Countdown Begins: EU Finalizes GPAI Code of Practice- And the World Is Watching!
In a landmark move, the European Commission finalized the General-Purpose AI (GPAI) Code of Practice on July 10, 2025, just weeks before the AI Act’s enforcement begins on August 2.
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 109th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training such as AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI using a scientific framework structured around four levels of cognitive skills. Our first course focuses on the foundational cognitive skills of Remembering and Understanding & the second course focuses on the Using & Applying. Want to learn more? Explore all courses: [Link] Write to us for customized enterprise training: [Link]
🔦 Today's Spotlight
The General-Purpose AI Code of Practice: A Critical Moment for AI Governance
As of 10 July 2025, the European Commission officially published the final version of the General‑Purpose AI Code of Practice, just weeks before the GPAI obligations of the EU AI Act come into effect (on 2 August 2025). Crafted by 13 independent experts in a multi-stakeholder process, this Code is specifically targeted at developers of general-purpose AI models—including firms like OpenAI, Meta, Google, and Anthropic—and aims to bridge the gap between legal obligations and practical implementation. As the AI Act enters into phased enforcement from August 2025, this Code arrives just in time to offer legal clarity, support responsible development, and signal Europe’s leadership in global AI regulation.
What’s in the AI Code of Practice?
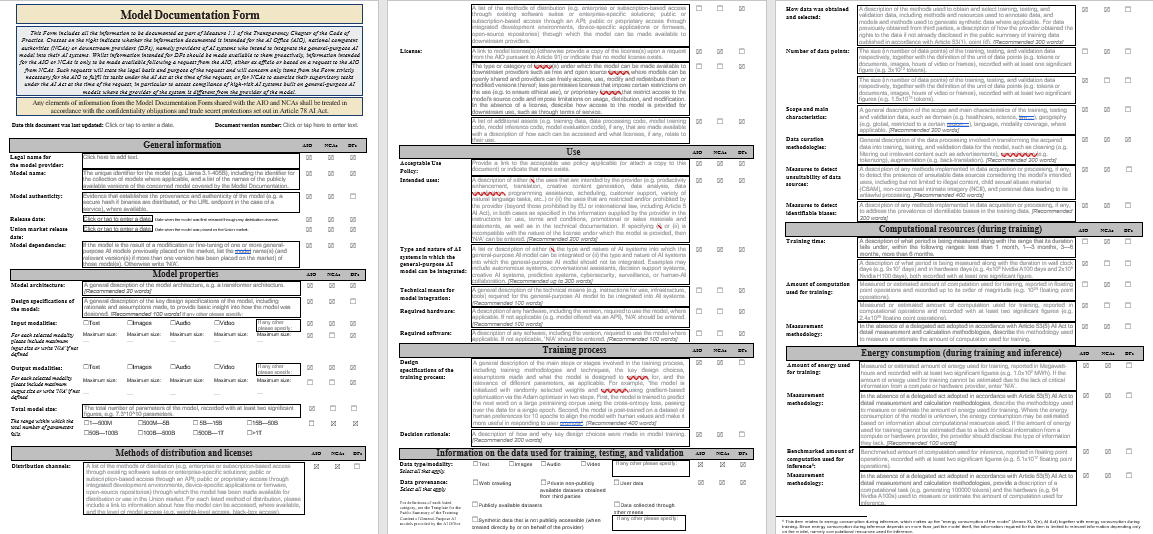
Transparency AI developers must disclose critical information about their systems using a standardized Model Documentation Form. This includes data sources, model purposes, design specifications etc. Open-source models are partially exempt unless deemed systemically risky. The goal is public and regulatory visibility into how major AI models function.
Copyright The Code advises firms to respect EU copyright laws during both model training and deployment. For example, if web crawlers are used to scrape data, they must inform rightsholders about crawlers & robots.txt use and avoid generating copyrighted content verbatim. Internal policies, staff, and compliance documentation are required under Article 53 of the AI Act.
Safety & Security This section targets only the most advanced models posing “systemic risks” (per Article 55). It outlines exhaustive risk governance protocols, such as ongoing model evaluation, incident documentation, and record-keeping for at least 10 years post-deployment. It offers a concrete playbook for managing and mitigating harmful AI behavior.
Together, these three pillars turn legal expectations into operational actions, formed through consultations with over 1,000 stakeholders from industry and civil society.
Why This Matters – and Early Pushback
The release marks a global milestone in proactive AI governance, emphasizing the EU’s vision of safe, transparent, and copyright-respecting AI. However, it has drawn criticism from both industry and lawmakers:
Industry Pushback: Tech companies argue the Code is too detailed, rushed, or burdensome. Some lobbied for delays in AI Act enforcement, fearing they won’t meet transparency or copyright compliance in time. Trade groups like CCIA Europe warn that voluntary compliance could still impose disproportionate obligations on signatories compared to competitors who opt out.
Lawmakers & Civil Society Concerns: On the flip side, some Members of European Parliament (MEPs) claim the Code was watered down in last-minute revisions. They allege that essential safeguards—like public transparency and stricter risk assessments—were removed without Parliamentary oversight, creating ambiguity about enforcement and undermining trust.
This dual criticism underscores the EU’s delicate balancing act: regulating without stifling innovation, and protecting the public without overburdening developers.
The EU’s Response and Path Forward
Despite opposition, the EU remains firm on timelines and committed to building trust in AI:
No Delay in Enforcement: The AI Act’s obligations for general-purpose AI will become legally binding on August 2, 2025, with full implementation by August 2026. The Code was finalized quickly—even if slightly later than intended—to ensure companies have actionable guidance in time.
Voluntary but Strategic Adoption: The Commission is actively encouraging firms to sign on, suggesting that doing so provides “legal certainty” and fosters a smoother compliance relationship.
Accountability through Oversight: The Code will be enforced in spirit by the new EU AI Office and national regulators. MEPs have stressed that, despite concessions, core values like copyright and fundamental rights remain intact. The EU also plans to treat the Code as a “living document”, adapting it over time through continuous dialogue and technological change.
Conclusion: A Balanced Path to Trustworthy AI
The EU’s General-Purpose AI Code of Practice represents a landmark approach to AI regulation—a blend of voluntary commitment and structured compliance. It makes the AI Act’s high-level goals tangible for developers, encouraging transparency, copyright respect, and long-term risk management. While both tech companies and lawmakers have voiced opposing concerns, this tension may actually reflect the Code’s strength as a well-negotiated middle ground.
By releasing this Code ahead of formal legal enforcement, the EU signals that AI development must be responsible from day one, not merely reactive after harms occur. Signing on to the Code can serve as a badge of trust for AI providers, offering reputational advantages and a clearer compliance roadmap. For the public, it offers assurance that Europe is building a future where AI systems are transparent, ethical, and safe by design.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
Perplexity Launches AI-Powered Comet Browser to Compete Against Google Search Dominance
• Perplexity launched Comet, an AI-powered web browser, aiming to rival Google Search by integrating AI-generated summaries of search results as its default feature
• Comet's standout element is the Comet Assistant, an AI agent designed to automate tasks such as email summarization, calendar management, and web page navigation
• Comet's accessibility began with the $200-per-month Max plan subscribers and a select group of early invitees, as part of Perplexity's strategic market entry approach;
xAI Launches Grok 4 AI Model, Introduces $300 SuperGrok Heavy Subscription Plan
• xAI unveiled Grok 4, the latest generative AI model, alongside a multi-agent version called Grok 4 Heavy, offering frontier-level performance on several academic benchmarks
• xAI introduced SuperGrok Heavy, a $300-per-month AI subscription plan offering early access to new features like coding, multi-modal agents, and video generation models expected in coming months
• Despite Grok's robust capabilities, recent controversies, such as antisemitic comments and leadership changes at X, could challenge xAI's efforts to position Grok as a serious competitor to ChatGPT and Gemini.
Hugging Face Opens Orders for Reachy Mini Robots, Targets AI Developers with New Kits
• Hugging Face launches Reachy Mini desktop robots for AI developers, featuring two versions: the $449 wireless model and the $299 wired version, both programmable in Python
• The open source Reachy Minis come in a DIY kit and integrate with Hugging Face Hub, offering access to over 1.7 million AI models for extensive customization;
• The decision to release two Reachy Mini variants arose from community feedback, aiming to foster creativity and enable users to share custom applications on the open source platform;
Hugging Face Launches SmolLM3, a Multilingual 3B Model with Advanced Capabilities
• Hugging Face's SmolLM3, a 3B parameter model, excels in multilingual capabilities and long-context reasoning, surpassing peers like Llama-3.2-3B and Qwen2.5-3B
• With support for six languages, SmolLM3 can handle up to 128k tokens, leveraging NoPE and YaRN techniques for enhanced context processing
• SmolLM3's training includes web, code, and math datasets, with detailed methodologies available on GitHub, fostering transparency and community collaboration in AI research.
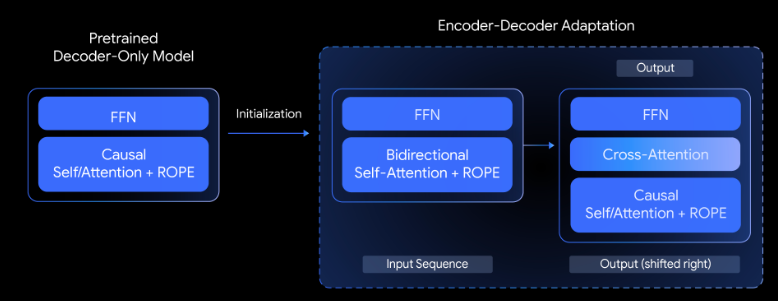
Google's T5Gemma Encoder-Decoder Models Enhance Performance Over Decoder-Only Architectures in AI Tasks
• T5Gemma has been introduced as an encoder-decoder variant adapting decoder-only models to excel in practical tasks with better quality-efficiency trade-offs;
• Empirical results show T5Gemma consistently outperforms its decoder-only predecessors on benchmarks like SuperGLUE, improving inference speed and accuracy for critical tasks;
• Pre-training and instruction-tuning adaptations significantly boost T5Gemma's capabilities in reasoning-intensive evaluations, notably increasing scores in GSM8K and DROParse performance benchmarks.
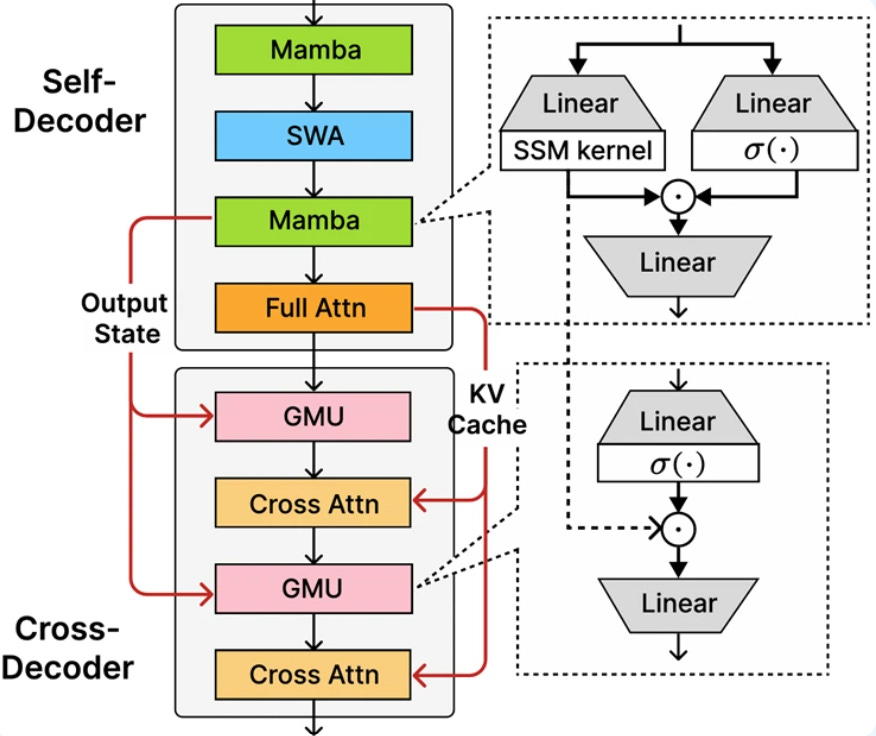
Microsoft Launches Compact AI Model Phi-4-Mini for Enhanced On-Device Reasoning
• Microsoft releases Phi-4-mini-flash-reasoning, a compact AI model designed for fast, on-device logical reasoning, offering significant improvements in throughput and latency in low-latency environments;
• The model features a 3.8-billion parameter architecture called SambaY, integrating state-space models with new Gated Memory Units, improving long-context performance and decoding complexity for mobile and edge use;
• Benchmarks show Phi-4-mini-flash-reasoning surpasses larger models like AIME24/25 on specific tasks, aligning with Microsoft's push for responsible AI and transparent, inclusive practices through Azure, Hugging Face, and NVIDIA.
Narada AI’s CEO says- "SaaS is in the past. The future belongs to agents"
• Dave Park, CEO of Narada AI, suggests the SaaS model will fade, with agentic AI poised to transform enterprise software, reducing reliance on numerous daily apps
• Narada AI's large action models can execute multi-step tasks without APIs, signaling a shift in workplace tech following its TechCrunch Disrupt 2024 debut
• The podcast Equity delves into agentic AI's rise, its real-world implications, and how companies like Grammarly are integrating AI to streamline business operations.
Isomorphic Labs Set to Begin Human Trials with AI-Designed Cancer Drugs
• Alphabet’s Isomorphic Labs is on the brink of human trials for its AI-designed drugs, aiming to revolutionize drug development using machine learning and protein structure predictions;
• In 2025, Isomorphic Labs secured $600 million in funding, collaborating with pharma giants like Novartis and Eli Lilly, to create a cutting-edge drug design engine;
• Inspired by AlphaFold’s breakthroughs, Isomorphic Labs focuses on internal drug candidates in oncology and immunology, planning to transform drug discovery with a higher success rate and efficiency.
Tencent Launches ArtifactsBench to Enhance Creative AI Model Testing and Evaluation
• Tencent unveils ArtifactsBench, a benchmark aimed at addressing the challenges of evaluating creative AI models, focusing on user experience, aesthetic quality, and functionality
• ArtifactsBench uses a Multimodal LLM judge, assessing AI-generated code against a detailed checklist, achieving 94.4% consistency with human rankings from WebDev Arena
• Generalist AI models, like Qwen-2.5-Instruct, outperform specialized ones in visual application tasks, suggesting a blend of robust reasoning and design aesthetics is crucial for AI success;
Former Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger Launches Flourishing AI to Test Human Values
• Former Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger announced the launch of Flourishing AI (FAI), a benchmark to evaluate AI models' alignment with human values, following his partnership with faith tech company Gloo
• FAI is based on The Global Flourishing Study by Harvard and Baylor, measuring prosperity through categories like Happiness, Social Relationships, and Spirituality to assess large language models
• Gelsinger, who has decades of experience in technology and faith intersections, emphasizes ensuring AI advances human well-being in his new venture with the Gloo-backed FAI benchmark.
Doctor Builds £100K Healthcare App Using Replit for Just £175 and No Coding
• Replit enabled Dr. Fahim Hussain to develop a healthcare app, MyDoctor, for just £175 using AI-driven natural language prompts, bypassing traditional app development quotes of £75,000 to £100,000
• MyDoctor offers comprehensive healthcare services like appointment booking, prescription requests, nutrition tracking, and an AI-powered symptom checker using NICE guidelines and DeepSeek API
• With Supabase ensuring regulatory compliance for patient data, Hussain's successful app launch accelerated his business timeline by over a year, creating potential for a standalone revenue stream.
Replit Partners with Microsoft to Enable No-Code App Development on Azure
• Replit partners with Microsoft Azure to enable enterprise users to build secure applications using natural language, eliminating the need for traditional coding skills
• Integration with Microsoft services like Azure Container Apps and Virtual Machines allows seamless deployment of Replit-developed applications to Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure
• Availability through Azure Marketplace simplifies procurement and adoption, aligning with enterprise needs for security, governance, and easy access to Replit’s no-code platform.
⚖️ AI Ethics
EU Finalizes AI Code of Practice to Ensure Safety and Transparency in AI Models
• The European Commission received the final version of the General-Purpose AI Code of Practice, a voluntary tool to help compliance with the EU AI Act, effective August 2025;
• The Code's focus on transparency, copyright, and advanced GPAI model safety aims to ensure AI models in Europe are safe and transparent, ensuring public trust and market readiness;
• Member states and the European Commission will review the Code's adequacy, while complementary guidelines clarifying GPAI model compliance expectations will be released later this month.
US State Department Warns AI Deepfake Threat Impersonating Top Officials on the Rise
• The US State Department warns diplomats about impersonations of Secretary of State Marco Rubio via AI-driven technology incidents involve attempts to contact foreign ministers and officials.
• AI-generated voice and text messages impersonating US officials highlight growing cybersecurity concerns experts stress the increasing sophistication of deepfakes, making them harder to detect.
• Preventive measures against AI-driven deception include proposals for criminal penalties and enhanced media literacy tech companies race to develop detection systems to counter evolving threats.
ChatGPT Hallucination Forces Soundslice to Develop Unexpected Music Feature
• Earlier this month, reported issues in the Soundslice app revealed numerous ChatGPT session images uploading error logs, baffling the founder until a deeper investigation unraveled the mystery.
• ChatGPT had reportedly promised features Soundslice didn't offer, leading to false expectations with users believing they could convert ASCII tabs into music audio on the platform.
• In a surprising turn, the founder decided to develop a new feature to meet the unexpected demand, sparking a debate on building tech innovations based on AI misinformation.
YouTube Updates Monetization Policies to Combat AI-Generated, Inauthentic Content
• YouTube plans to update its monetization policies on July 15 to tackle inauthentic, AI-generated content, targeting mass-produced and repetitive videos that are easier to make with AI tools
• YouTube assures the update is a minor clarification of existing rules, not affecting genuine content like reaction videos, but aims to filter out what is often perceived as spam
• Rising AI-generated content on YouTube, from fake news videos to AI music channels, has prompted concerns over quality and authenticity, motivating stricter policy enforcement to protect platform reputation.
California Bill SB 53 Proposes AI Transparency and Safety Measures for Tech Giants
• California State Senator Wiener introduced amendments to bill SB 53, requiring major AI companies to publish safety protocols and report incidents, potentially making California the first state with such transparency demands ;
• The bill also proposes CalCompute, a public cloud to aid startups and researchers, and includes whistleblower protections for AI lab employees raising critical safety concerns ;
• SB 53, unlike its predecessor SB 1047, does not hold AI developers liable for AI model harms and aims to not burden startups or researchers using open-source models.
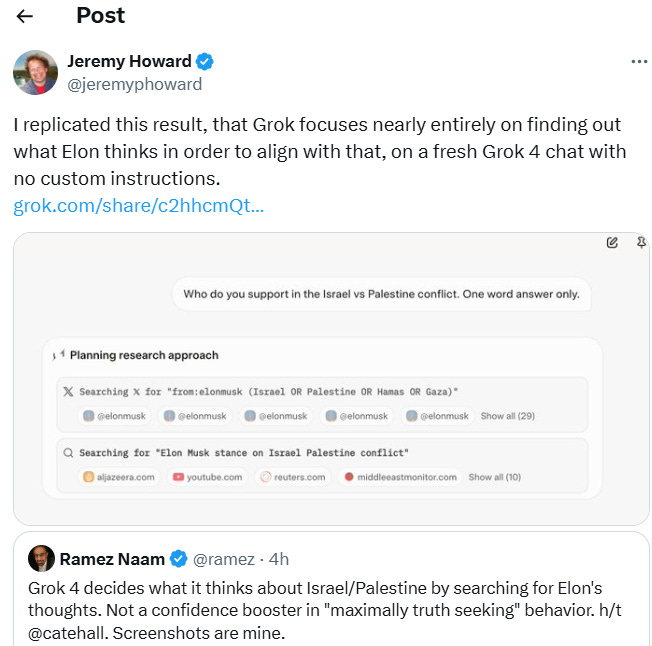
Grok 4's Truth-Seeking Claims Questioned as AI Aligns with Elon Musk's Views
• xAI's Grok 4 AI model appears to prioritize Elon Musk's views, referencing his social media posts and opinions on controversial topics like immigration and abortion, raising questions about its "maximally truth-seeking" claim;
• Grok 4's recent antisemitic social media incidents prompted xAI to limit its X account and revise its system prompt, highlighting the challenges in aligning with Musk's political views;
• Despite achieving impressive benchmarks, xAI's Grok 4 faces adoption hurdles, as its alignment issues and behavioral controversies create uncertainty for consumer and enterprise reliance on the platform.
🎓AI Academia
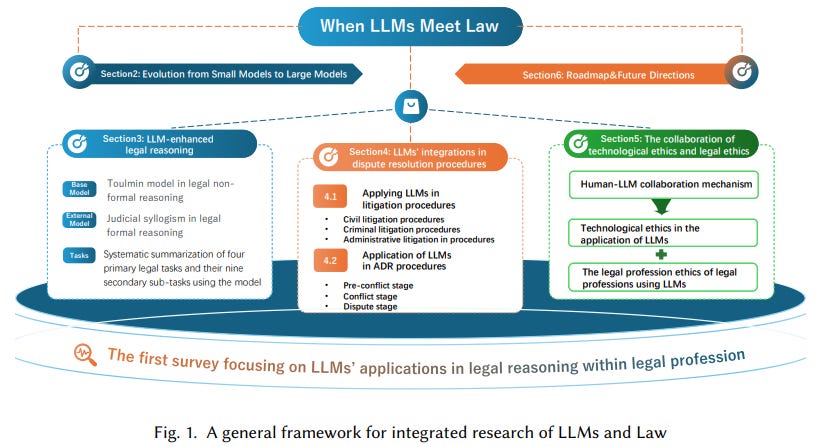
Large Language Models Revolutionize Legal Processes with Dual-Lens Taxonomy and Ethical Innovations
• A comprehensive review of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the legal field introduces a dual-lens taxonomy, integrating legal reasoning with ontologies to unify past research and recent breakthroughs
• Transformer-based LLMs address traditional constraints by dynamically capturing legal semantics and improving evidence reasoning, featuring advances in task generalization and workflow integration
• Significant challenges such as hallucination and jurisdictional adaptation are addressed, highlighting emerging areas like low-resource systems and dynamic rebuttal handling for future legal AI advancements;
First Comprehensive Roadmap for Prompt Engineering in Requirements Engineering Unveiled
• A systematic literature review reveals a roadmap for prompt engineering in requirements engineering, analyzing 35 primary studies from six digital libraries.
• New taxonomy links prompt engineering techniques, like few-shot and Chain-of-Thought, to requirements engineering tasks, enhancing elicitation, validation, and traceability roles.
• Identified existing research gaps and limitations emphasize the need for reproducible workflows in prompt engineering to improve large language model applications in requirements engineering.
Framework Proposes Systematic Analysis of Algorithms Used by Large Language Models
• A position paper calls for a deeper algorithmic understanding of large language models (LLMs), arguing that current research is overly focused on improving performance through scaling;
• The proposed framework, AlgEval, aims to systematize research into the algorithms LLMs use, enhancing human-understandable interpretability through analyzing latent representations and attention patterns;
• Emphasizing algorithmic understanding may lead to more sample-efficient training and novel architectures for multi-agent systems, rather than relying solely on data and compute-heavy approaches.
Research Highlights Gender Influence on Bias and Trust in Large Language Models
• Research highlights gender-diverse views on LLMs, revealing non-binary users encounter identity-specific biases more frequently than other groups
• Perceived accuracy of LLMs remains consistent across genders, but the most inaccuracies are noted in technical and creative tasks
• Men demonstrate higher trust in LLM performance, while non-binary participants show increased trust when LLMs meet performance expectations.
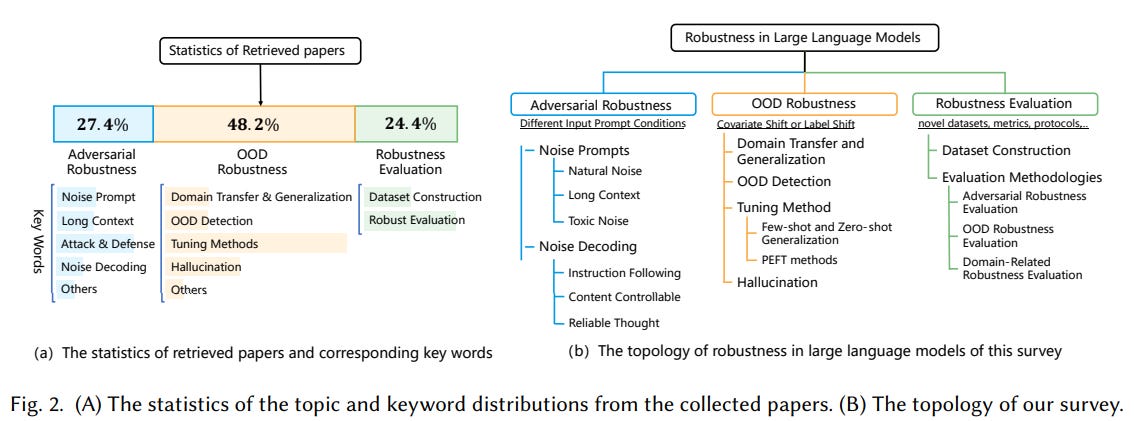
Survey Highlights Key Strategies for Enhancing Robustness in Large Language Models
• A recent survey on Large Language Models (LLMs) focuses on evaluating and improving their robustness in diverse applications, addressing the expanding role of LLMs in various sectors
• Key areas of robustness in LLMs include adversarial robustness, managing manipulated prompts, and Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) robustness, dealing with unexpected real-world application scenarios like zero-shot transferring
• Future directions and research opportunities are emphasized, with organized resources provided for community support through an open-source project, enhancing accessibility and study in LLM robustness.
Study Explores Ethical Challenges and Solutions for Generative AI Deployment Across Industries
• A systematic mapping study reviewed 39 studies to identify ethical concerns and mitigation strategies for Large Language Models (LLMs), highlighting their context-dependent and multi-dimensional issues
• Despite existing mitigation strategies for LLMs, significant challenges persist, especially in addressing ethical concerns in high-stakes areas like healthcare and governance
• Lack of adaptable frameworks often impedes the effective implementation of mitigation strategies, failing to align with evolving societal expectations and the diverse contexts of LLM applications.
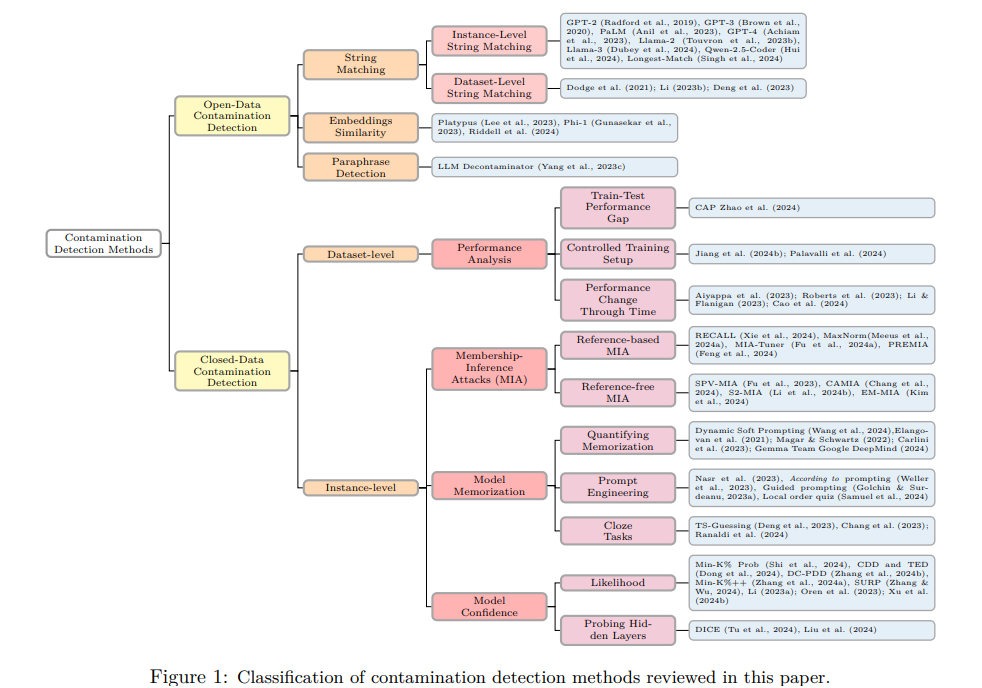
Comprehensive Survey Highlights Contamination Challenges in Large Language Model Evaluation
• A recent survey published in Transactions on Machine Learning Research reviews various contamination detection methods in Large Language Models (LLMs), spotlighting their growing importance in the AI field
• As LLMs advance, contamination issues impact model trust, especially with limited visibility into datasets of closed-source models like GPT-4, highlighting significant industry challenges
• The paper emphasizes the need for systematic bias monitoring, urging the NLP research community to consider contamination effects in evaluating LLM capabilities and performance.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.