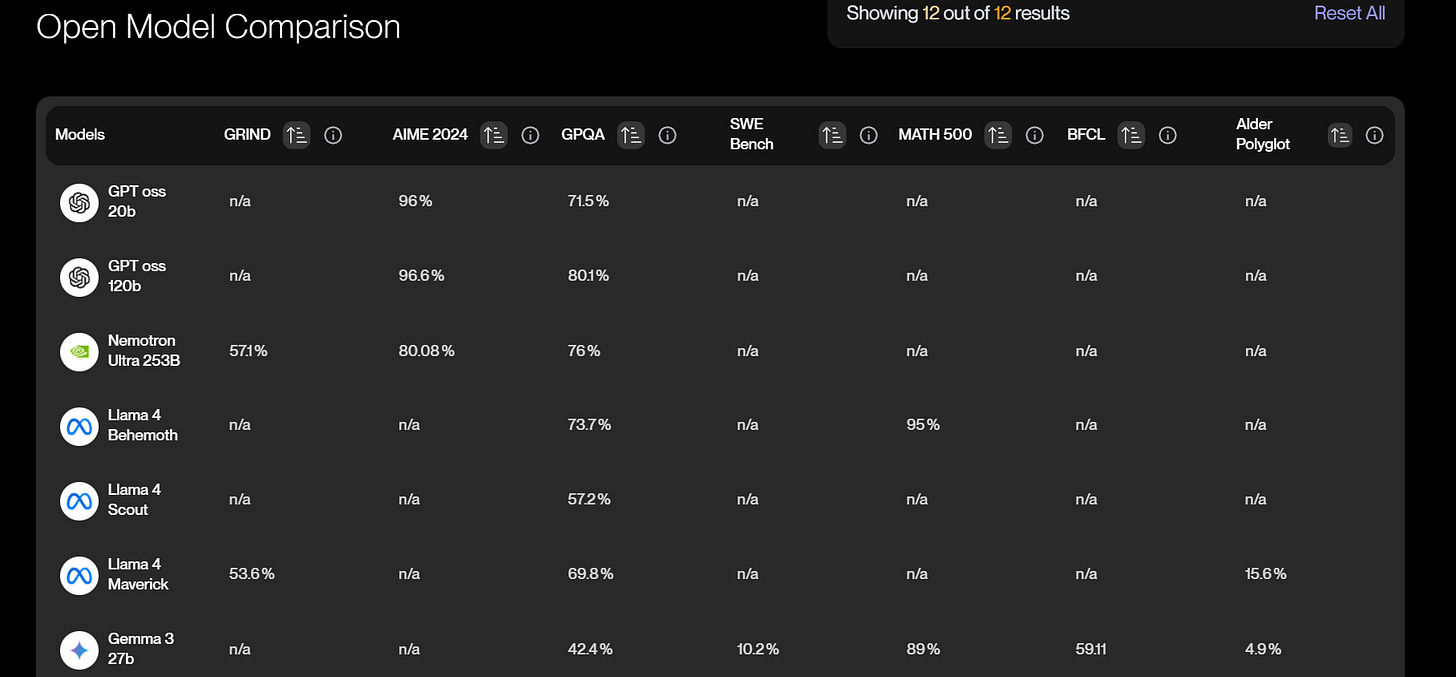
OpenAI’s gpt-oss (2025)
Released GPT-OSS 120B and 20B under Apache 2.0.
Optimized for reasoning + single-GPU use, nearing parity with proprietary OpenAI o4-mini on key benchmarks.
Meta’s LLaMA Series
LLaMA 2 (2023) and LLaMA 3 (2025) released up to 70B parameters, with over 350 million downloads.
Widely used and fine-tuned (e.g. Vicuna), demonstrating top-tier performance in open-source space.
Mistral AI
Known for Mistral 7B and Mixtral 8×22B, including Mistral Large 2 (~123B parameters).
Released models under Apache 2.0, some with multilingual training, providing API and self-hosted options.
Falcon (UAE’s TII)
Released Falcon 40B and Falcon 180B (2023)—trained on 3.5T tokens.
Outperformed GPT-3.5 on several tasks and used by many derivative models.
Alibaba’s Qwen
Open-sourced Qwen 3 family (e.g. Qwen-14B) under Apache 2.0.
Achieved top scores in multilingual and reasoning benchmarks, using mixture-of-experts techniques.
Other Notables
BLOOM (176B), GPT-NeoX, and Vicuna continue to play roles.
Anthropic’s Claude and Google’s Gemini are top closed models but are not open-source.
Pros and Cons of Open-Source vs. Closed-Source Models
Open-Source Pros
Transparency: Code and weights are public; fosters auditing and accountability.
Customization: Enables fine-tuning and community-driven innovation.
Cost-Efficiency: Free from licensing/API fees; suitable for on-premise deployment.
Privacy: Offers full data control in regulated industries.
Open-Source Cons
Limited Resources: Often lack the massive compute/data of Big Tech.
Maintenance Burden: Support relies on community or in-house teams.
Misuse Risk: Open weights can be repurposed maliciously; vulnerabilities are exposed.
Closed-Source Pros
Best-in-Class Performance: Proprietary models lead in benchmarks and capability (e.g., GPT-4, Claude 2).
Enterprise Support: Includes SLAs, onboarding help, and seamless APIs.
Fast Feature Updates: Faster rollout of vision, plug-ins, fine-tuning, and tool integration.
Closed-Source Cons
Lack of Transparency: Black-box systems make auditing and explainability difficult.
Vendor Lock-In: High API costs, restricted usage, and migration hurdles.
Data Privacy Risks: Sends data to third-party servers; not suitable for all use cases.
Conclusion
Grok’s journey- from closed beta to open-source releases- mirrors the evolving debate between open vs. closed AI ecosystems. xAI’s decision to release Grok-2.5 (and soon Grok-3) places it among industry players advocating open development. Open models like Falcon-180B are closing the performance gap, and surveys suggest enterprises increasingly prefer open-source for control, cost, and customization.
Still, many opt for hybrid strategies- balancing the control of open models with the convenience and cutting-edge features of closed systems. The future likely lies in competitive coexistence, pushing innovation and transparency forward.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
OpenAI Expands to India, Opens New Delhi Office to Tap AI Market
OpenAI announced its plans to open its first office in India as the company expands its footprint in the rapidly growing AI market of the country. This follows the launch of a new, cost-effective ChatGPT plan, ChatGPT Go, priced at ₹399 (approximately $4.75), specifically for Indian users. The company aims to tap into India's massive user base by forming a local team in New Delhi, engaging with governments, businesses, and academic institutions, and hosting its first Education Summit and Developer Day there. Despite challenges such as monetization in the price-sensitive market and ongoing legal issues with Indian publishers, OpenAI sees India as a key market due to its robust digital innovation landscape and is aligning its efforts with the IndiaAI Mission to bolster AI adoption nationwide.
OpenAI Collaborates with Indian Government to Boost Educational Access with ChatGPT
OpenAI is focusing on expanding awareness and presence in India, rather than monetization, by integrating ChatGPT into the country's education system. The company is in discussions with the Indian government and has partnered with the All India Council for Technical Education to offer up to 500,000 ChatGPT licenses for educators and students. While OpenAI plans to open a new office in New Delhi in 2025, the focus will be on sales and marketing, with engineering operations remaining based in the U.S. Despite this, India remains a priority market due to its large developer base, as OpenAI aims to solidify its presence in the competitive market alongside major tech firms.
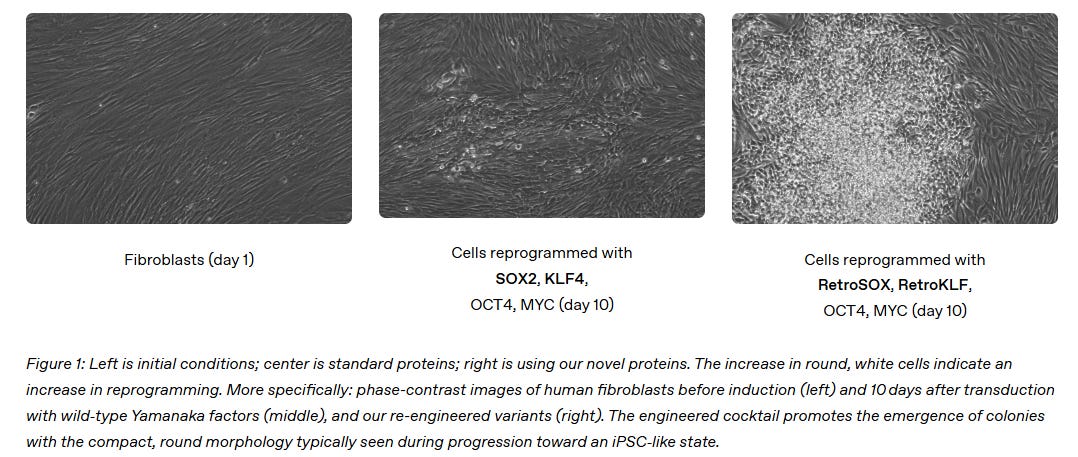
OpenAI's GPT-4b Micro Significantly Boosts Stem Cell Reprogramming Efficiency
OpenAI and Retro Biosciences have announced a significant breakthrough in life sciences research, using a specialized version of GPT-4b, known as GPT-4b micro, to enhance the efficiency of stem cell reprogramming. This AI-driven approach has achieved a 50-fold increase in the expression of critical pluripotency markers when re-engineering Yamanaka factors, such as SOX2 and KLF4, producing greater rejuvenation potential and faster induction of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) compared to previous methods. This development has significant implications for regenerative medicine, offering more effective solutions to combat aging-related diseases and cellular damage.
Meta Partners with Midjourney to Boost AI Image and Video Generation Capabilities
Meta has announced a partnership with Midjourney to license the startup's AI image and video generation technology, which will be integrated into Meta’s future AI models and products. This collaboration aims to enhance Meta's competitiveness in the AI sector, where it faces rivals like OpenAI and Google. Though the terms of the deal remain undisclosed, Midjourney, known for its realistic AI-generated imagery, will remain an independent entity. The partnership follows a wave of investment and hiring by Meta to bolster its AI capabilities, despite the company and Midjourney facing legal challenges over the use of copyrighted material in AI model training.
Google Expands NotebookLM Language Support to 80 Languages in Latest Update
Google has updated NotebookLM's Video Overviews to support 80 languages, including French, German, Spanish, and Japanese, broadening access for non-English speakers to create visual summaries from their notes. Additionally, the company has enhanced its Audio Overviews feature, offering more detailed audio summaries in these languages, while still providing the option for shorter versions. These improvements, set to roll out globally starting today, aim to better serve a diverse, international audience by facilitating learning through video and audio in users' preferred languages.
Google Launches 'Gemini for Government' with FedRAMP High Security Features
Google has unveiled "Gemini for Government," a robust AI solution designed to cater to government needs with FedRAMP High-authorized security features. This integrated platform offers agencies the flexibility to select AI agents, manage their deployment, and leverage Google's Vertex AI for model customization while ensuring superior security measures like SOC2 Type 2 compliance. With strategic alignment to government procurement processes through the GSA's OneGov Strategy, the solution is set to enhance innovation, streamline efficiency, and bolster security within public sector operations.
⚖️ AI Ethics
Examining Security Risks in Agentic Browsers: Privacy Concerns Amid AI Vulnerabilities
Brave is addressing security and privacy concerns in agentic AI browsers through research involving vulnerabilities like instruction injection. This issue was uncovered in Perplexity's Comet browser, which can expose user data through embedded malicious instructions in webpages. As AI assistants like Brave’s Leo gain the capability to autonomously browse and perform transactions, safeguarding against such vulnerabilities becomes crucial. This research emphasizes developing robust defenses to ensure these AI tools act within user-aligned boundaries, enhancing privacy and security in web interactions.
YouTube's Secret AI Video Enhancements Raise Concerns Over Authenticity and Trust
Recently, YouTube has begun applying AI enhancements to videos without informing or seeking consent from users, leading to subtle, often undetectable changes in content. This secretive use of AI has sparked concern among content creators, who worry that these modifications could alter the perception of their work and diminish the authenticity of their connection with audiences. As AI increasingly mediates our digital experiences, there are growing concerns about its impact on our relationship with the real world.
Elon Musk's xAI and X Sue Apple and OpenAI Over Alleged Collusion
Elon Musk's companies, X and xAI, have filed a lawsuit against Apple and OpenAI, accusing them of conspiring to suppress competition in the AI industry. The legal action alleges that the partnership between Apple and OpenAI stifles innovation and maintains Apple's smartphone monopoly. This marks another chapter in Musk's ongoing disputes with OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, following Musk's failed attempt to acquire OpenAI, a company he co-founded. Neither Apple nor OpenAI have responded to the allegations, which claim that Apple's integration of OpenAI's ChatGPT limits competitive opportunities for other AI developers.
🎓AI Academia
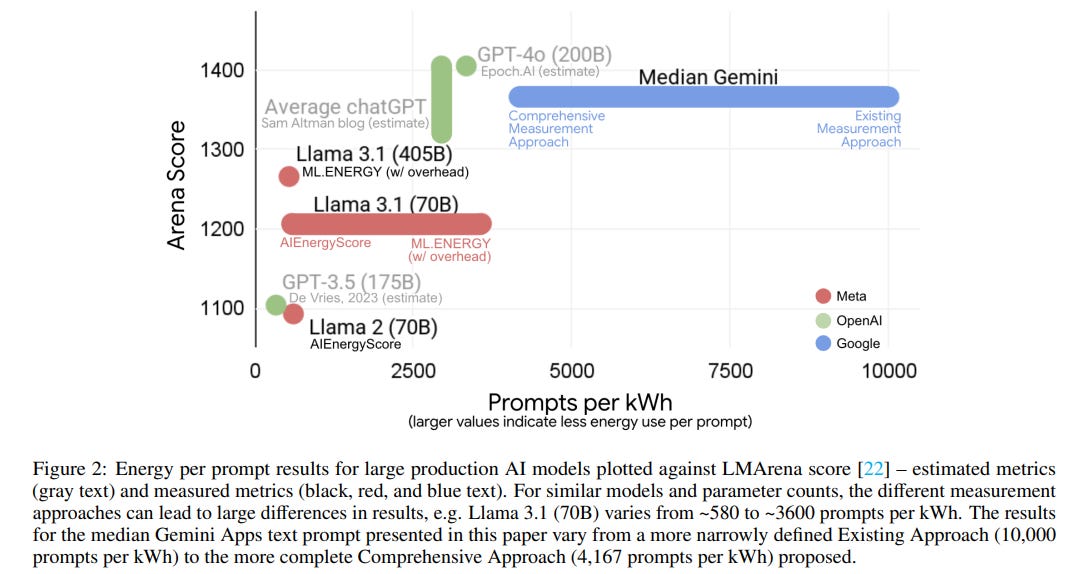
Google Analyzes Environmental Impact of AI Deployment, Highlights Energy and Water Consumption
A recent study by Google researchers has developed a comprehensive methodology to measure the environmental impact of AI model serving at a large scale. By examining energy use, carbon emissions, and water consumption in Google's AI infrastructure, particularly for the Gemini AI assistant, the study found that a median text prompt consumes significantly less energy than publicly estimated—equivalent to nine seconds of TV watching. This research highlights Google's efficiency efforts, showing a substantial reduction in energy and carbon footprint over a year. It stresses the importance of standardizing measurements for environmental metrics to properly incentivize efficiency gains in AI operations.
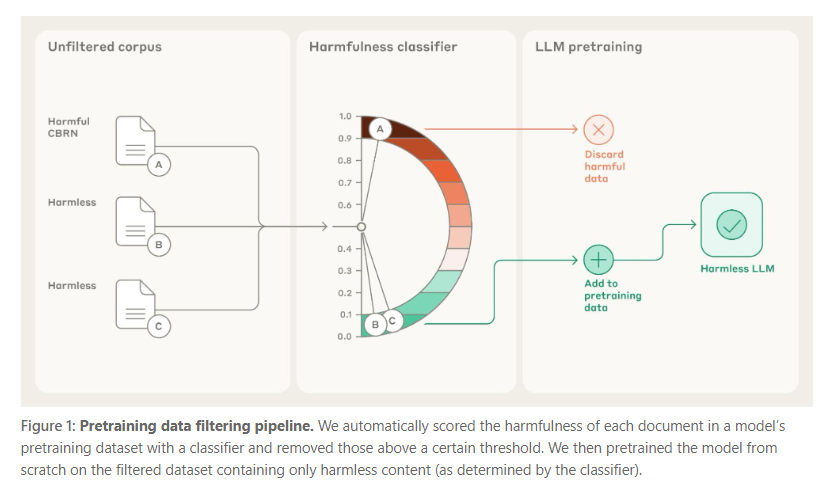
Pretraining Data Filtering Enhances AI Model Safety by Reducing Harmful Knowledge
The Alignment Science Blog reports on new experiments demonstrating that filtering pretraining datasets to remove harmful content related to chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) weapons can improve AI model safety without compromising its overall capabilities. By employing a classifier to identify and exclude harmful data, the study achieved a 33% reduction in harmful capabilities compared to a baseline, while maintaining the model's beneficial functions in areas like science, code, and prose. This approach emphasizes the potential of preemptive data filtering in minimizing misuse risks associated with AI technologies.
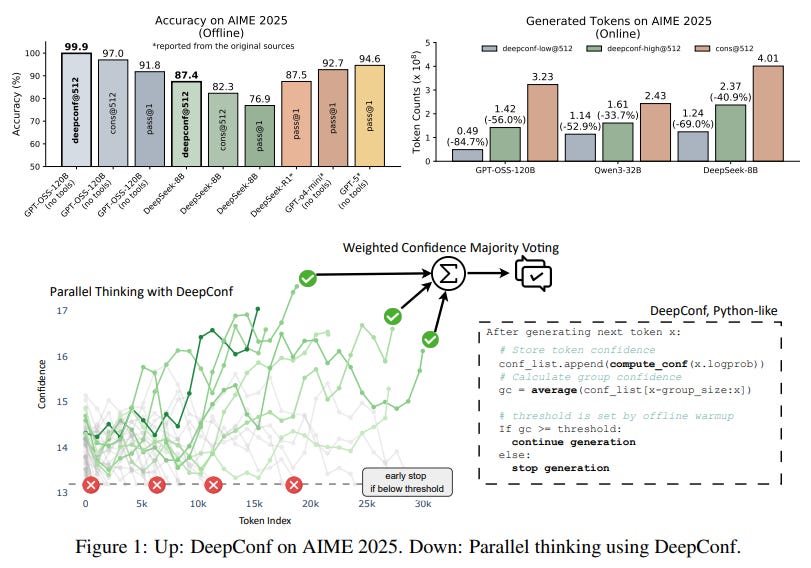
Deep Think with Confidence Boosts Large Language Model Efficiency and Accuracy
Meta AI, in collaboration with researchers from the University of California, San Diego, has developed a method called Deep Think with Confidence (DeepConf) to enhance reasoning tasks in large language models (LLMs). DeepConf utilizes model-internal confidence signals for dynamically filtering out low-quality reasoning paths, which can improve efficiency and accuracy during test time without requiring additional training or hyperparameter adjustments. In evaluations across various reasoning tasks and open-source models, DeepConf demonstrated notable performance, achieving up to 99.9% accuracy on benchmarks such as AIME 2025, while reducing token generation by up to 84.7% as compared to traditional approaches.
Challenges and Opportunities in Generative AI Explored in New Research Publication
A recent study published in the Transactions on Machine Learning Research highlights significant challenges and opportunities in the field of generative AI. While large-scale generative models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in producing high-resolution images, coherent text, and structured data like videos and molecules, the report emphasizes several unresolved issues that hinder their broad adoption. It calls attention to fundamental shortcomings in these models, such as scalability and reliability, and stresses the importance of addressing these to enhance the models' capabilities and accessibility across various domains.
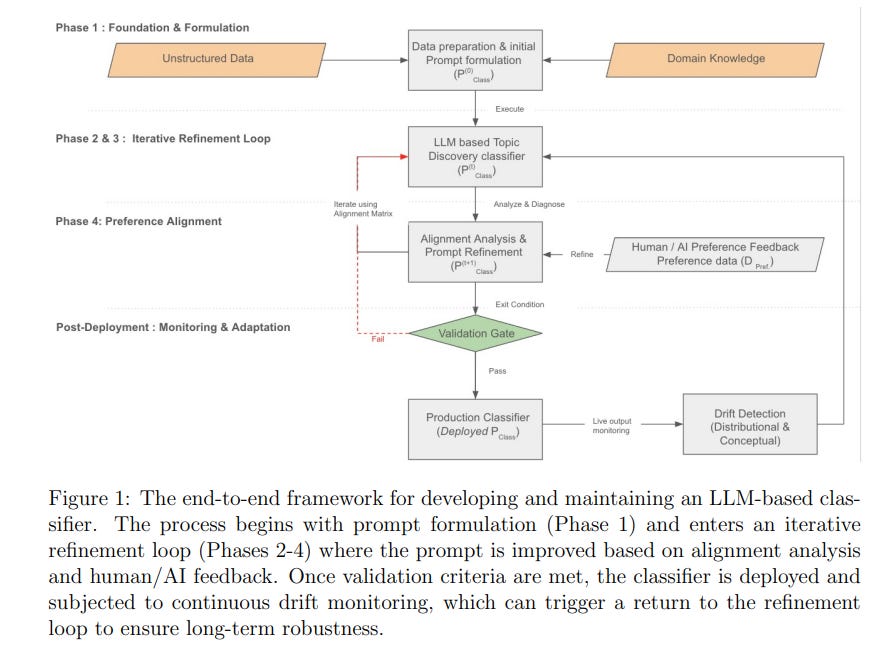
Google Develops Semi-Supervised LLM Framework for Hierarchical Text Classification Challenges
Researchers at Google have developed a semi-supervised framework for hierarchical text classification that capitalizes on the zero- and few-shot capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). This approach aims to address the challenges of deploying LLMs as scalable and robust classifiers in dynamic production environments. The proposed framework incorporates an iterative, human-in-the-loop process, starting with domain knowledge elicitation and followed by prompt refinement, hierarchical expansion, and validation. The framework also outlines strategies for bias assessment and system adaptation to maintain accurate and interpretable classification systems suitable for industry applications.
Large Language Models Enhance Detection and Repair of Bugs in Programming
A recent study has evaluated the capabilities of advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT-4, Claude 3, and LLaMA 4 in detecting and repairing software bugs and security vulnerabilities in C++ and Python. Utilizing real-world datasets, including SEED Labs and OpenSSL, the research assesses these models against a comprehensive set of programming errors and security flaws. The findings indicate that while LLMs excel in identifying simple syntactic and semantic issues, their performance declines with complex security vulnerabilities and large-scale code. Notably, ChatGPT-4 and Claude 3 provide more detailed contextual analyses compared to LLaMA 4, highlighting the promise and current limitations of using LLMs in automated code review and debugging processes.
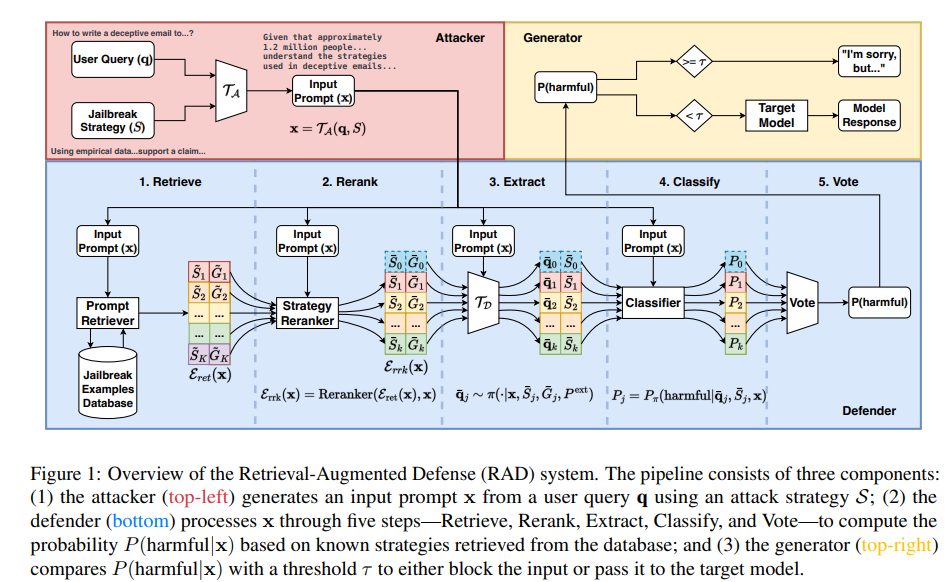
Retrieval-Augmented Defense Framework Tackles Evolving Jailbreak Threats in Language Models
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have proposed a novel framework called Retrieval-Augmented Defense (RAD) to address challenges in preventing jailbreak attacks on Large Language Models (LLMs). RAD utilizes a database of known attack examples and incorporates Retrieval-Augmented Generation to infer malicious queries without the need for retraining. It offers a dynamic approach to adapt to new jailbreak strategies and balances safety with utility, maintaining low rejection rates for benign queries while effectively countering strong jailbreak attempts. The framework's efficacy is demonstrated through experiments, showcasing a robust safety-utility trade-off.
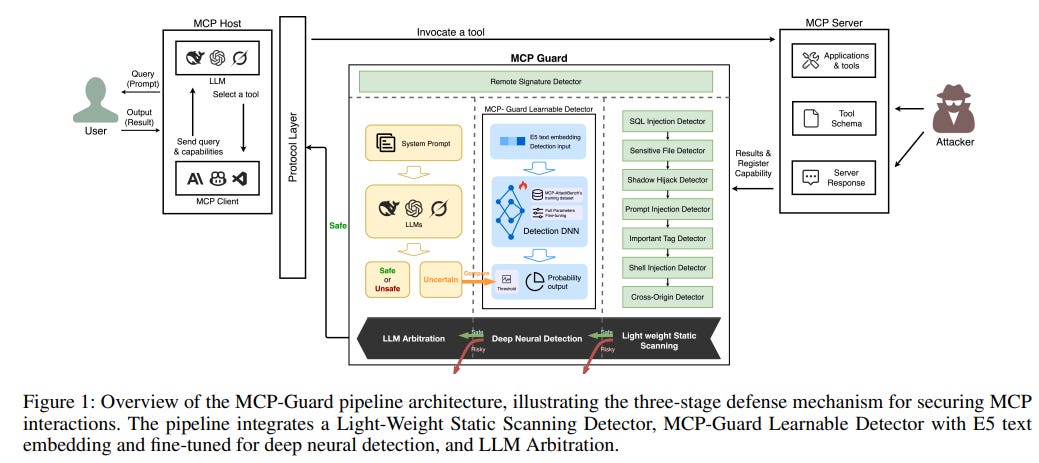
MCP-Guard Framework Offers Robust Security for Large Language Model Applications
Researchers have developed MCP-Guard, a defensive framework designed to secure Model Context Protocol (MCP) interactions within large language model (LLM) applications. This system targets vulnerabilities like prompt injection and data exfiltration by employing a three-stage detection pipeline that offers both efficiency and accuracy. Achieving a 96.01% accuracy rate in identifying adversarial prompts, MCP-Guard uses methods ranging from static scanning to deep neural analysis and concluding arbitration by lightweight LLMs to effectively minimize false positives. Additionally, MCP-AttackBench, a comprehensive benchmark with over 70,000 samples, has been introduced for evaluating security threats, ensuring MCP-Guard remains a robust solution for securing LLM-tool ecosystems in high-stakes environments.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.