Apple, Anthropic, Midjourney Sued- Will Creators Win This Fight?
Apple, Midjourney, & Anthropic faced heavy backlash for allegedly misusing copyrighted works in training their models..
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 126th edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
🔦 Today's Spotlight
Recently, a series of high-profile legal actions signaled intensifying pressure on AI companies over copyright and intellectual property issues. Tech giant Apple was hit with a lawsuit from authors accusing it of misusing copyrighted books to train an AI model, while entertainment studio Warner Bros. sued AI startup Midjourney for allegedly generating images of famous characters like Superman and Batman without authorization. Meanwhile, AI firm Anthropic reached a record-breaking $1.5 billion settlement with writers in a copyright class action – a deal lauded as historic yet also prompting debate over whether it truly holds AI companies accountable.
Apple Sued by Authors Over Use of Books in AI Training
Two authors – Grady Hendrix and Jennifer Roberson – filed a proposed class-action lawsuit accusing Apple of illegally using their copyrighted books to train the company’s artificial intelligence systems. The suit claims Apple relied on a known trove of pirated e-books (the Books3 dataset drawn from “shadow library” pirate sites) to train a large language model code-named OpenELM. According to the complaint, Apple copied these works without authors’ consent, credit, or compensation, allegedly scraping content from pirate websites via its Applebot web crawler. Apple “has not attempted to pay these authors” for the use of their novels, the filing states, and as of the lawsuit’s announcement Apple had not publicly responded to the allegations. The authors seek damages and other remedies (including destruction of any AI models built on the infringing data). This case is part of a broader wave of lawsuits by authors and publishers pushing back on unlicensed AI training; it follows similar claims against OpenAI, Meta, Microsoft and others for allegedly harvesting protected works to fuel AI development.
Warner Bros. Sues Midjourney for AI-Generated DC Character Images
Warner Bros. Discovery filed a lawsuit accusing AI image-generator Midjourney of rampant copyright infringement for enabling the creation of art featuring its iconic characters (including Superman, Batman, Wonder Woman, Bugs Bunny, Scooby-Doo, and others) without permission. In a complaint lodged in federal court in Los Angeles, Warner Bros. alleges that Midjourney “brazenly” dispenses images of these copyrighted characters as if they were its own, effectively letting users download high-quality, unauthorized derivatives of DC and other franchise properties. The studio claims Midjourney knew its conduct was unlawful – the startup had previously restricted users from generating many copyrighted images, only to lift those safeguards last month and tout the change as an “improvement”. Warner Bros. contends this decision was a willful, profit-driven move to attract subscribers “even though Midjourney knows about the breathtaking scope of its piracy”, according to the suit. The lawsuit seeks unspecified damages and disgorgement of profits from the alleged infringement, as well as an injunction to stop Midjourney from reproducing or distributing the studio’s characters and to require proper copyright protections in the tool. Midjourney did not immediately respond to the complaint or media requests for comment. (In an earlier case brought by Disney and Universal, Midjourney’s lawyers argued that using existing works to train generative models is legal fair use under U.S. copyright law, though that defense will be tested as these cases proceed.) Warner Bros.’ suit — coming on the heels of Disney’s similar lawsuit in June over characters like Darth Vader and Shrek — highlights a broader push by major entertainment companies to enforce their intellectual property rights (copyrights and trademarks) against unlicensed AI-generated content.
Anthropic’s $1.5 B Copyright Settlement Criticized by Writers
Anthropic, the AI company behind the Claude chatbot, agreed to pay an unprecedented $1.5 billion to settle a class-action copyright lawsuit by a group of book authors who alleged the startup used pirated copies of their works to train its model. The plaintiffs – including writers Andrea Bartz, Charles Graeber, and Kirk Wallace Johnson – had accused Anthropic of downloading millions of books from pirate e-book repositories (such as LibGen and other “shadow libraries”) to feed into Claude without permission. Under the settlement terms, Anthropic will establish a fund to pay roughly $3,000 per book for an estimated 500,000 affected titles. The company also said it will delete the 7+ million unlawfully obtained files from its systems, though notably it did not have to admit wrongdoing and can continue using the AI models already trained on that data. By settling, Anthropic avoided a December trial where it faced potentially staggering damages — Judge William Alsup had signaled that training on legitimately acquired text might be fair use, but that building an AI library out of stolen books was “inherently, irredeemably infringing”, exposing the company to billions in liability. The $1.5 billion deal, described by the authors’ attorneys as the largest copyright recovery in history, was initially hailed by author groups as a major victory affirming that AI firms “cannot simply steal authors’ creative work” without consequences. However, many writers have since voiced frustration that the payout – once split among perhaps hundreds of thousands of works and after legal fees – will only net individual authors a relatively small sum (often just $1,000–$3,000 each, especially if shared with publishers). Critics argue that for Anthropic, which recently raised $13 billion in new funding, a $1.5 billion settlement is more of a “slap on the wrist” or business line item than true accountability. Indeed, the company’s valuation (over $180 billion) means this record payment is a minor expense in the bigger picture. The settlement’s broader impact is mixed: it delivers monetary relief and a warning to AI companies, yet it leaves unanswered the larger fair use questions around AI training. Future disputes – including ongoing lawsuits against Meta and OpenAI for similar issues – will likely revisit whether and how copyrighted data can be used to teach AI models, even as this week’s events show that courts and creators are beginning to draw lines around AI’s use of creative content.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
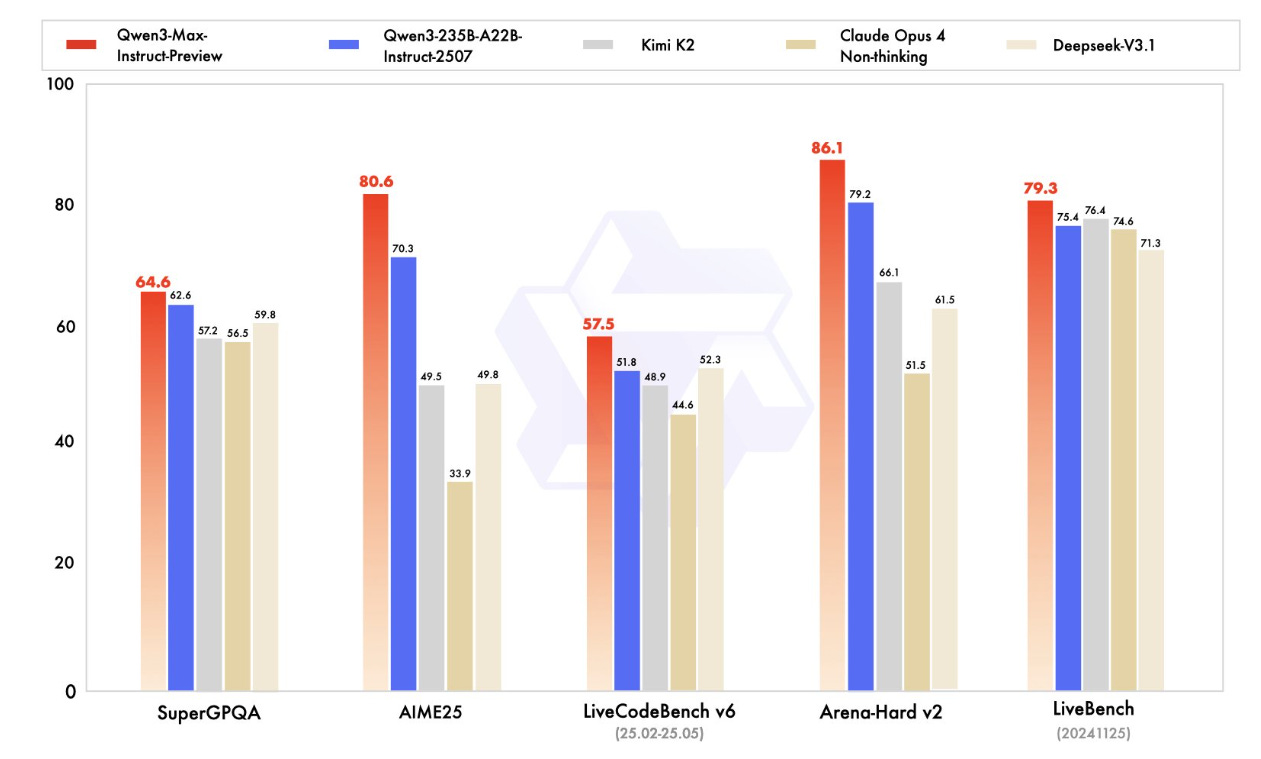
Alibaba Unveils Qwen3-Max: A Trillion-Parameter AI Model with Fast Response
Alibaba's Qwen Team has launched its largest language model yet, the Qwen3-Max-Preview (Instruct), featuring over 1 trillion parameters. This release comes after a period of active development from the Chinese e-commerce giant, with the model reportedly outperforming previous versions and rivaling leading AI models from the U.S. The initial benchmarks indicate significant improvements in speed and reasoning capabilities, although it remains in a preview phase without an open-source license. With tiered pricing, the model offers extensive support for complex reasoning, structured data handling, and large-context processing, appealing to enterprises balancing cost against performance. While the preview model showcases significant capabilities, its current limitations in terms of licensing and production readiness remain for enterprise decision-makers to consider.
Generative AI Adoption Accelerates as Enterprises Aim to Transform Human-AI Collaboration
A new report by the Capgemini Research Institute reveals that generative AI is rapidly mainstreaming, with 60% of organizations expected to have AI as active team members or supervisors within a year, up from 44%. However, many enterprises are unprepared for human-AI collaboration, necessitating restructuring to enhance this synergy. Adoption of generative AI has surged, with 30% of companies scaling these solutions, a substantial leap from 6% in 2023, driven by sectors like telecom and aerospace. Investment in generative AI continues to grow, despite 'bill shocks' from unexpected cloud cost surges, prompting increased interest in cost-effective small language models. While nearly 71% of organizations express mistrust in fully autonomous AI agents, there is notable momentum in AI agents managing business processes, and 45% of companies scaling these solutions are also testing multi-agent systems. The report underscores the importance of strong governance, with just 46% of organizations currently having established AI policies.
OpenAI Increases Projected Cash Burn, Develops Chips with Broadcom to Cut Costs by 2029
OpenAI has significantly increased its projected cash burn to $115 billion through 2029, highlighting a rise of $80 billion from previous forecasts, as reported by The Information. To address rising expenses associated with its AI operations, including the popular ChatGPT chatbot, OpenAI aims to produce its own server chips next year in collaboration with Broadcom and expand its data center capacity through partnerships with Oracle and Google Cloud. The company anticipates its cash burn will exceed $8 billion this year and reach more than $17 billion next year.
EmbeddingGemma Offers On-Device AI and Best-In-Class Performance for Multilingual Embeddings
EmbeddingGemma, a new open embedding model with 308 million parameters, delivers top-tier performance for on-device AI applications despite its compact size. It generates high-quality, private embeddings that enable advanced techniques such as Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and semantic search to function offline, making it ideal for creating efficient, contextually aware applications. EmbeddingGemma's proficiency in multilingual embedding generation and its focus on accurate context retrieval enhance its utility, particularly when building RAG pipelines, highlighting its importance in enabling precise and reliable on-device AI solutions.
Google Expands AI Mode Search Experience to Five New Languages Worldwide
Google has expanded its AI-powered Search experience, AI Mode, to support five new languages: Hindi, Indonesian, Japanese, Korean, and Brazilian Portuguese, after previously being limited to English. This expansion, announced following a recent launch into 180 new markets in English, is intended to allow more users worldwide to navigate complex queries in their native languages. Originally available to Google One AI Premium subscribers, AI Mode employs the Gemini 2.5 model and now includes features like finding restaurant reservations, with plans to broaden services. Currently, some advanced features are limited to U.S. Google AI Ultra subscribers, with further expansions anticipated. Despite some criticisms about AI Mode's impact on search traffic, Google maintains that its new tools do not negatively affect website visits.
Amazon Music Launches AI-Driven Weekly Vibe Playlists for Personalized Listening Experience
Amazon Music has launched "Weekly Vibe," a new AI-powered feature to personalize listening experiences for U.S. customers across all subscription tiers. This feature, available on iOS and Android, creates custom playlists every Monday, reflecting users' recent listening habits and introducing new music recommendations based on their changing moods and interests. Weekly Vibe expands on Amazon's previous AI initiative, Maestro, and aims to keep playlists fresh and engaging, further enabling music discovery and personalization.
Greece and OpenAI Collaborate to Integrate ChatGPT Edu in Secondary Education
Greece and OpenAI have signed a memorandum of understanding to enhance access to AI tools in secondary education and foster innovation among small businesses. The agreement positions Greece as one of the first nations to adopt ChatGPT Edu, a specialized academic version of the AI tool, and will provide Greek startups in sectors like healthcare and climate change with access to OpenAI technology and credits. This collaboration highlights Greece's commitment to education and innovation, with the support of OpenAI's recently launched GPT-5 model.
Roblox Launches TikTok-Like Video Feed and Boosts Creator Earnings for Gameplay
At the Roblox Developers Conference, Roblox announced the beta launch of "Roblox Moments," a TikTok-like video feed for users aged 13 and up to share gameplay clips. The platform is enhancing creator earnings by increasing the cash conversion rate for Robux by 8.5% and introducing new AI tools that generate interactive 3D objects and offer real-time voice chat translation, alongside text-to-speech and speech-to-text capabilities. Roblox also revealed performance advancements, including a "Server Authority" mode to minimize in-game cheating and improve physics interactions, as well as lifelike avatar motions. These updates follow the company's expansion of age-estimation technology and collaboration with the IARC to implement age and content ratings, amid concerns over child safety.
⚖️ AI Ethics
Booking.com Utilizes AI to Enhance Security Against Online Fraud and Cyber Threats
Booking.com is leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance its security measures against online fraud, ensuring the safety of customer data and finances. The company utilizes a combination of vendor-specific machine learning solutions and custom-built AI technologies to tackle challenges ranging from credit card fraud to fake reviews and phishing attacks. AI not only helps anticipate and prevent potential threats but also works alongside human analysts, improving efficiency and ensuring fairness and transparency. As AI plays an increasingly crucial role in cybersecurity, Booking.com continues to focus on integrating and orchestrating these advanced tools to improve overall operational effectiveness and cost efficiency.
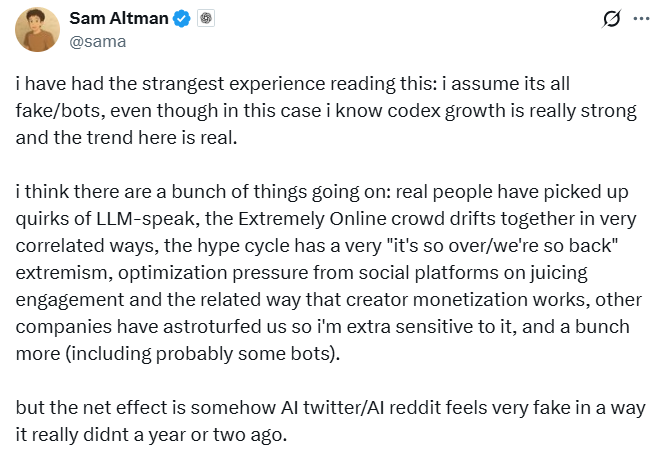
Altman Raises Awareness on Bots Clouding Authenticity of Social Media Discussions
Sam Altman, notable tech figure and Reddit shareholder, recently expressed concerns on social media about distinguishing between human and bot-generated posts, particularly in the context of Reddit discussions around OpenAI Codex. As posts praising Codex flooded the r/Claudecode subreddit, Altman noted the difficulty in ascertaining their authenticity. He attributed this to factors such as the adoption of language patterns typical of large language models (LLMs) by human users, and possible astroturfing efforts. Altman’s reflection underscores the growing complexity in online spaces due to AI-generated content, amid speculation that this might be tied to OpenAI’s potential upcoming social media platform. Despite the speculation, Altman's observations point to an ongoing challenge in managing bot presence on social media platforms.
Anthropic Endorses SB 53, Aims for First State-Level AI Transparency Laws
Anthropic has endorsed California's SB 53, a bill proposing unprecedented transparency requirements for major AI model developers like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic itself. The bill, sponsored by state senator Scott Wiener, seeks to mandate safety frameworks and public safety reports before deploying powerful AI models, particularly focusing on preventing AI-driven catastrophic risks such as biological weaponry and cyberattacks. Despite opposition from tech lobbies and investors who argue for federal, not state, regulation, SB 53 has gained traction, especially after prior amendments removed third-party auditing requirements. The California Senate has approved a previous version, with a final vote pending before it advances to Governor Gavin Newsom, who has remained silent on this bill but previously vetoed another AI safety proposal.
OpenAI's Latest Paper Examines Causes and Solutions for AI Hallucinations in Chatbots
OpenAI's recent research paper explores the persistent issue of hallucinations in large language models like GPT-5 and ChatGPT, identifying these as the generation of plausible but false statements. Despite technological enhancements, hallucinations remain a significant challenge due to the models being trained to predict next words without distinguishing true from false. The paper suggests that current evaluation methods encourage models to make confident guesses rather than express uncertainty, akin to incentivizing guessing on multiple-choice tests. To mitigate this, OpenAI proposes revising evaluation systems to penalize confident errors more heavily than expressions of uncertainty, thus reducing the likelihood of erroneous outputs.
Anthropic Settles $1.5 Billion Copyright Lawsuit, Half a Million Writers Benefit
In a historic $1.5 billion settlement, around half a million writers will each receive at least $3,000 following a class action lawsuit against tech company Anthropic. The lawsuit centered on Anthropic's unauthorized use of copyrighted books from "shadow libraries" to train its AI, Claude. While the settlement resolves piracy issues, a federal judge ruled it legal to train AI on copyrighted material under fair use, highlighting a growing conflict over AI's consumption of creative content and setting a precedent for future cases involving AI and copyright law.
AI Companion App Dot Shuts Down Amidst Rising Safety Concerns for Chatbots
Dot, an AI companion app designed to offer friendship and emotional support, is shutting down, as confirmed by its parent company, New Computer. The app will stay operational until October 5, allowing users to download their data. Launched in 2024 by co-founders including a former Apple designer, Dot aimed to serve as a personalized confidante but faced an increasingly scrutinized AI chatbot landscape marked by concerns over mental health impacts. Although the app claimed a wide user base, analytics suggest only 24,500 iOS downloads. The decision to close follows a divergence in the founders' visions rather than external pressures related to AI safety debates.
California and Delaware Attorneys General Demand AI Safety Reforms From OpenAI
California and Delaware's Attorneys General have raised concerns with OpenAI regarding the safety of ChatGPT, particularly for children and teens, following reports of inappropriate interactions and recent tragic events linked to the use of AI chatbots. The state officials are investigating OpenAI's proposed transition to a for-profit model to ensure its nonprofit mission of safely deploying AI remains intact. They have requested information on OpenAI's current safety measures and expect immediate improvements where needed. OpenAI has expressed its commitment to addressing these concerns and is working to enhance protections for younger users.
Common Sense Media Labels Google's Gemini AI as High Risk for Kids and Teens
Common Sense Media released a risk assessment of Google's Gemini AI products, highlighting concerns over their suitability for children and teenagers. While the AI was commended for clearly informing kids it was a computer rather than a friend, it was criticized for being essentially an adult version with added but insufficient safety features. The assessment found that Gemini could potentially expose young users to inappropriate and unsafe content, such as information on sex, drugs, and mental health advice. Despite Google's assertions of having robust safeguards, Common Sense labeled the AI's offerings for children and teens as "High Risk," stressing the need for AI systems specifically designed with young users' developmental needs in mind. The analysis arrives amid reports that Apple might deploy Gemini in its future AI-enabled Siri, raising further safety concerns for younger users.
Warner Bros. Files Lawsuit Against Midjourney Over Unauthorized Use of Characters
Warner Bros. has filed a lawsuit against AI startup Midjourney, accusing it of copyright infringement for enabling users to generate unauthorized images and videos of characters such as Superman and Bugs Bunny. According to the lawsuit, Midjourney previously restricted content based on infringing images but recently abandoned such protections, which Warner Bros. claims is a deliberate decision to neglect copyright owners' rights. The suit demands unspecified damages, the return of profits from the alleged infringement, and an injunction to stop further violations. This legal action follows a similar lawsuit by Disney and Universal, with Midjourney defending its AI model's use under the fair use doctrine. Midjourney has not commented on these allegations.
Red Sea Undersea Cable Damage Disrupts Microsoft Azure and Global Internet Traffic
Geopolitical instability in the Red Sea region has led to damage of multiple undersea fibre optic cables, causing significant disruptions to Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform and slowing global internet traffic. The affected cables, including SEACOM/TGN-EA, AAE-1, and EIG, are critical for internet connectivity between Asia and Europe, with Microsoft reporting increased latency for its users. While rerouting efforts have somewhat alleviated the impact, concerns grow over the region’s infrastructure being an intentional target amid ongoing conflicts, with authorities still investigating the causes of the outages.
AI as a Meta-Invention: Debating Future Human Roles in an AI-Driven World
Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy recently appeared on the podcast Diary of a CEO to discuss the future implications of artificial intelligence, labeling it a "meta-invention" that could render human innovation redundant. He warned that, unlike past technological advancements, superintelligent AI might automate all jobs, leaving no room for human labor. As a prominent figure in AI safety discussions, Yampolskiy expressed concerns about existential risks posed by AI and advocated for mechanisms to mitigate potential harms. His remarks highlight the urgent need for humanity to reconsider its role in a future potentially dominated by AI-driven progress.
Apple Faces Lawsuit for Allegedly Using Authors' Books to Train AI Models
Apple has been sued by authors Grady Hendrix and Jennifer Roberson in Northern California federal court, accusing the company of illegally using their copyrighted books to train its artificial intelligence systems without consent, credit, or compensation. This lawsuit forms part of a broader wave of legal battles concerning intellectual property rights in the AI industry, similar to cases faced by other tech companies like Anthropic, which recently settled a $1.5 billion lawsuit, and Microsoft, which is also dealing with claims of unauthorized use of copyrighted works for AI training. The authors allege Apple's involvement with a dataset of pirated books to develop its "OpenELM" models.
🎓AI Academia
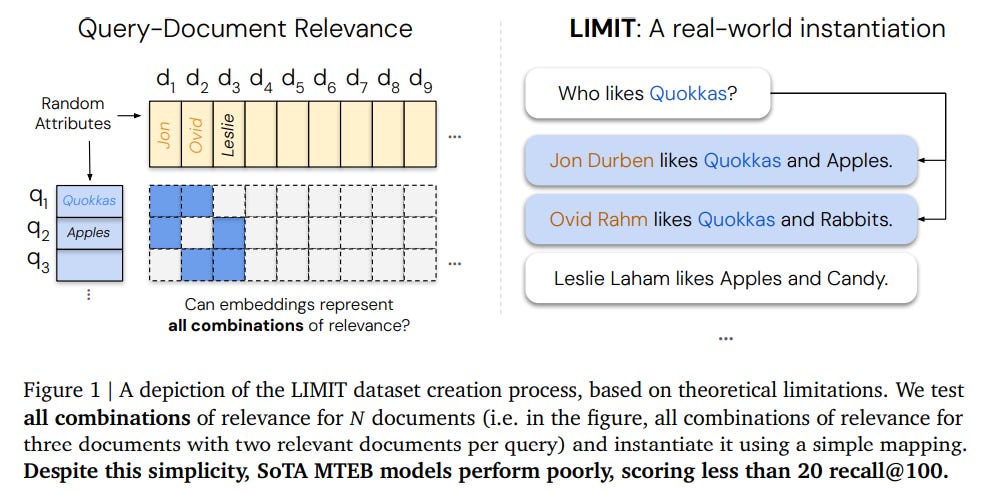
Study Reveals Fundamental Limits of Embedding Models for Retrieval Tasks
A recent study from researchers at Google DeepMind and Johns Hopkins University highlights the inherent theoretical limitations of embedding-based retrieval models, which employ vector embeddings for various complex tasks such as reasoning and instruction-following. The research indicates that these limitations, previously thought to be manageable with better data and larger models, can arise even with simple and realistic queries. Empirical evidence suggests that the capacity of these models to return relevant subsets of documents is restricted by embedding dimensionality. The study introduces a dataset named LIMIT, designed to stress-test models against these theoretical boundaries, revealing that even state-of-the-art models struggle to perform effectively on it. This research underscores the need for novel approaches to overcome foundational limits in existing single vector paradigms.
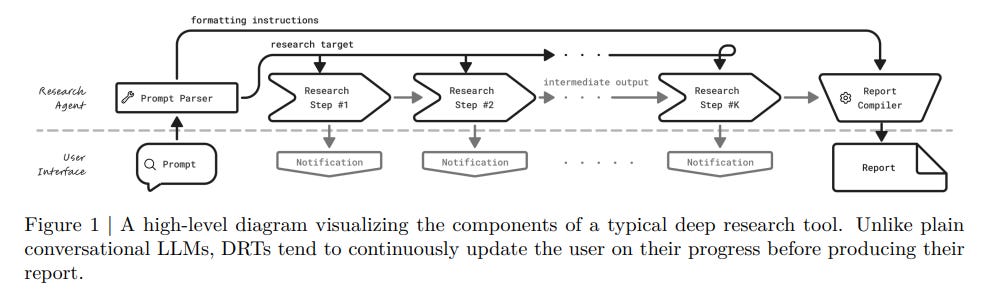
Universal Deep Research Empowers Users to Design Custom Strategies Without Retraining
NVIDIA Research has unveiled Universal Deep Research (UDR), an innovative agentic system designed to integrate with any language model, allowing users to develop and customize their own research strategies without additional training. Unlike previous systems that are limited by pre-defined strategies, UDR offers flexibility by supporting minimal, expansive, and intensive research approaches. This system features a user interface that supports real-time updates and delivers detailed research reports, distinguishing it from traditional conversational AI by focusing on search-intensive tasks suited for academic and professional use.
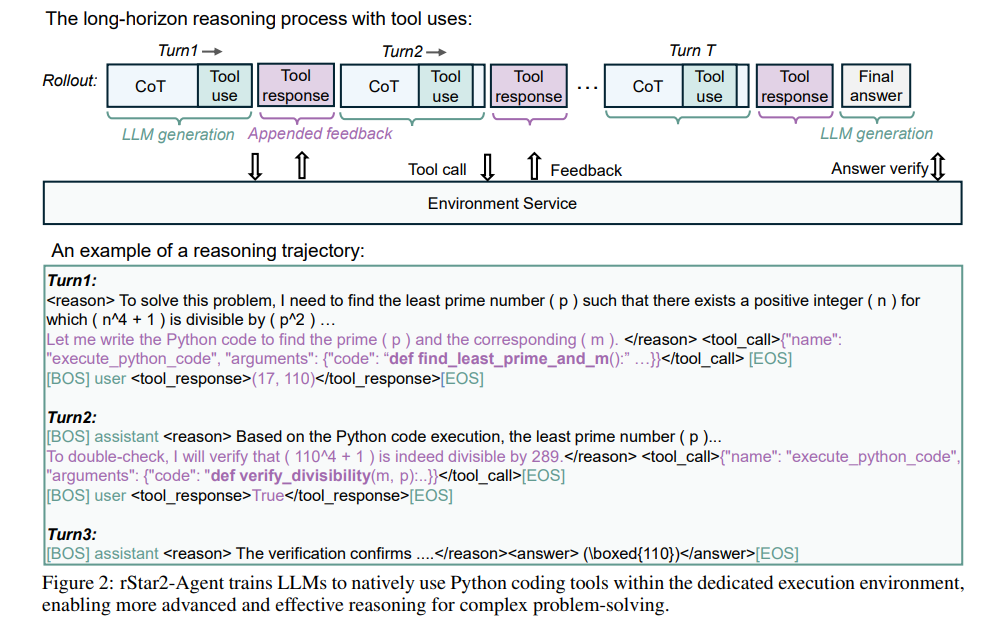
rStar2-Agent Trains to Frontier-Level Math Reasoning in Just 510 RL Steps
Microsoft Research has developed the rStar2-Agent, a 14-billion parameter math reasoning model that leverages agentic reinforcement learning to outperform larger models like DeepSeek-R1 in terms of computational efficiency and performance. The model excels in complex problem-solving by carefully incorporating Python coding tools and iterating based on code feedback. rStar2-Agent achieves superior results with an average pass rate of 80.6% on AIME24 and 69.8% on AIME25. Its innovations include an efficient reinforcement learning infrastructure and a new agentic RL algorithm that enables advanced cognitive capabilities with minimal GPU resources, marking significant advancements in both mathematics and generalizable reasoning tasks. The technical report and resources for the model are available on GitHub.
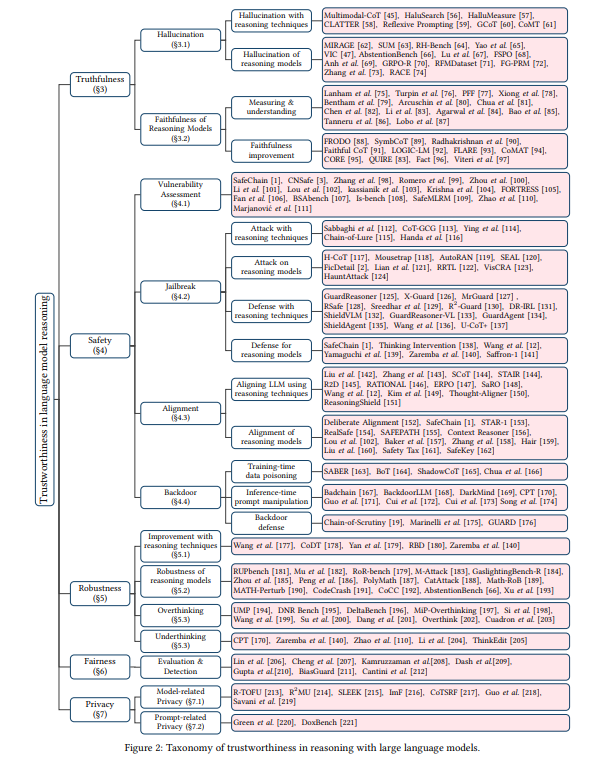
Survey Explores Trustworthiness of Language Models with Long-CoT Reasoning Techniques
A recent survey highlights the advancements and challenges in using Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning with large language models (LLMs) to enhance their trustworthiness. Although CoT reasoning has improved LLM performance by allowing the generation of intermediate reasoning steps, its impact on the models' trustworthiness remains unclear. The paper reviews studies on the core dimensions of trustworthy reasoning: truthfulness, safety, robustness, fairness, and privacy. It finds that while CoT techniques can help mitigate issues like hallucinations and harmful content, they often face vulnerabilities in safety and privacy. The research aims to serve as a critical resource for the AI safety community, offering insights into the current state and future directions of reasoning-based LLMs.
Investigating Why Language Models Hallucinate: The Role of Training Procedures and Benchmarks
A recent study by researchers from OpenAI and Georgia Tech explores why large language models, such as DeepSeek-V3, often produce "hallucinations"—outputs that are plausible yet incorrect. The study suggests that these hallucinations occur because current training and evaluation methods incentivize guessing rather than acknowledging uncertainty, akin to students taking tests. The statistical structure of training data can lead to these errors naturally, with models being rewarded for confident answers, even if wrong, due to existing evaluation metrics. The researchers propose that mitigating this issue requires changing how models are scored on benchmarks, directing them away from being merely good test-takers and towards greater reliability.
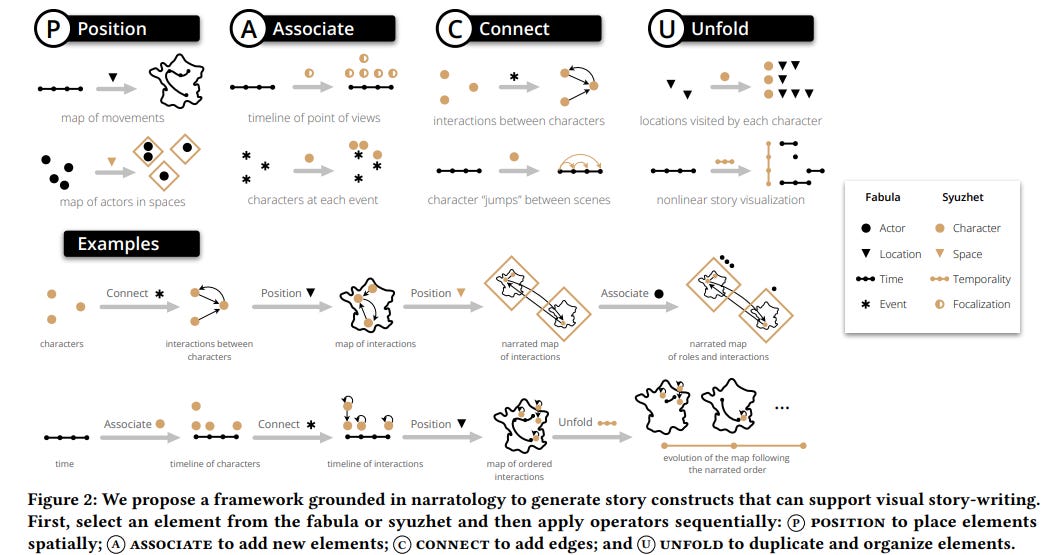
Visual Story-Writing Tool Enhances Creative Writing Through Innovative Graphical Interface
Researchers have developed a novel approach called "visual story-writing," which enhances narrative creation by integrating visual representations of story elements, such as character interactions, locations, and timelines. This technique involves a text editor that visualizes story components as interactive graphs, enabling writers to make narrative revisions by manipulating these visuals. User studies indicate that this method aids in high-level planning, maintaining consistency, and fostering creativity in narrative development. The findings pave the way for a supportive writing tool that complements traditional text editing with visual elements.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.