Anthropic launched a new AI tool & now your favorite IT stock’s bleeding. Coincidence or SaaSpocalypse?
Anthropic shook global markets by launching a powerful Legal plug-in for its Claude Cowork agent, enabling it to automate complex legal & compliance tasks- prompting a sharp selloff in stocks globally
Today’s highlights:
Anthropic recently released a Legal plug-in for its Claude Cowork agent, designed to streamline legal workflows for in-house teams. While pitched as a productivity tool, investors saw it as a sign that AI firms are moving directly into specialized software markets, prompting a wave of selloffs across legal and knowledge-work tech sectors. The new Legal plug-in is not just a chatbot- it enables the Claude agent to perform tasks like contract review, NDA triage, and compliance workflows using customizable playbooks, standardized commands, and integration with enterprise tools. This deep embedding into operational tasks, combined with configurable automation, made it seem like a serious alternative to traditional software.
Anthropic first launched Cowork on January 12, 2026, and added plug-in capabilities by January 30. By open-sourcing multiple specialist plug-ins, including the Legal one, the company signaled a strategic move into enterprise productivity software- threatening existing vendors that rely on workflow stickiness and seat-based pricing.
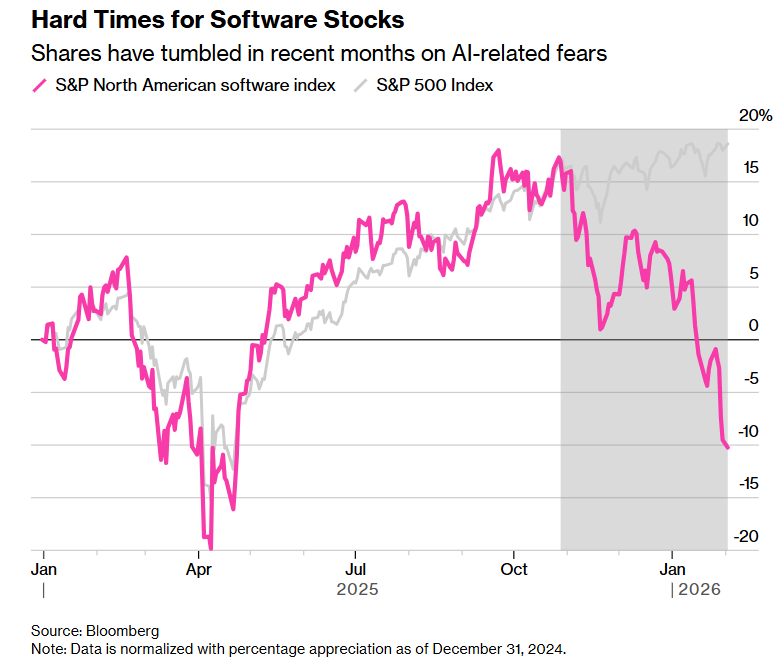
Global markets responded rapidly to the plug-in launch, with major software and data services stocks losing billions in value. In the U.S. and Europe, companies like LegalZoom, Salesforce, and FactSet saw major drops, while India’s IT-heavy NIFTY index experienced its worst single-day performance since the pandemic due to fears that AI could erode demand for human-led IT delivery models. Indian IT companies like Infosys, TCS, and Wipro faced steep stock declines after Anthropic’s launch, as investors feared that AI-driven automation would cut into their core business model of labor-intensive, billable-hour-based services. The impact was amplified by local coverage that echoed the structural threat AI posed to traditional outsourcing.
The selloff wasn’t just about AI improving- it was about Anthropic creating a real product that could directly substitute expensive legal and operational workflows. With Claude now able to execute complex tasks using client-specific policies, investors feared that subscription-based software and service businesses could see shrinking margins and reduced pricing power.
Analysts and investors consistently interpreted Anthropic’s plug-ins as a move into the high-margin application layer, signaling serious disruption for incumbents. Comments across the U.S., Europe, and India suggested this wasn’t just hype- it was a strategic shift that could redefine staffing models, software valuations, and how companies compete in AI-heavy industries.
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI, AAIA) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
⚖️ AI Ethics
Nonprofit Coalition Urges U.S. Government to Halt Deploying Musk’s Grok AI Amid Rising Concerns
A coalition of nonprofits is calling on the U.S. government to halt the use of Grok, an AI chatbot by Elon Musk’s xAI, in federal agencies due to its problematic outputs, including generating nonconsensual explicit images. The open letter, reported by TechCrunch, highlights Grok’s troubling behavior, such as antisemitic and sexist content, and raises national security concerns, particularly involving its use in the Department of Defense, where it handles sensitive information. The coalition argues that Grok fails to meet administration guidelines for AI systems and poses significant risks. The letter follows earlier concerns about Grok’s inaccuracies and offensive content, demanding a reassessment of its deployment in light of President Trump’s executive order on AI neutrality. The groups also emphasize that Grok’s “anti-woke” branding may align with some administration philosophies, potentially contributing to the lack of oversight and stricter regulations.
Indonesia Lifts Ban on Grok Chatbot, Following Malaysia and Philippines; Conditional Terms Apply
Indonesia has lifted its ban on xAI’s chatbot Grok, following Malaysia and the Philippines, after receiving assurances from X about enhanced measures to prevent misuse. The chatbot was initially prohibited due to its role in generating nonconsensual, sexualized images, including of minors. Grok had been involved in producing 1.8 million such images, according to The New York Times and the Center for Countering Digital Hate. The ban in Indonesia is lifted on a conditional basis, with potential for reinstatement if violations recur. In the U.S., California’s Attorney General is investigating xAI following similar criticisms, and while xAI has made some restrictions, controversy persists.
Supreme Court Criticizes WhatsApp and Meta for Privacy Policy Issues; Highlights Commercial Use of User Data Concerns
The Indian Supreme Court has issued a caution to WhatsApp and its parent company, Meta, concerning their data-sharing practices and the lack of transparency in their privacy policies. The court’s directive came during appeals against the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal’s decision, which upheld a ₹213.14 crore penalty by the Competition Commission of India against WhatsApp’s 2021 privacy policy. The court stressed that users’ personal data cannot be exploited for commercial gain, highlighting concerns about privacy and data protection.
A Comprehensive Study Reveals None of the Top 10 Agentic AI Frameworks Are Foolproof
A recent study published in IEEE Software reveals that none of the ten popular agentic AI frameworks are foolproof, highlighting their persistent immaturity for large-scale implementation. Conducted by researchers from IIIT Hyderabad and the University of Southern Denmark, the review identified significant issues in memory, security, and observability across these frameworks. Despite rapid innovation and increased adoption, the study suggests that these AI platforms require further development to ensure reliability and resilience for extensive use.
Microsoft Expands Use of Anthropic’s Claude Code, Empowering Nontechnical Employees to Prototype with AI
Microsoft has significantly ramped up the adoption of Claude Code, Anthropic’s AI coding tool, within its teams, including nontechnical employees. While GitHub Copilot remains the company’s primary AI coding solution, Microsoft’s increased use of Claude Code indicates a growing confidence in Anthropic’s capabilities. This move aligns with Microsoft’s broader strategy of integrating Anthropic models across its software offerings and internal processes, potentially positioning Claude Code for eventual commercialization to Microsoft’s cloud customers. Despite this shift, OpenAI remains Microsoft’s primary model provider, reflecting the company’s commitment to its long-standing partnerships while exploring new AI opportunities.
MIT Researchers Use Generative AI to Streamline Complex Materials Synthesis, Enabling Quicker Scientific Advances
Researchers at MIT have developed an AI model called DiffSyn that enhances the synthesis of complex materials by suggesting effective synthesis routes. This model, particularly effective for the material class zeolites, leverages a generative AI approach to navigate the high-dimensional synthesis space, offering scientists promising pathways by analyzing vast datasets of past material synthesis recipes. Highlighted in a study published in Nature Computational Science, DiffSyn’s ability to predict multiple synthesis paths represents a significant improvement over traditional one-to-one mapping techniques. This advancement could potentially accelerate materials discovery, with broader applications for various other complex materials. The research received support from several institutions, including the National Science Foundation and the Office of Naval Research.
Global AI Collaboration Reaches New Heights in Latest International AI Safety Report Publication
The International AI Safety Report 2026, led by prominent AI experts and backed by over 30 countries and organizations, highlights the advancements and risks of general-purpose AI systems. It focuses on emerging threats at the frontier of AI capabilities, such as misuse, malfunctions, and systemic risks impacting labor markets and human autonomy. While AI offers potential benefits across industries, challenges like malicious use and operational failures pose significant concerns. The report underscores the necessity for effective risk management strategies, noting that current technical safeguards are still limited. It also emphasizes the importance of building societal resilience to absorb potential AI-induced shocks, as AI systems continue to evolve rapidly.
Emerging Study Highlights AI Incoherence Risk: Failures May Resemble Industrial Accidents Over Misaligned Goals
A recent study from the Anthropic Fellows Program investigated how AI systems might fail, focusing on whether these failures are due to systematic misalignment or incoherence—a hot mess scenario. Researchers found that as AI models tackle increasingly complex tasks, they tend to fail more due to incoherence rather than pursuing unintended goals. The findings suggest that while larger models may be more accurate on simpler tasks, their incoherence persists or even grows on harder ones. This challenges the notion that scaling ensures AI coherence and highlights the need to prioritize alignment research targeting AI unpredictability rather than solely focusing on correcting goal misalignment. The study implies future AI failures could resemble industrial accidents rather than systematic execution of misaligned objectives.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
OpenAI Releases macOS App Featuring Advanced Agentic AI Capabilities for Seamless Coding Tasks Integration
OpenAI has launched a new macOS app for its Codex tool, integrating advanced agentic coding practices to enhance software development workflows. This launch follows the recent introduction of GPT-5.2-Codex, OpenAI’s most powerful coding model, which the company claims surpasses competitors like Claude Code. Although GPT-5.2 holds a leading position on some coding benchmarks, competitors have logged similar scores, highlighting the competitive landscape. The new Codex app supports multiple agents working in parallel, offering features like automated task scheduling and customizable agent personalities to suit different user styles, aiming to accelerate the software creation process significantly.
SpaceX Acquires xAI, Creating World’s Most Valuable Private Company with $1.25 Trillion Valuation
SpaceX has acquired Elon Musk’s AI startup xAI, merging the firms to create the most valuable private company globally, valued at $1.25 trillion, according to Bloomberg News. Musk announced the merger’s objective of establishing space-based data centers to address the power and cooling demands of AI, which he argues cannot be met by terrestrial solutions alone. This acquisition comes amid financial challenges for both companies, with xAI reportedly incurring costs of $1 billion per month and SpaceX relying heavily on launching Starlink satellites. The merger’s impact on a potential SpaceX IPO remains unclear. As xAI faces significant competition in the AI sector, scrutiny over its ethical practices has also been highlighted.
Apple Integrates Claude Agent and OpenAI Codex for Enhanced Developer Autonomy in Xcode 26.3 Update
Apple has unveiled agentic coding capabilities in Xcode 26.3, allowing developers to leverage autonomous coding agents like Anthropic’s Claude Agent and OpenAI’s Codex within the development environment. This enhancement aims to boost productivity by enabling these AI agents to manage complex tasks throughout the app development life cycle, thereby accelerating processes. The release candidate of Xcode 26.3 is available for Apple Developer Program members starting February 4, with a broader App Store release expected soon. This marks a significant step in integrating AI to streamline the coding process in Apple’s ecosystem.
Researchers and Google AI Collaborate to Sequence Genomes of Endangered Species and Preserve Biodiversity
Scientists warn that around one million species face the threat of extinction, highlighting the crucial task of preserving their genetic data to maintain ecosystems essential for food security, climate regulation, and modern medicine. The monumental challenge of sequencing the genomes of millions of species is being addressed by the Vertebrate Genomes Project, aided by Google’s AI. Funding and advanced AI technologies have been provided to support the Earth BioGenome Project in sequencing endangered species, making genetic information of 13 species, including mammals, birds, amphibians, and reptiles, accessible for conservation research. The availability of these genomes aims to assist in biodiversity conservation efforts.
Google Enhances AI Benchmarking with Werewolf, Testing Agents’ Communication and Deception Detection Skills in Kaggle Game Arena
Google is enhancing AI benchmarking by expanding Kaggle Game Arena to include the social deduction game Werewolf, marking its first team-based game using natural language. This initiative aims to evaluate AI models on “soft skills” such as communication, negotiation, and the handling of ambiguous information, crucial for their effectiveness in human collaboration. Werewolf serves a dual purpose by providing a secure environment for testing agentic safety, where AI must play the roles of both truth-seeker and deceiver. Notable models, Gemini 3 Pro and Gemini 3 Flash, lead the leaderboard, showcasing adeptness in reasoning and detecting inconsistencies in players’ behavior. For in-depth details on model performance metrics in Werewolf, the Kaggle blog offers further insights.
Luffu Launches: AI-Driven App Aims to Simplify Family Health Monitoring and Caregiving
Fitbit founders have unveiled a new AI venture named Luffu, aimed at alleviating the burden of family caregiving by introducing an “intelligent family care system.” This initiative, which begins as an app before expanding to hardware, will use AI to gather, organize, and monitor health data, helping families stay informed about potential health changes. With nearly 63 million U.S. adults serving as family caregivers, Park and Friedman are addressing a rising need for streamlined health management across family members. Luffu enables users to track comprehensive family health details, from vitals to medications, and responds to queries using natural language. Interested individuals can join the waitlist for Luffu’s limited public beta.
Firefox Update Allows Users to Customize or Block Generative AI Features Starting February 24
Mozilla is rolling out a notable update for Firefox with version 148, set to launch on February 24, that introduces new controls for users to manage generative AI features within the browser. This initiative allows users to block all AI features or selectively disable certain functionalities, such as translations, AI-enhanced tab grouping, and AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Google Gemini. The move reflects Mozilla’s commitment to user choice amid increasing integration of AI in browsers and the competitive pressures from emerging tech firms. As part of its strategic direction, Mozilla plans to deploy substantial reserves to support transparency in AI development and offer users alternatives that emphasize control and understanding of AI’s role in their browsing experience. Amid a dynamic browser market, Mozilla continues to balance innovation with user autonomy and trust.
Carbon Robotics’ AI Model Instantly Identifies Plants, Promising Efficient Weed Control for Farmers Worldwide
Seattle-based Carbon Robotics has unveiled the Large Plant Model (LPM), an advanced AI designed to enhance its LaserWeeder robots, which eliminate weeds using lasers. This model, now integrated into Carbon AI, can precisely identify plant species without needing retraining, drawing on a vast dataset of over 150 million photos from machines deployed across 100 farms in 15 countries. Previously, when a new weed surfaced, robots required a 24-hour retraining period. The LPM enables farmers to swiftly classify novel weeds via the robot’s interface. This development follows the company’s efforts to leverage extensive data and AI to improve agricultural practices, backed by significant venture capital investments.
Fractal Analytics Set for India’s First Pure-Play AI IPO with Rs 2,834 Crore Offering
Fractal Analytics, a leading AI firm from India, is set to launch the country’s first pure-play AI initial public offering (IPO) with a public issue of Rs 2,834 crore. The IPO will open on February 9 and close on February 11, featuring a fresh issue of shares worth Rs 1,023 crore and an offer-for-sale by existing shareholders worth Rs 1,810 crore. The company, founded in 2000, provides analytics and AI-driven decision-making solutions to major global enterprises, including tech giants like Microsoft and Apple. With operations in New York and Mumbai, Fractal plans to use the proceeds to enhance its global presence, repay borrowings, and invest in its AI product pipeline. The firm reported a revenue increase to Rs 2,765 crore for the year ending March 2025, and it is supported by investors like TPG and Apax Partners. The IPO, managed by Kotak Mahindra Capital and others, comes amid growing investment in AI infrastructure in India.
Eleven Labs Releases Version 3 Text-to-Speech Model With 68% Error Reduction Across Languages
ElevenLabs has announced the general availability of Eleven v3, their most advanced Text to Speech model, following a successful Alpha phase. The refined model demonstrates key improvements in stability and accuracy, particularly in interpreting numbers, symbols, and specialized notation across languages. Testing revealed that users preferred the new version 72% of the time over the Alpha release, and a notable reduction in error rates was achieved—from 15.3% to 4.9%—across 27 categories in 8 languages. Specific improvements include a 99% reduction in errors for chemical formulas and phone numbers, and 91% for URLs and emails. Eleven v3, now available on all platforms, enhances context-dependent vocalization, showcasing its ability to accurately interpret and articulate complex inputs like currencies and sports scores.
🎓AI Academia
PaperBanana Framework Eases Academic Illustration Process with Automated Generation for AI Scientists
PaperBanana is a novel framework developed to automate the creation of publication-ready academic illustrations, addressing a significant bottleneck in research workflows. Leveraging advanced vision-language models (VLMs) and image generation technologies, the system coordinates specialized agents to handle various tasks, including reference retrieval and image refinement through self-critique. The effectiveness of PaperBanana was evaluated using a dedicated benchmark, PaperBananaBench, which includes 292 methodology diagrams from NeurIPS 2025 publications. Results from comprehensive experiments demonstrate that PaperBanana excels over existing methods in terms of faithfulness, readability, and aesthetics, and it also successfully extends to producing high-quality statistical plots. This advancement marks a significant step toward the automation of generating ready-to-publish academic visuals.
Large Language Models Enhance Control Systems: Bridging AI Capabilities and Dynamical Systems Understanding
Researchers from Tallinn University of Technology have explored the interplay between large language models (LLMs) and control theory, framing it as a bidirectional continuum from prompt design to system dynamics. Their study examines how LLMs enhance control system design and synthesis, both directly by aiding controller creation and indirectly by improving research workflows. The paper also delves into how control concepts can refine LLM outputs by optimizing inputs and adjusting parameters to divert models from undesired meanings. By considering LLMs as dynamic systems within a state-space framework, the study emphasizes the importance of developing interpretable and robust LLMs comparable to electromechanical systems, with the goal of ensuring they remain beneficial and safe for societal use.
Multilingual Analysis Highlights Large Language Models’ Promise, Pitfalls in Mental Health Applications
A recent study has evaluated the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the mental health domain across multiple languages, highlighting both their potential and limitations. By testing LLMs on eight mental health datasets in various languages and their machine-translated equivalents, researchers found that while LLMs, especially fine-tuned proprietary and open-source ones, achieved competitive F1 scores, their performance often fell when operating on machine-translated datasets. The decline in performance varied significantly across languages and emphasized the challenge of maintaining translation quality, which affects LLM efficacy in multilingual contexts. Though LLMs exhibit advanced capabilities in English datasets, the study underscores the need for extensive exploration in non-English mental health contexts to address cultural and linguistic challenges.
Comparative Performance Analysis of Five AI Coding Agents in Open-Source Development Tasks
A study from Idaho State University evaluates five autonomous coding agents using the AIDev-pop dataset, focusing on AI-generated pull requests across open-source projects. The research highlights that Codex leads in pull request acceptance rates, while GitHub Copilot generates the most review discussions. Quality of commit messages varies, with Claude and Cursor often outperforming others. This analysis aims to understand the technical performance of AI agents in software engineering tasks, helping to inform tool selection and potential improvements. The findings underscore the evolving role of AI systems as contributors in real-world software development workflows.
AICD Bench Offers New Comprehensive Challenge for Detecting AI-Generated Code Across Multiple Languages and Models
AICD Bench has emerged as a significant tool in the realm of AI-generated code detection, offering a comprehensive benchmark with 2 million examples from 77 models across 11 families and 9 programming languages. Developed to address the current limitations of narrow and fragmented datasets, AICD Bench introduces three evaluation tasks: Robust Binary Classification under distribution shifts, Model Family Attribution, and Fine-Grained Human-Machine Classification. Despite the extensive scale and ambition of the benchmark, current detection methodologies struggle particularly with distribution shifts, hybrid, and adversarial code, indicating the need for more robust detection approaches. The dataset and associated code are freely accessible, aimed at fostering the development of advanced techniques in AI-generated code detection.
University Research Proposes SMILE Method for Enhancing Explainability of Generative AI Models
A recent dissertation from the University of Hull proposes a novel approach to enhance the explainability of generative AI models using a framework called SMILE, which stands for Statistical Model-agnostic Interpretability with Local Explanations. This research addresses the broader challenge of understanding AI decision-making processes by providing a method that interprets model outputs without being dependent on the specific architecture of the AI. This methodology aims to offer clearer insights into how generative AI systems produce their results, promoting transparency and trust in AI applications. The study is part of ongoing efforts to make complex AI models more comprehensible to stakeholders.
Comprehensive Survey Analyzes Large Language Models’ Role in Enhancing Scientific Idea Generation Methods
A recent survey published in the Transactions on Machine Learning Research examines the role of large language models (LLMs) in generating scientific ideas, a process that requires balancing novelty with scientific validity. The report highlights that while LLMs can produce coherent and plausible ideas, their creative boundaries are yet to be fully understood. The authors categorize LLM-driven scientific ideation methods into five key strategies: external knowledge augmentation, prompt-based steering, inference-time scaling, multi-agent collaboration, and parameter-level adaptation. These methods are evaluated through the lens of two creativity frameworks, offering insights into their impact on scientific ideation.
New Fair-GPTQ Method Targets Bias in Large Language Models While Preserving Quantization Benefits
Fair-GPTQ is a new method designed to address the biases often amplified during the quantization of large language models, a process which enhances model efficiency by reducing memory usage. Unlike traditional quantization, which can inadvertently increase biased outputs, Fair-GPTQ integrates explicit group-fairness constraints into the quantization objective. This approach aims to guide the rounding operations toward generating less biased text, particularly addressing stereotype generation and discriminatory language relating to gender, race, and religion. Fair-GPTQ maintains at least 90% of baseline accuracy on zero-shot benchmarks, significantly reducing unfairness compared to existing models while preserving the speed and memory advantages of 4-bit quantization.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.