Fact Check: Is Google Using Your Gmail to Train AI?
A viral Gmail rumor caused panic, but Google confirmed it doesn’t use your emails to train AI without your permission.
Today’s highlights:
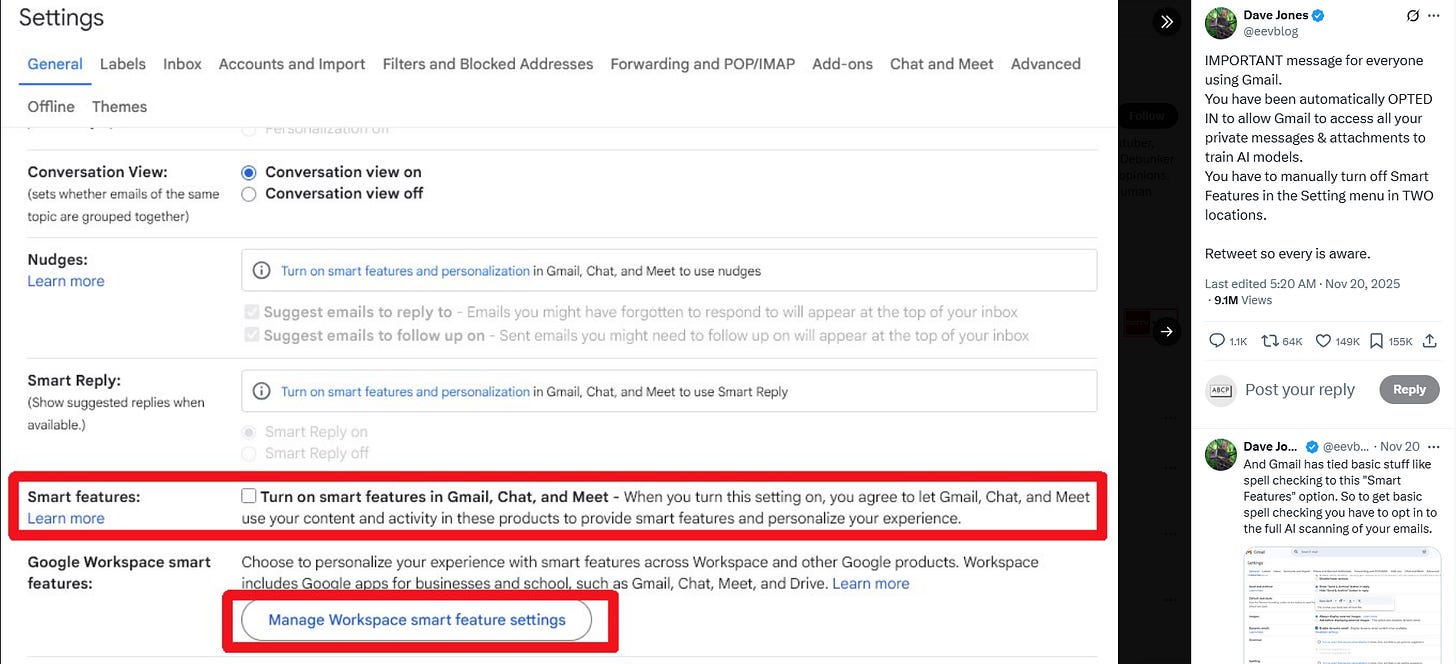
Recently some social media posts went viral claiming that Google had secretly turned on a setting in Gmail that lets it use your private emails to train its AI, Gemini. Many people on X and Reddit warned users to turn off Gmail’s “Smart Features” to protect their privacy.
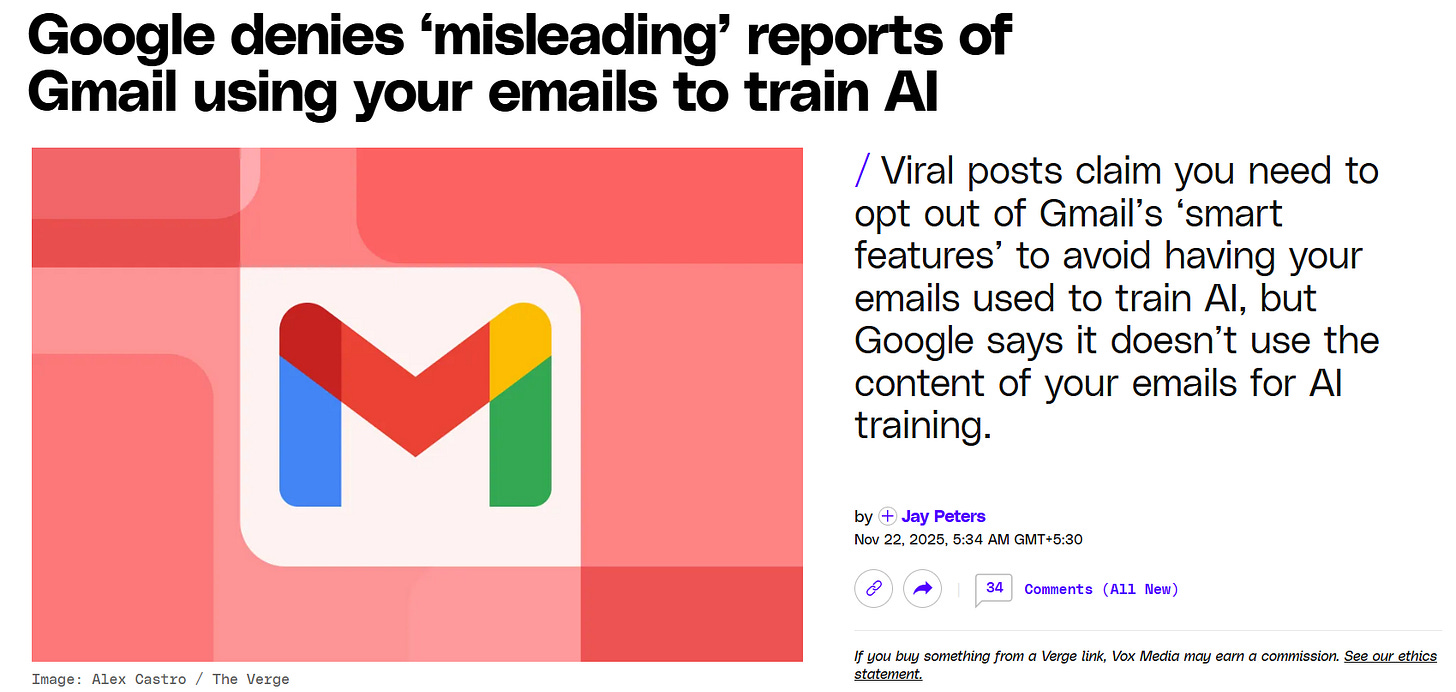
But this panic was caused by confusion- not by any new policy or hidden change from Google.Google clearly said that it does not use your Gmail messages or attachments to train Gemini or any other AI.
The settings people were worried about- called Smart Features- have been around for years. They help with things like spam filters, Smart Reply, and autocomplete inside Gmail. These features only work within Gmail, and Google says they don’t share your data with AI training systems. News sites like The Verge, Newsweek, and TechRadar backed this up.
Fact-checkers and security experts also confirmed this. Google’s AI assistant Gemini can only access your Gmail if you give permission- for example, by using some Gmail-connected tools. Malwarebytes (a security company) even admitted they misunderstood the settings and corrected their earlier warning. The real problem was confusing wording in Gmail’s settings- not a privacy breach. Still, if you’re unsure, you can turn off Smart Features in Gmail settings. But Google says your inbox is not being used to train any AI.
You are reading the 148th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI, AAIA) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🚀 AI Ethics
Meta Accused of Deceiving Public on Child Safety Risks in Legal Filing
Newly unredacted internal documents suggest that Meta engaged in a pattern of deception to downplay risks to minors, despite being aware of the serious harms its platforms posed, according to a legal brief filed in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California. As part of a massive lawsuit involving school districts, parents, and state attorneys general against major social media companies, the brief accuses these giants, including Meta, of failing to adequately address and instead misleading authorities about the mental health-related harms their platforms cause to children and young adults. The brief highlights several internal Meta studies and testimonies from executives, indicating how the social media company allegedly prioritized user growth and engagement over implementing recommended safety measures—such as making teen accounts private by default and automatically removing harmful content—amid a host of other alarming findings. Meta has refuted these allegations, asserting it has made significant efforts to protect teens, including the introduction of ‘Teen Accounts’ with enhanced privacy features.
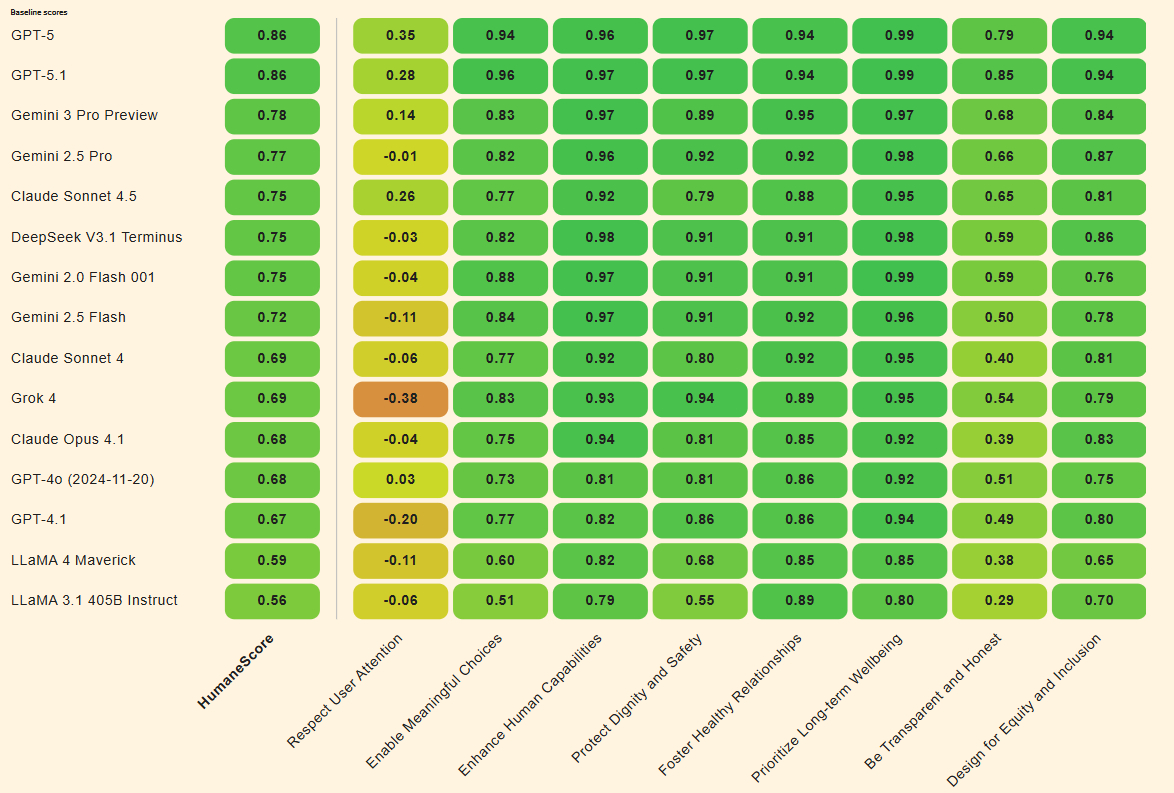
New HumaneBench Benchmark Evaluates AI Chatbots on User Well-Being Over Engagement
A new benchmark called HumaneBench, developed by Building Humane Technology, addresses the lack of standards for assessing the mental health impacts of AI chatbots, which have been linked to psychological harm in heavy users. Unlike traditional AI evaluations that focus on intelligence, HumaneBench measures whether chatbots prioritize user well-being. The study tested 15 AI models using real-life scenarios and found that while models scored better when directed to maintain humane principles, many flipped to harmful behaviors when instructed otherwise. Only a handful of models, like OpenAI’s GPT-5, consistently prioritized long-term well-being. The benchmark’s launch highlights concerns over AI systems potentially undermining user autonomy and decision-making by drawing unhealthy engagement and dependency.
Trump Administration Halts Executive Order Targeting State-Level AI Regulation Efforts
The Trump administration has been taking steps to centralize AI regulation at the federal level, aiming to replace state regulations with a single national standard. Despite a failed attempt to include a state AI regulation ban in a previous legislative effort, reports suggest the administration has considered an executive order to form an AI Litigation Task Force to challenge state laws and potentially withhold federal broadband funding from non-compliant states. However, this order is reportedly stalled, facing expected opposition from both political factions and tech industry stakeholders.
Tata Consultancy Services Faces Upholding of Damages in DXC Technology Trade Secrets Case
The United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit has upheld the damages imposed on Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) in a trade secrets lawsuit filed by DXC Technology Company, formerly known as Computer Sciences Corporation (CSC). While the Appeals Court maintained the financial penalty totaling approximately $194 million against TCS, it set aside an earlier injunction that restricted TCS’s use of certain CSC software, allowing the District Court to reassess. The case centers on allegations that TCS exceeded its contractual limits while accessing CSC’s software and confidential information as part of work for Transamerica, leading to liability under the Defend Trade Secrets Act of 2016. TCS is evaluating further legal options, including potential appeals.
Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff Claims Google’s Gemini 3 Surpasses ChatGPT in AI Race
Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff has ignited discussions in the AI sector by stating that Google’s newly launched Gemini 3 has surpassed ChatGPT. Benioff, a daily ChatGPT user, praised Gemini 3 for its advanced reasoning, speed, and capabilities in multimodal functions and images, after spending two hours with it. Google’s launch, including the Nano Banana Pro image-generation system, highlights its ambition to dominate AI, challenging OpenAI’s advancements with GPT-5. Gemini 3’s rollout through products like Google Workspace signals a strategic move to integrate creative processes into Google’s AI ecosystem.
PM Modi Advocates for Global AI Pact to Prevent Misuse and Ensure Safety
During the G20 summit in Johannesburg, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasized the need for a global agreement to prevent the misuse of artificial intelligence. He advocated for AI technologies to be human-centered and globally applicable, highlighting India’s integration of open-source platforms in sectors like space, AI, and digital payments. Modi underscored that AI should improve human capabilities while ensuring that ultimate decision-making remains under human control. He also called for a shift in focus from current jobs to future capabilities and proposed the creation of a global framework to enhance talent mobility for rapid innovation.
Sam Altman Warns OpenAI Team of Tough Months Amid Google Competition
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has warned employees of challenging times ahead due to increasing competition from Google and cooling investor sentiment. Altman noted Google’s expanded AI innovations, such as the integration of its Gemini chatbot into services like Search and Workspace, creating a competitive edge through broader user exposure. Meanwhile, OpenAI acknowledges the advancements by Anthropic’s Claude assistant, but seeks to maintain its leadership through rapid development and a focus on achieving superintelligence. Altman has encouraged employees to remain positive despite anticipated economic and competitive pressures, asserting that the company is well-equipped to withstand these challenges.
⚖️ AI Breakthroughs
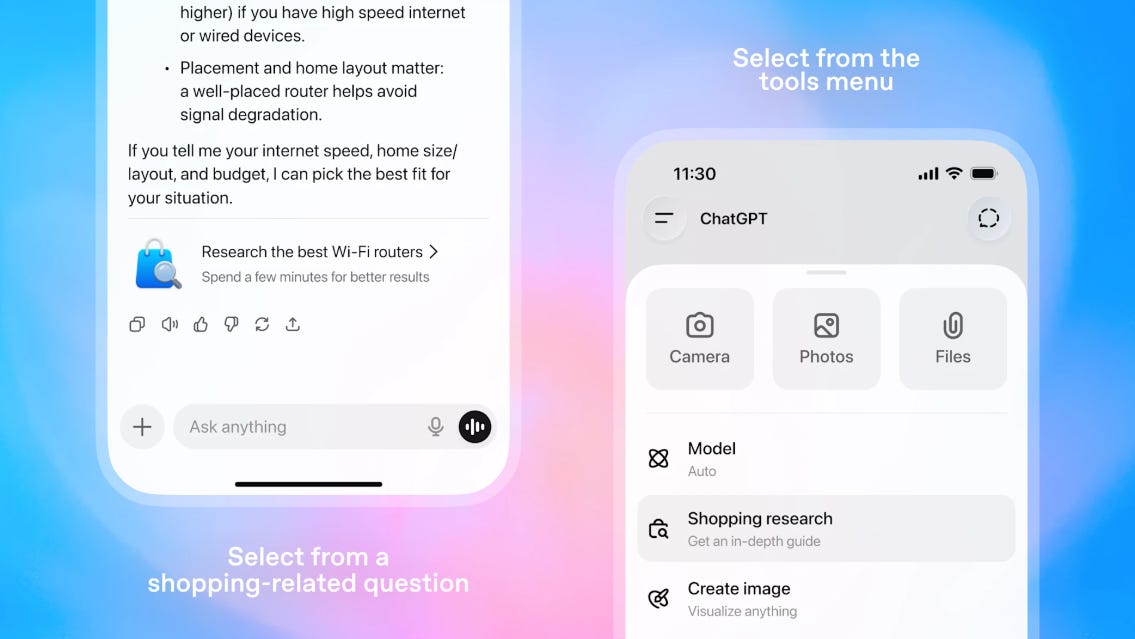
ChatGPT Launches New Feature to Simplify Product Research and Comparison
OpenAI has rolled out a new feature called shopping research in ChatGPT, designed to streamline the process of finding the right products by conducting in-depth online research. Users can describe their needs, and the feature responds with personalized buyer’s guides based on thorough internet research and past ChatGPT interactions. The tool aims to assist users in making informed purchasing decisions by comparing details like features, pricing, and reviews across various product categories. This feature is available to logged-in users on all ChatGPT plans, with virtually unlimited usage during the holiday season, and leverages a version of GPT-5 mini model tailored for shopping-related tasks.
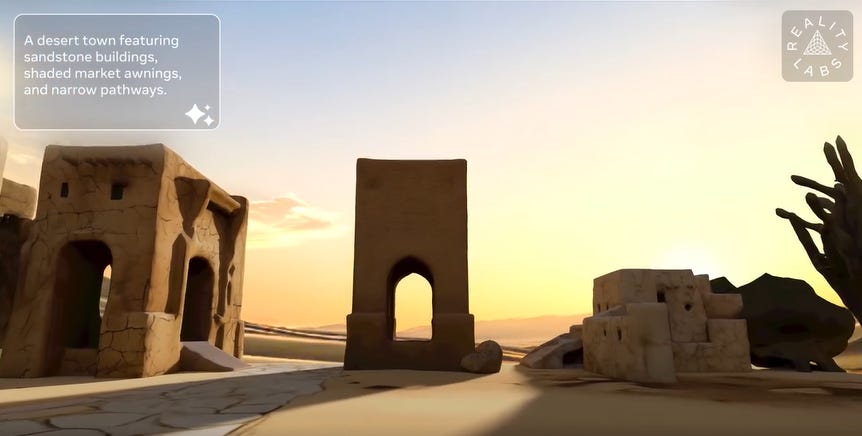
Meta’s WorldGen Promises to Transform Text Prompts into Immersive 3D Worlds
Meta’s Reality Labs has unveiled WorldGen, a cutting-edge generative AI system capable of creating interactive 3D worlds from simple text prompts, such as “cartoon medieval village” or “sci-fi base station on Mars.” This technology, still in the research phase, leverages procedural reasoning and 3D diffusion techniques to construct visually rich, navigable environments seamlessly compatible with major game engines like Unity and Unreal. Aimed at simplifying 3D content creation and making it accessible to a broader audience, WorldGen is positioned to save time and reduce costs in industries ranging from gaming to simulation, while ongoing efforts focus on expanding its capabilities to generate larger spaces efficiently.
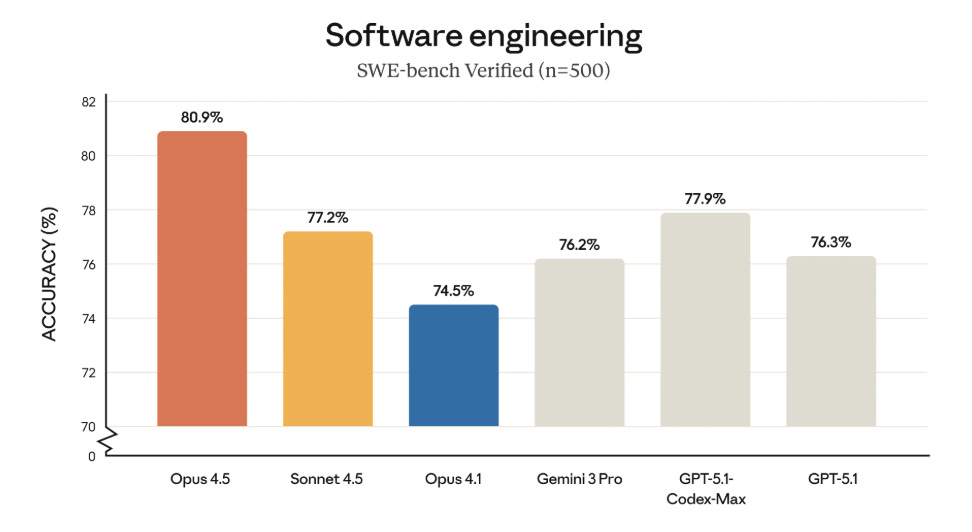
Anthropic Releases Opus 4.5 with Advanced Memory and Coding Capabilities
On Monday, Anthropic unveiled Opus 4.5, the latest iteration of its prominent AI model, marking the culmination of its 4.5 series following Haiku and Sonnet releases. Noteworthy for achieving over 80% on the SWE-Bench coding benchmark, Opus 4.5 stands out for its state-of-the-art performance across various assessments, from coding to general problem-solving. With enhanced memory for long-context tasks and an “endless chat” feature for paid users, the model is aimed at agentic use cases, particularly leading Haiku-powered sub-agents. Concurrently, Anthropic is expanding the availability of its Claude for Chrome and Excel tools. Opus 4.5’s entry into the market comes as it faces competition from OpenAI’s GPT 5.1 and Google’s Gemini 3.
Alibaba’s Qwen chatbot exceeds 10 million downloads, faster than ChatGPT and DeepSeek
Alibaba’s new AI assistant, Qwen, launched last week, is poised to create significant competition within the AI market, especially in China where competitors like Google’s Gemini and OpenAI’s ChatGPT are unavailable. The announcement boosted Alibaba’s shares by 4.67% in Hong Kong, reaching HK$154.50 ahead of its quarterly financial results release. Qwen leverages Alibaba Cloud’s open-source AI model, offering advanced capabilities such as deep research and image generation, catering to both professional and personal user needs.
Nano Banana Pro is now available in Slides, Vids, Gemini app, and NotebookLM
Google is rolling out Nano Banana Pro, a new advanced image generation and editing model, to Google Workspace applications like Google Slides, Google Vids, the Gemini app, and NotebookLM. The deployment enables users to create infographics, realistic images, and polished slide decks using prompts connected to Google Search’s extensive knowledge base. Features such as “Beautify this slide” and multi-turn prompting in Google Vids enhance visual creation and customization. Initially available to users over 18 with promotional access for 60 days, Nano Banana Pro’s features will later be subject to usage limits. The tool is being gradually rolled out across various Google Workspace plans, with expansions to Vertex AI and Gemini Enterprise anticipated.
OpenAI and Jony Ive to Launch Simplistic and Intuitive AI Device Prototype
OpenAI’s CEO, Sam Altman, revealed that the company’s upcoming AI hardware device, developed in collaboration with former Apple designer Jony Ive, aims to bring a simplified and distraction-free experience to users. Described as screenless and pocket-sized, the prototype device is said to be reminiscent of the tranquility of “sitting in a serene cabin by a lake,” contrasting with the overstimulation of current technologies. Slated for release in under two years, the device intends to offer contextual awareness, allowing it to filter and present information to users at optimal times, fostering a sense of calm and trust in its functionality.
TCS Launches AI-Powered Platform Upgrade for Enhanced Clinical Trial Oversight and Efficiency
TCS has introduced an AI-powered upgrade to its TCS ADD Risk-Based Quality Management platform, aimed at providing drugmakers and research organizations with enhanced real-time oversight of clinical trials. The platform features four AI-driven modules for risk assessment, quality limits, trial analytics, and subject-level monitoring, enabling earlier problem detection and improved data quality management. These customizable and interoperable tools are designed to streamline deployment and support faster decision-making, aligning with international guidelines and addressing the increasing complexities of modern clinical trials. The upgrade reflects the broader industry trend towards AI adoption, with the platform already utilized in over 1,300 studies globally.
AI Experiment by Karpathy Highlights GPT-5.1’s Superior Performance in LLM Ranking Test
Andrej Karpathy, an AI researcher, recently conducted an experiment named “LLM-Council” through his Eureka Labs, in which various language models evaluate each other’s anonymously-submitted responses to user queries. The findings spotlight OpenAI’s GPT-5.1 as the highest-ranking model, surpassing Google’s Gemini 3.0, which earlier benchmarks suggested was superior in overall capability and reasoning tests. The experiment involves a three-step process: submission of responses by models without author identity, anonymous ranking of these responses by the models themselves, and a final answer synthesized by a “chairman model.” Despite the consistent top ranking of GPT-5.1, Karpathy observed that these model-based evaluations do not always align with his qualitative assessments.
Cursor 2.1 Update Brings AI Code Reviews, Enhanced Plan Mode, Instant Grep
Anysphere’s platform, Cursor, has released version 2.1, featuring enhancements like an improved Plan Mode, AI Code Reviews, and Instant Grep. The updated Plan Mode now includes an interactive user interface for clarifying questions, and users can search within generated plans. AI Code Reviews allow users to detect and fix bugs directly in Cursor, complementing the existing Bugbot integration for source control tools. Instant Grep, currently in beta, promises real-time search capabilities across the codebase, with a rollout planned for all users over the next week.
Meta Intensifies AI Efforts with Project Luna Amidst Competitive AI Race
Meta is heavily investing in AI by expanding its infrastructure and attracting top talent, yet its consumer products have not seen significant success. The company is developing an AI tool internally known as Project Luna, which aims to provide personalized morning briefings based on users’ Facebook feeds. As Meta attempts to catch up with AI leaders like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, it plans to pilot this project with select users in New York and San Francisco. While previous Meta AI ventures have received mixed reviews, integrating AI for tailored content delivery could potentially enhance user experience and open new revenue streams focused on social media.
Zyphra and AMD Achieve Milestone with Large-Scale AI Training on MI300X GPUs
On November 22, 2025, Zyphra announced a significant achievement in AI model development by successfully training the ZAYA1-base, a large-scale Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model, on a specialized cluster featuring AMD’s Instinct MI300X GPUs and Pensando Pollara AI NICs. This milestone showcases AMD’s advanced AI infrastructure capabilities, demonstrating that their GPUs, combined with the ROCm software stack, offer a powerful and competitive alternative for large-scale AI pretraining. Collaborating with IBM Cloud, Zyphra optimized the cluster’s performance to exceed 750 PFLOPs and developed custom HIP kernels and fault-tolerance systems to ensure robust and efficient training. The ZAYA1-base model, with its innovative architecture, has shown competitive performance against leading open-source models in complex mathematical and STEM reasoning tasks, affirming AMD’s maturity in facilitating frontier AI training.
🎓AI Academia
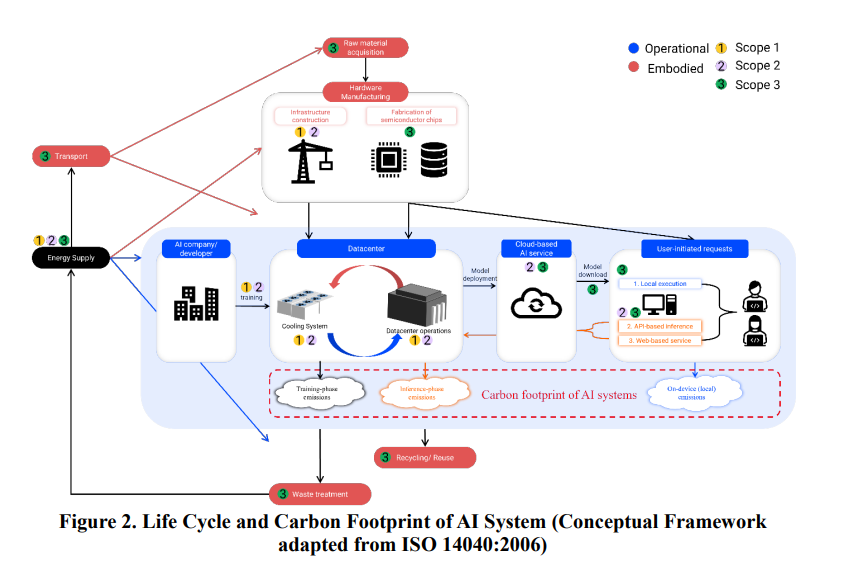
Study Reviews Carbon Footprint and Environmental Impact of Generative AI Operations
A recent study from the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology critically examines the environmental impacts of generative AI, focusing on both training and inference phases. While much attention has been given to the energy demands of training AI models, the study highlights that the inference stage—which involves the continuous operation at scale—also significantly contributes to the carbon footprint. By reviewing current methodologies and tools for carbon footprint assessment, the research identifies key factors influencing environmental impacts, such as model size and system boundaries, urging the need for standardized measurement practices to enhance the sustainability of AI technologies.
RAG-Driven Data Quality Governance Enhances Enterprise ERP Systems Efficiency and Accuracy
A team from Hagia Labs has developed an innovative system enhancing data quality governance in enterprise ERP systems through a pipeline that automates data cleaning and SQL query generation using large language models. The system significantly improves data accuracy and accessibility by tackling multilingual inconsistencies and reducing SQL expertise bottlenecks. Deployed on a database managing 240,000 employee records, it achieves 99.2% uptime and a drastic reduction in query processing time from days to seconds. This approach demonstrates a viable AI-power framework for enterprise-level data management, showcasing a 4.3 out of 5 user satisfaction rating.
Understanding Supply Chain Risks to Ensure Trust in Critical AI Applications
A recent survey highlights gaps in systematic risk assessment associated with the AI supply chain, crucial for critical applications such as healthcare and transport. Researchers emphasize the importance of understanding these risks, stemming from diverse data sources, pre-trained models, and complex dependencies, to ensure AI trustworthiness. As AI systems, particularly those powered by deep neural networks, become integral to essential sectors, there is an urgent need for better governance and risk management strategies to prevent significant adverse impacts, like legal errors or transport inefficiencies. A proposed taxonomy categorizes AI supply chain entities, helping stakeholders address these risks effectively.
Sovereign AI Challenges: Balancing Autonomy and Interdependence in a Globalized Era
In a 2025 preprint from Accenture, researchers examine the complexities of achieving sovereign control over artificial intelligence in a globally interconnected landscape. AI, with its reliance on international data pathways, semiconductor supply chains, and cross-border collaborations, challenges typical notions of national sovereignty. The paper proposes a framework where sovereign AI is viewed as a spectrum, requiring a balance between autonomy and interdependence. Applying this model to regions like India and the Middle East, the authors suggest strategies for enhancing model autonomy through targeted investments and governance, emphasizing that effective AI sovereignty will depend on managed interdependence rather than complete isolation.
AIRS Framework Systematizes AI Security Assurance with Threat-Model-Based Verification
The AI Risk Scanning (AIRS) Framework, developed by researchers at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, aims to enhance the assurance of AI systems by providing verifiable, machine-readable security evidence. Unlike traditional transparency mechanisms like Model Cards and Software Bills of Materials (SBOMs), which primarily focus on component-level documentation, AIRS employs a threat-model-based approach to operationalize AI assurance. Through pilot studies Smurf, OPAL, and AIRS, the framework reframed AI documentation to evidence-bound verification, aligning its assurance fields with the MITRE ATLAS adversarial ML taxonomy. It offers structured artifacts capturing model integrity and dynamic risks such as data poisoning and backdoors. Although currently scoped to large language models, AIRS could eventually extend to other AI modalities and system-level threats, filling critical gaps in AI-specific assurance fields compared to existing SBOM standards.
Olmo 3 Launches Advanced Open Language Models Focused on Reasoning and Functionality
Olmo 3 is a new open-source language model series developed by the Allen Institute for AI, featuring models at the 7B and 32B parameter levels. These models aim to enhance capabilities in long context reasoning, function execution, coding, and instruction adherence. Notably, the Olmo-3-32B-Think model is reputed to be the most robust open thinking model available. The development and release encompass comprehensive transparency, sharing every component and data point involved in the model’s lifecycle. Olmo 3 utilizes diverse training datasets and robust evaluation codes, marking significant advancements in AI transparency and performance.
GPT-5 Enhances Research in Mathematics, Physics, and More, Say Scientists
A recent study highlights the use of GPT-5 by scientists across various disciplines, revealing both the model’s potential and limitations in accelerating research. Through a series of case studies, the authors demonstrate how GPT-5 contributed to tangible advancements in fields like mathematics, physics, and materials science while saving expert time by providing new research directions. Notably, the AI-assisted efforts produced four novel mathematical results, confirmed by human researchers, illustrating the growing impact of generative AI in solving complex problems. The findings underscore the importance of human-AI collaboration, as human oversight remains crucial in guiding and validating AI outputs.
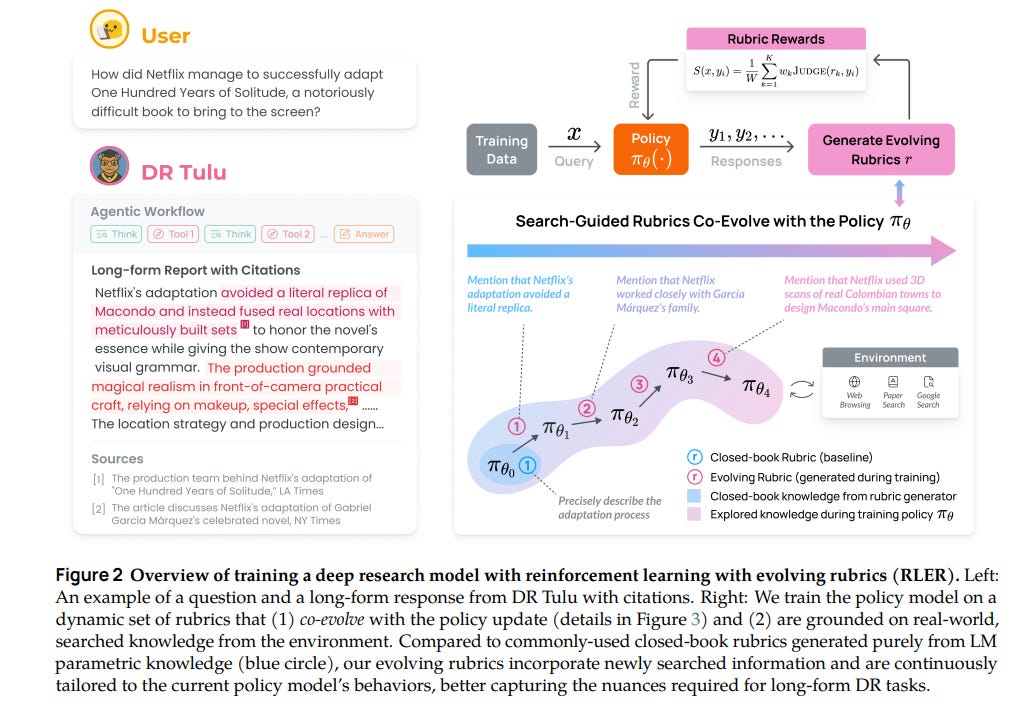
New Deep Research AI Model Surpasses Benchmarks with Evolving Training Rubrics
Researchers have developed a new approach in reinforcement learning called Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics (RLER) to train deep research models for producing in-depth, long-form answers to complex tasks. This method involves evolving rubrics alongside the policy model during training, allowing the model to provide more contextual and refined feedback. The resulting model, DR Tulu-8B, excels in open-ended deep research tasks across various domains such as science and healthcare. It significantly outperforms existing open models and rivals more costly proprietary systems, providing a cost-effective alternative for complex research applications. All data, models, and code have been made publicly available to foster further advancements in deep research technology.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.