Can You Go to Jail for Misusing AI? Italy’s new AI law says so
Italy made history by becoming the first EU country to pass a comprehensive AI law aligned with the EU AI Act..
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 130th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🔦 Today's Spotlight
Italy’s New AI Law: A First in the EU
Italy has become the first European Union country to enact a comprehensive national law on artificial intelligence. Approved on 18 September 2025 after a year of debate, the law aligns with the EU’s landmark AI Act and explicitly enshrines “human-centric, transparent and safe” principles for AI use. It covers a broad range of sectors – from healthcare and education to justice, public administration and sports – requiring that AI systems remain traceable and subject to human oversight. As Reuters and the Guardian report, the legislation emphasizes innovation, cybersecurity and privacy protections alongside these safeguards. For example, children under 14 will not be allowed to use AI tools without parental consent, reflecting Italy’s precautionary stance. At the same time, the law dedicates up to €1 billion (about $1.18 billion) in state-backed funding to support domestic AI, cybersecurity and telecom companies.
A key focus of Italy’s law is protecting minors. Anyone under 14 must obtain parental permission before using AI applications. This follows Italy’s earlier action – in 2023 it famously became the first country to suspend ChatGPT on privacy/age-check grounds, prompting OpenAI to add age-verification features. The new law cements that precautionary approach: minors are seen as especially vulnerable to AI-generated content. In practice, schools and companies must now implement age-gates and parental controls on chatbots, virtual assistants or any AI-enabled service.
Key Provisions of the Law
Italy’s AI law introduces several major provisions that together shape how the technology can be developed and used:
Human-Centric, Cross-Sector Rules: The law applies across society – in healthcare, education, justice, sport, public administration and workplaces – and requires that AI systems be explainable, traceable and subject to meaningful human oversight. Medical AI tools can assist doctors but doctors retain the final decision on diagnosis or treatment. In courts, judges cannot delegate verdicts to algorithms. Employers must inform employees whenever AI is used on the job. The law’s goal is to ensure AI complements rather than replaces human judgment.
Child Safety Measures: As noted, no one under 14 may use AI services without parental consent. Providers must implement age checks. This builds on earlier Italian privacy law (GDPR) and the ChatGPT case. It also mirrors emerging global efforts (for example, some US states and regulators are probing AI’s risks to kids).
Criminal Penalties for Misuse: The law creates new crimes for harmful AI misuse. Publishing or sharing malicious AI-generated content – such as deepfake videos or images that defame or mislead – is now punishable by 1–5 years in prison if it causes damage. Moreover, using AI in the commission of other crimes (like fraud, identity theft or money laundering) is an aggravating factor that leads to tougher sentences. Italian courts will even have the power to order rapid takedowns of harmful AI content. These strict penalties are meant to deter digital impersonation and AI-driven scams.
Transparency and Oversight: To ensure accountability, the law mandates that organizations keep records of AI decision processes and outcomes, and be able to explain them if challenged. The government has assigned the Agency for Digital Italy and the National Cybersecurity Agency as lead regulators for AI. Existing watchdogs (Bank of Italy, securities regulator Consob, etc.) retain authority in their fields but must coordinate with the new agencies. The Department for Digital Transformation will also produce a national AI strategy, updated over time.
Intellectual Property and Innovation: The law clarifies how AI-generated content is treated under copyright. Works “created with AI assistance” receive protection only if they result from genuine human creative effort. Purely AI-autogenerated art or text get less protection. Text and data mining with AI is allowed only on public-domain material or for scientific research by approved institutions. To spur AI development, up to €1 billion in state-backed venture funds is earmarked for Italian companies in AI, cybersecurity, quantum and telecoms. (Some critics say this funding is “puny” compared to US/China levels, but supporters view it as a start.)
Enforcement and Impact
The new law carries real teeth and practical implications:
Prison and Fines: Violating the criminal AI provisions can mean jail time (1–5 years) Companies or individuals that facilitate illegal AI abuses (e.g. by selling unauthorized AI-deepfake services) face prosecution. Civil fines and business sanctions (for example under EU rules) will also apply for non-compliance.
Sector Rules: In healthcare, AI tools may assist with diagnosis or treatment suggestions, but only if the doctor gives final approval. Patients must be informed when an AI system is used in their care. In workplaces, companies must notify employees of AI monitoring or decision-making tools. Such measures give citizens more control and awareness.
Children and Education: The parental-consent rule means schools, online platforms and app stores have to verify users’ ages. Educational AI apps for children will require explicit approval processes. Italy will likely issue guidelines (through the Digital Agency) on safe AI usage in schools.
Industry Compliance: Businesses developing or deploying AI in Italy must audit their systems for bias/discrimination (none are allowed), ensure cybersecurity, and register certain “high-risk” AI with regulators. The law covers both Italian-made AI and foreign systems used in Italy, aligning with the EU Act’s territorial reach. Tech firms should prepare to document their AI’s data sources and safety measures.
Privacy and Data: Though GDPR already applies, the new law reinforces privacy by demanding more transparency in AI’s use of personal data. For example, algorithms that profile individuals or use biometric data are heavily restricted by the EU Act and mirror rules (social scoring AI is banned). Italian users may now have stronger rights to know when AI is making decisions about them.
Commentary and Reactions
Digital officials and experts have generally welcomed the law as balancing innovation and rights. Italy’s digital transformation undersecretary Alessio Butti praised it as a way to “steer AI toward growth, rights and full protection of citizens”. Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni emphasized an “Italian way” of governing AI – one that unlocks its “greatest revolution of our time” but keeps it within an ethical framework focused on people and their needs. Both Meloni and the law’s supporters argue this approach tailors global AI principles to Italy’s culture and legal system.
Critics, however, warn of potential drawbacks. Some industry observers say the €1 billion investment is relatively small by international standards Others caution that overly strict rules (especially on deepfakes and minors) could slow startup innovation. In contrast, tech champions point out that setting clear rules may actually foster trust and growth. For example, the law explicitly protects AI-created works (with human oversight), which could encourage creative AI applications under copyright law.
Italy’s new AI law sets EU-wide firsts (parental consent for minors, deepfake jail terms), aligns with the EU AI Act, and combines regulation with investment. It imposes human-over-sight in critical sectors, expands criminal liability for AI abuse, and could prompt other countries to speed up their own AI policies. The law marks a shift toward treating AI governance as a core public policy issue – underlining both the technology’s risks and its national importance.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
Google Chrome Enhances User Experience with New AI Features and Updates
Google Chrome has introduced a series of AI-driven features aimed at enhancing user experience, boosting productivity, and improving online safety. These updates include the rollout of Gemini, an AI assistant designed to simplify complex information and automate repetitive tasks, as well as new tools for integrating with Google apps, managing browser tabs, and detecting scams with Gemini Nano. Additional features such as an AI-powered search in the omnibox and improved notification and permission management have been integrated to streamline the browsing experience and provide more robust security measures. The updates are currently available to Mac and Windows users in the U.S., with plans to expand to other platforms and regions soon.
YouTube Unveils AI Tools and Monetization Options in Major Creator Update
At the annual Made on YouTube event, YouTube introduced a range of new features and tools aimed at enhancing the creator experience across its platform. Updates to the YouTube Studio include "likeness" detection for facial recognition, a collaboration feature for multiple creators on a single video, and new AI tools to assist podcasters in content promotion. YouTube Live received upgrades such as AI-powered highlights, simultaneous dual-format broadcasting, and new monetization opportunities. Additionally, YouTube is rolling out a custom version of its text-to-video generative AI model, Veo 3, to Shorts, along with an "Edit with AI" feature. YouTube Music and new monetization strategies were also highlighted, offering creators expanded ways to engage with audiences and earn revenue through features like product tagging and brand deals.
Google Launches Gemini for TV to Enhance Interactive Entertainment with Conversations
Google has introduced Gemini for Google TV, enhancing the interaction with televisions by allowing users to engage in free-flowing conversations in addition to existing Google Assistant features. This AI upgrade enables users to find entertainment that's well-suited to their mood or preferences, plan activities like family trips, and even tackle complex questions by simply asking their TV. Gemini facilitates effortless searches for entertainment, offering personalized recommendations and the ability to follow up on previous shows or identify trending new series.
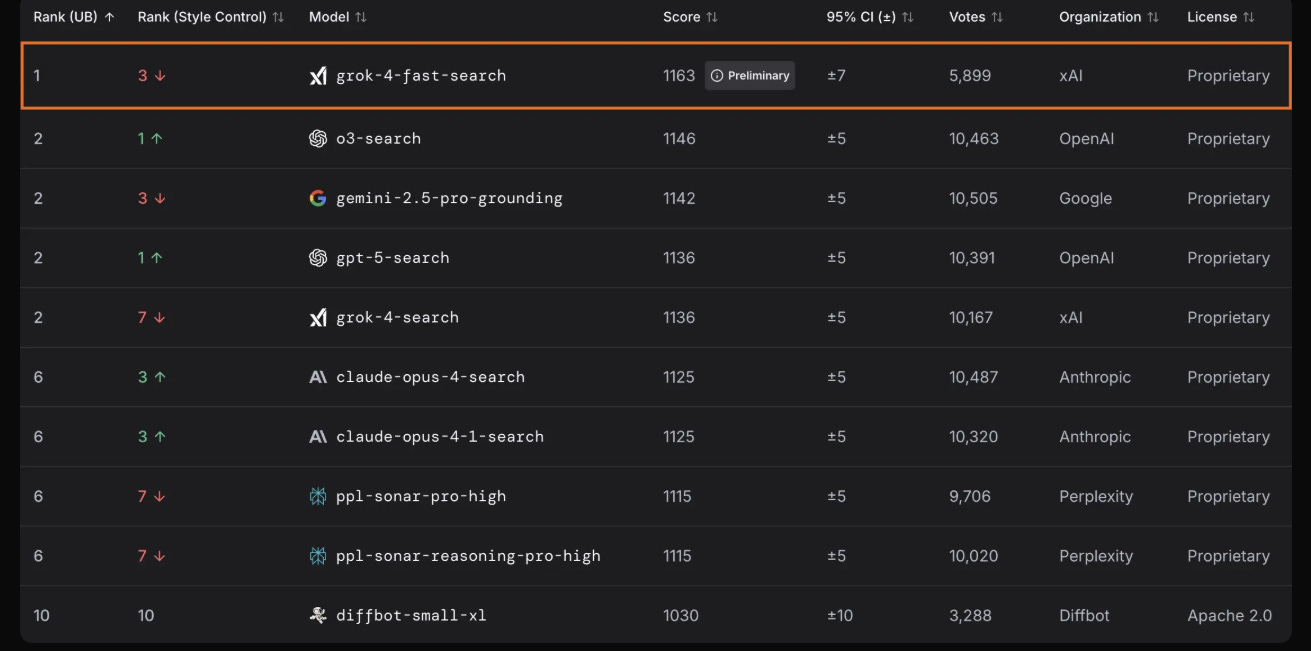
Grok 4 Fast Enhances Cost-Efficiency and Intelligence Density in AI Models
Grok 4 Fast represents a significant breakthrough in cost-efficient AI, providing high-caliber reasoning capabilities in both enterprise and consumer applications. Built on the learnings from Grok 4, this new model offers exceptional token efficiency, boosting performance while greatly reducing costs by using 40% fewer tokens on average. Grok 4 Fast features a robust 2M token context window and combines reasoning and non-reasoning functionalities to maintain top-tier price-to-intelligence ratios, a detail recognized by Artificial Analysis. The model's reinforcement learning enables effective tool visits, demonstrating advanced web and X search abilities, and propelling Grok 4 Fast to lead in competitive environments like LMArena's Search Arena.
OpenAI Plans Smart Speaker Without Display With Former Apple Designer Jony Ive
OpenAI, in collaboration with former Apple design chief Jony Ive, is reportedly working on a range of AI devices, including a smart speaker without a display, planned for release by late 2026 or early 2027, according to sources familiar with the matter. The company has secured a contract with Luxshare and approached Goertek for component supply, tapping into Apple's supply chain. OpenAI is exploring various products like glasses, a digital voice recorder, and a wearable pin, though CEO Sam Altman previously stated the initial focus would be on a pocket-sized, screen-free device. The collaboration has reportedly attracted former Apple hardware employees seeking less bureaucracy and more collaboration at OpenAI.
Citi Launches 5,000-Person AI Agent Pilot to Transform Workplace Efficiency
Citigroup has initiated a pilot program involving 5,000 employees to test the efficacy of AI "agentic" technology within its proprietary platform, enabling users to automate complex tasks across multiple systems with a single prompt. Developed over two years, this technology, equipped with models like Google’s Gemini and Anthropic’s Claude, aims to enhance tasks such as research and client profiling. The pilot will assess usage impacts, cost-effectiveness, and potential workforce implications during a four to six-week period.
Facebook Dating Introduces New Features: Dating Assistant and Meet Cute to Enhance Connections
Facebook Dating is rolling out two new features, a dating assistant and Meet Cute, designed to enhance the online dating experience for young adults in the US and Canada by reducing swipe fatigue. The dating assistant is a chat tool that provides personalized match recommendations and dating tips, allowing users to refine searches based on specific interests such as career and location. Meet Cute offers a fresh approach to dating by automatically pairing users with surprise matches weekly, leveraging a personalized matching algorithm. Both features aim to simplify the process of connecting with potential partners without the need for endless swiping or additional costs.
NVIDIA and OpenAI Partner to Deploy 10 Gigawatts of Advanced AI Infrastructure
OpenAI and NVIDIA have formed a strategic partnership to build and deploy at least 10 gigawatts of AI data centers powered by NVIDIA systems, representing millions of GPUs, as part of OpenAI's next-generation AI infrastructure plans. NVIDIA plans to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI as the infrastructure develops, with the first gigawatt set to come online in the latter half of 2026 via the NVIDIA Vera Rubin platform. This collaboration aims to drive forward the development and deployment of superintelligence by integrating advanced compute resources, supporting OpenAI’s mission to deliver artificial general intelligence for the benefit of humanity.
⚖️ AI Ethics
U.S. Government Agencies Gain Approval to Utilize Meta's AI System Llama
The U.S. government has approved Meta Platforms' AI system Llama for use by federal agencies, as confirmed by a senior administration official. The General Services Administration (GSA) will now list Llama, a comprehensive language model capable of processing text, video, images, and audio, as an approved AI tool. This move aligns with the Trump administration's efforts to incorporate commercial AI technologies into government processes. The GSA has previously approved AI tools from several other tech giants like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Anthropic, and OpenAI, who provide these services at discounted rates while meeting security requirements. Agencies can use Llama for tasks such as efficiently reviewing contracts and resolving IT issues.
Technology Boosts Audit Efficiency, Detects Frauds in India's Government Schemes
The Comptroller and Auditor General of India highlighted the role of technology in uncovering fraud within government schemes in various states, emphasizing the importance of artificial intelligence and forensic tools in audits. Speaking at a conference in the capital, he noted the institution's focus on evaluating urban local governments in 100 cities with populations over half a million, assessing their progress in essential services, renewable energy, sustainable transport, and improving living standards to enhance job creation and investment opportunities.
AI Earnings Pose Greater Threat to Stock Rally Than Geopolitical Tensions
JPMorgan Asset Management has raised concerns that disappointing earnings from AI companies could significantly impact the tech-induced global stock rally, surpassing the risks posed by geopolitical tensions. The heightened focus on AI has driven equities to record highs, buoyed by strong demand and expectations for Federal Reserve interest rate cuts. However, setbacks in tech earnings, especially given their high valuations, could lead to a market downturn similar to the April selloff. While U.S. equities may see limited gains at current levels, Europe might benefit from fiscal support, and Japan and emerging markets could experience growth due to corporate reform and attractive valuations, respectively.
North Korea Advances Drone Warfare with AI Integration, Kim Prioritizes Rapid Development
North Korean leader Kim Jong Un supervised a test of an attack drone and emphasized the use of artificial intelligence in military technology, according to state media reports. The images released showed the drone successfully destroying a target, with Kim expressing satisfaction over the "excellent combat effectiveness" of the tactical drones. Analysts have raised concerns over the drones' efficiency and potential links to North Korea's alliance with Russia. The push for AI advancements, drawing from Russian technology, highlights North Korea's focus on modernizing its military capabilities, especially amid reports of North Korean troops gaining warfare experience alongside Russia.
Trump Administration Accelerates Power Development Amid Rising Artificial Intelligence Energy Demands
The Trump administration initiated efforts to accelerate power infrastructure development as AI-driven demand increases, while also mandating the continued operation of certain fossil fuel plants that were slated for closure. The Department of Energy is seeking input from industry stakeholders on immediate investment opportunities and addressing power demand growth constraints. President Trump declared an energy emergency due to increased electricity demand from AI, data centers, and electric vehicles. The administration's Speed to Power program explores using federal funds to enhance power generation and grid capacity, amidst mixed reactions regarding the reliance on fossil fuels and the stability of renewable energy sources. Additionally, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has implemented measures to improve grid security and mitigate risks such as cyber attacks and extreme weather conditions.
TikTok Deal Nears Final Approval as US Gains Control Over Algorithm
The U.S. is set to gain control over TikTok's algorithm as part of a deal to acquire the app's American operations, according to statements from the White House. The anticipated agreement, driven by discussions between President Donald Trump and China's Xi Jinping, involves selling a majority of TikTok's U.S. assets to American investors, led by Oracle and others, with American representatives acquiring most TikTok board positions. The deal follows legislative moves to restrict TikTok unless it transitions to majority American ownership amid national security concerns, and aims to ensure the app's continued operation in the U.S. with around 170 million users.
Italy Enacts First Comprehensive AI Law in EU, Enforcing Strict Regulations
Italy has become the first European Union country to approve a comprehensive law regulating artificial intelligence, imposing prison terms for generating harmful content like deepfakes and requiring parental consent for AI access by children under 14. Aligned with the EU's AI Act, the legislation emphasizes human-centric, transparent AI use while enforcing stricter rules on transparency, innovation, and privacy across various sectors. It also authorizes €1 billion to support AI-related industries, despite criticism that this investment is modest compared to other global powers. The law will be enforced by the Agency for Digital Italy and the National Cybersecurity Agency.
Meta's New Smart Glasses Stumble at Connect Conference, Bosworth Blames Technical Glitches
At Meta Connect, several demos of Meta's new smart glasses failed due to unexpected technical difficulties. The Ray-Ban Meta glasses misfired a cooking demo by activating all devices in the venue simultaneously, overloading the server, while a live WhatsApp call between Meta executives failed due to a race condition bug in the software. Meta CTO Andrew Bosworth explained that these issues were not reflective of the product's overall functionality and attributed them to demo-specific circumstances, including a development server flood akin to a DDoS attack and a previously unseen bug, both of which have been addressed post-event.
🎓AI Academia
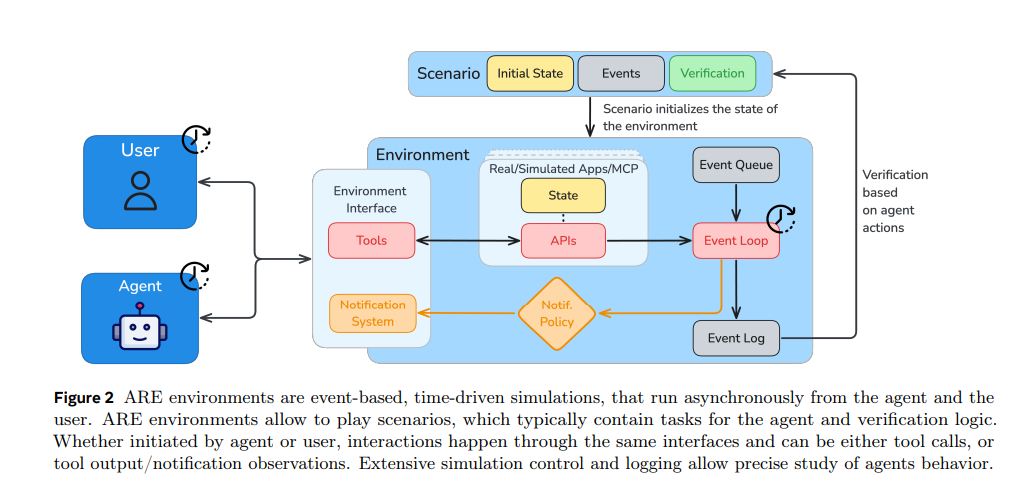
Meta Labs Expands AI Research with ARE Platform and Gaia2 Benchmark
Meta Superintelligence Labs has unveiled Meta Agents Research Environments (ARE), a platform designed to facilitate the creation of scalable environments and the integration of both synthetic and real applications for advanced agent evaluations. Additionally, a new benchmark called Gaia2 has been introduced within ARE to evaluate general agent capabilities, demanding adaptability to dynamic environments and collaboration under temporal constraints. Unlike traditional benchmarks, Gaia2 operates asynchronously, exposing new types of failures and highlighting the trade-offs between reasoning strength and efficiency. ARE's flexible frameworks allow for ongoing development of new benchmarks, aiming to drive advances in AI by defining meaningful tasks and robust assessments.
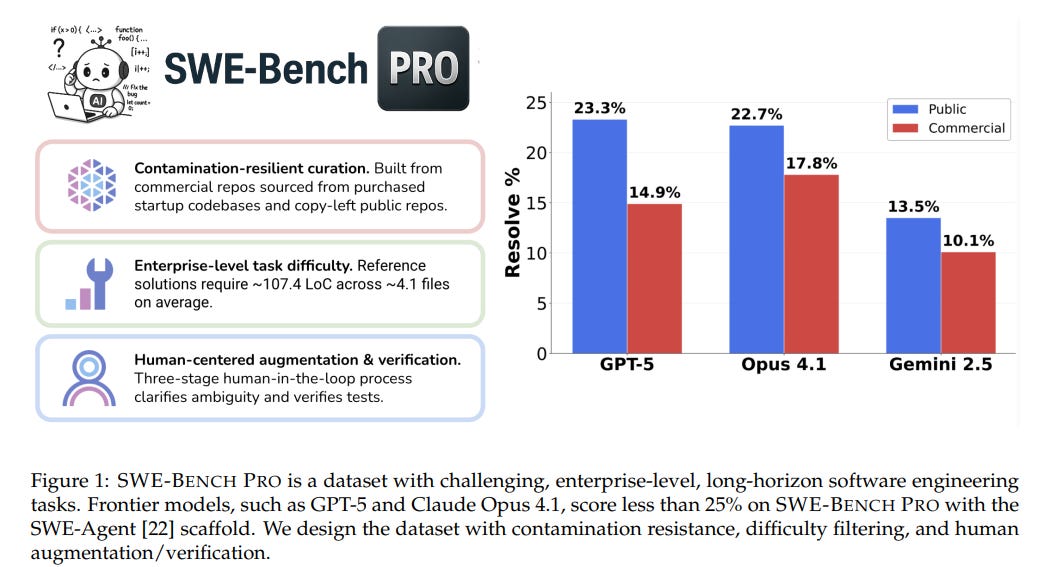
SWE-Bench Pro Challenges AI with Realistic Software Engineering Tasks Beyond Benchmark Norms
SWE-BENCH PRO, an advanced benchmark developed by Scale AI, builds upon the foundation of SWE-Bench to present more challenging, realistic software engineering problems. It includes 1,865 tasks drawn from 41 repositories, designed to test AI coding models on enterprise-level issues that require extensive code modifications and long completion times. Evaluations show current models struggle with these complex tasks, with top models like GPT-5 achieving only a 23.3% success rate. The benchmark aims to address limitations of current benchmarks and offer a robust testbed for future autonomous software engineering advancements.
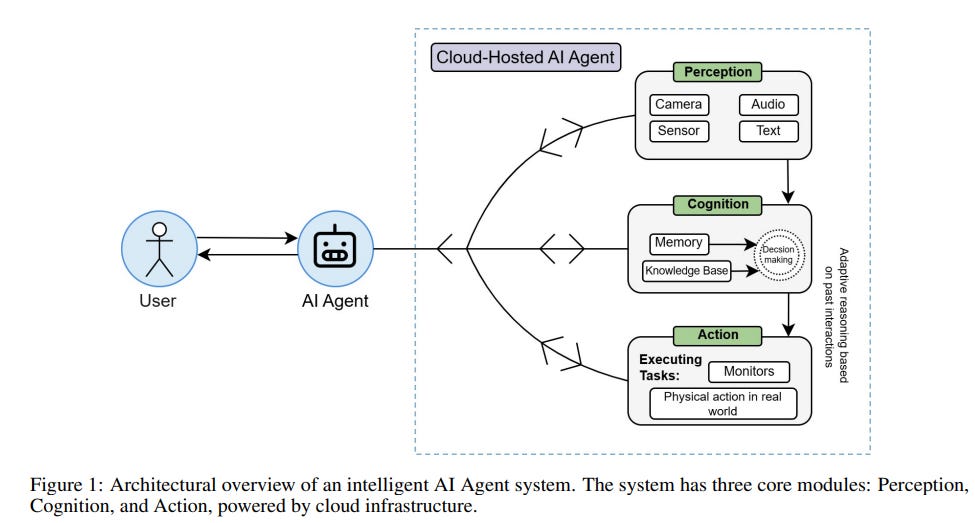
Agentic AI Set to Transform Computing with Cloud, Edge, and On-Premises Solutions
A recent study explores the transformative potential of agentic AI systems, highlighting their ability to operate autonomously, adaptively learn, and reduce dependency on large public cloud environments. The research suggests that agentic AI could drive a shift towards more locally distributed computing architectures, such as edge and on-premises systems, due to improved resource efficiency. This shift is likely to bring about a significant re-architecture of computing infrastructures and governance models, offering cost savings and reduced data usage. The study underscores the importance of strategically positioning agentic AI within the evolving landscape of computing environments.
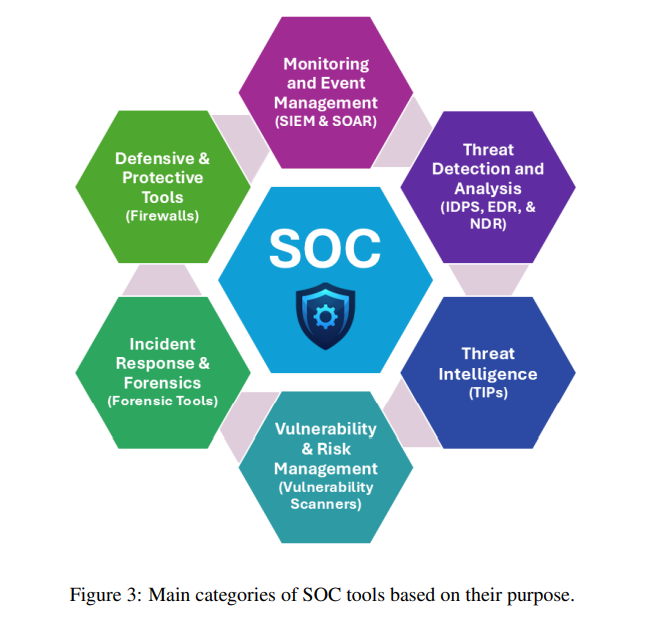
Large Language Models Enhance Efficiency in Security Operations Centers, Survey Finds
A recent survey explores the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into Security Operations Centers (SOCs), highlighting their potential to revolutionize cybersecurity operations. LLMs, known for their human-like text comprehension and generation abilities, are being considered to address SOC challenges such as high alert volumes, resource constraints, and the demand for expert knowledge. This comprehensive study delves into how LLMs can automate log analysis, streamline triage, and enhance detection accuracy within SOCs, offering insights into current capabilities and potential future directions in this evolving field.
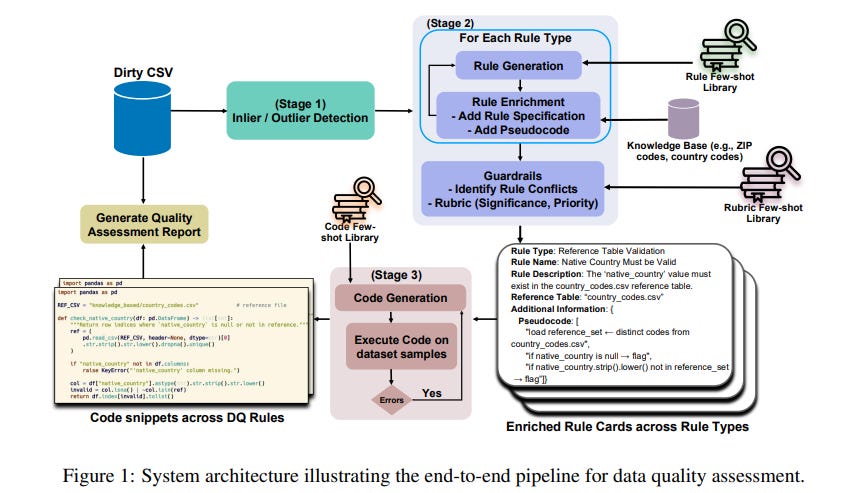
IBM Research Advances Tabular Data Quality Assessment with Large Language Models and Code Generation
Researchers at IBM have developed a three-stage framework using Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve data quality assessment in tabular datasets. This method combines statistical inlier detection and LLM-driven rule and code generation to create semantically valid quality rules. By incorporating retrieval-augmented generation with external knowledge, the approach addresses inefficiencies and high costs of traditional rule-based validation systems. The framework reportedly enhances the detection of context-dependent errors and semantic inconsistencies, demonstrating effectiveness in evaluations on benchmark datasets.
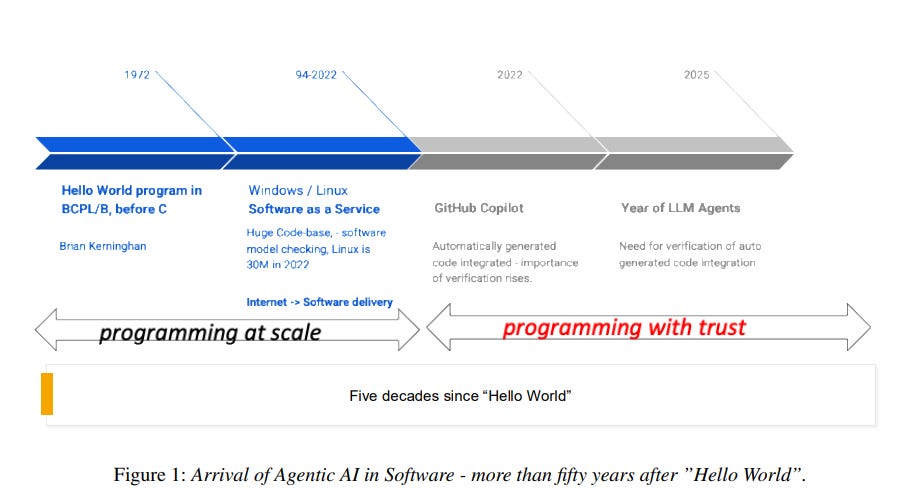
Agentic AI Advances in Software Engineering, Raising Trust and Automation Concerns
The software engineering community is witnessing a transformative shift with the integration of agentic AI, moving beyond mere code generation from prompts to more complex tasks like program repair, architecture exploration, and requirements understanding. These AI agents, envisioned as team members, can autonomously manage micro-decisions in software tasks, a capability exemplified by the AutoCodeRover integrated into SonarQube for intent inference. As the industry transitions from "programming in the large" to "programming with trust," a core challenge arises in ensuring the correctness and reliability of AI-generated code, with AI-based verification and validation becoming crucial. This development marks a significant evolution in software engineering, emphasizing trust alongside scale in an increasingly automated landscape.
Large Language Models Tested on Advanced Financial Analysis in CFA Level III Evaluation
A recent study has evaluated 23 state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) on the CFA Level III exam to assess their advanced financial reasoning capabilities. These models, including o4-mini, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Claude Opus 4, were tested using multiple prompting strategies like zero-shot, chain-of-thought, and self-discover. The findings indicate that while many LLMs perform well on multiple-choice questions, only a few excel in the complex essay questions requiring strategic thinking and synthesis, marking significant progress from earlier models that struggled with Level III's demands. The study also highlights ongoing challenges related to cost-effective deployment and the necessity for detailed performance evaluation in high-stakes financial environments.
Study Reveals Web AI Agents' Increased Vulnerability Compared to Standalone LLMs
A new security analysis reveals that Web AI agents are more vulnerable than standalone large language models (LLMs) due to their built-in flexibility and complex operational environment. Researchers from the University of Maryland and Capital One found that the integration of user goals within system prompts, multi-step action generation, and enhanced observational abilities in Web AI agents expose them to a wider array of adversarial inputs, heightening security risks. Unlike standalone LLMs, Web AI agents interact directly with web environments, creating potential avenues for misuse, such as distributing malware or facilitating phishing attacks. This study underscores the critical need for improved security measures and strategic defense solutions in the development of AI agents.
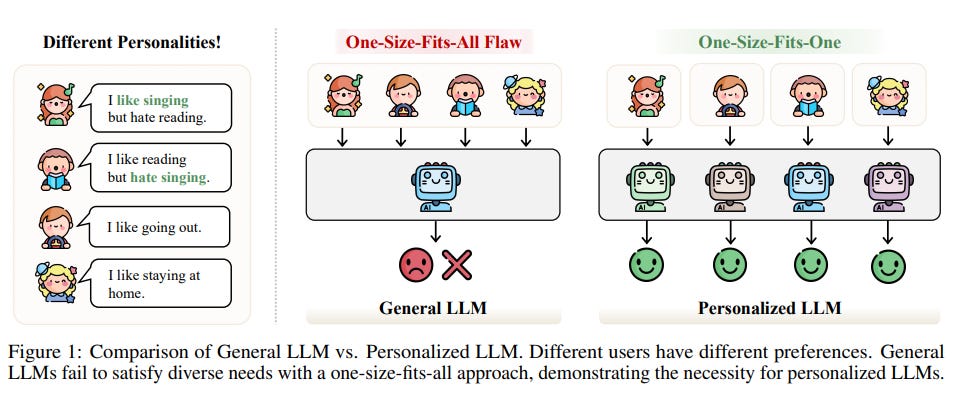
Survey Highlights Advancements and Challenges in Personalized Large Language Models Development
A recent survey highlights the advancements and challenges in developing Personalized Large Language Models (PLLMs) that improve upon general Large Language Models (LLMs) by tailoring responses based on individual user data, such as preferences and historical interactions. The study emphasizes the pressing need for PLLMs in various applications, including conversational agents and recommendation systems, due to the limitations of a one-size-fits-all approach in addressing diverse user needs. It reviews three technical strategies for personalization—prompting, finetuning, and alignment—while also discussing the limitations and future directions of this promising field.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.