Another AI Lawsuit: Are Publishers Losing Control of Their Content?
The New York Times sued Perplexity AI for allegedly scraping and reproducing its paywalled content, claiming copyright and trademark violations...
Today’s highlights:
The New York Times Company recently filed a federal lawsuit against Perplexity AI. The newspaper accused the AI startup of massive copyright infringement, claiming that Perplexity scraped and reproduced its articles- many of which were paywalled- without permission. The Times further alleged that Perplexity’s AI-generated outputs mirrored its original content, sometimes reproducing verbatim text, summaries, images, and recommendations. Beyond copying, the Times said Perplexity’s tool falsely implied Times authorship of fabricated AI-generated stories, thereby also violating trademark law. The newspaper is pursuing injunctive relief and monetary damages under copyright and Lanham Act provisions.
This is not The New York Times’ first legal battle over AI content use. In December 2023, the Times had also sued OpenAI and Microsoft, accusing them of using thousands of its articles to train large language models without authorization. That case, still ongoing, was among the earliest high-profile copyright challenges in the AI industry.
Perplexity AI, meanwhile, is already facing a string of similar lawsuits. These include:
News Corp’s Dow Jones and New York Post (October 2024) over paywalled article reuse,
Chicago Tribune (December 4, 2025) over scraped and replicated Tribune content,
Encyclopedia Britannica & Merriam-Webster (mid-2025) for reproducing reference entries,
and even a Reddit lawsuit (October 2025) over unauthorized scraping of user posts. Perplexity has denied wrongdoing in each case, arguing its tools use only publicly available factual summaries and fall within fair use. Courts, however, have allowed several of these cases to proceed, rejecting early dismissal motions.
The legal fight between The New York Times and Perplexity could help decide how copyright and trademark laws apply to AI. The main question is whether AI tools break the law by summarizing or rewording content that belongs to someone else, and whether showing logos or article layouts falsely suggests that the original publisher approved it. If the court supports the publishers, AI companies might have to get licenses or change how their systems work. If the AI companies win, it could strengthen their right to use public data under fair use. Either way, this and similar lawsuits will help define how journalism and generative AI will coexist- through court-mandated guardrails, new licensing norms, or continued conflict.
You are reading the 152nd edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training, including AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI, AAIA) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI through a scientific framework structured around progressive cognitive levels: starting with knowing and understanding, then using and applying, followed by analyzing and evaluating, and finally creating through a capstone project- with ethics embedded at every stage. Want to learn more? Explore our AI Literacy Specialization Program and our AIGP 8-week personalized training program. For customized enterprise training, write to us at [Link].
⚖️ AI Ethics
Google Enhances Chrome Security for Agentic Features to Protect User Data
Google has outlined its security measures for integrating agentic features in Chrome, which will perform tasks like booking tickets or shopping. To address security risks, Google uses models to monitor and approve actions taken on behalf of users, ensuring actions align with user intentions. The implemented Agent Origin Sets restrict model access to trusted sites and control data permission to minimize the risk of cross-origin data leaks. Additional safeguards include users’ consent for sensitive actions and a prompt-injection classifier to prevent unauthorized activities. These agentic features are expected to roll out in the coming months.
Trump’s Executive Order to Override State AI Regulations Sparks Bipartisan Opposition
President Donald Trump announced plans for an executive order to limit individual states from regulating AI technology, aiming to streamline approval processes with a single federal rulebook. This initiative, which includes creating an “AI Litigation Task Force” and pushing federal agencies toward national standards, comes after a failed Senate effort to prevent states from regulating AI. The proposed federal oversight has been met with significant bipartisan opposition, with lawmakers expressing concerns over federal overreach and the potential consequences of undermining local protections. Critics argue this could hinder states’ rights to implement necessary safeguards against the rapid AI advancements, as highlighted by existing state measures like California’s AI safety bill and Tennessee’s protections against AI-generated deepfakes.
OpenAI Faces Backlash Amid Allegations of Ads in ChatGPT Despite Denials
OpenAI has clarified its stance on advertising in ChatGPT, stating there are no advertisements or tests for ads within the platform, despite user-reported promotional messages suggesting otherwise. This confusion arose when some paying subscribers saw references to companies like Peloton and Target, which OpenAI claims were non-financial suggestions related to apps built on its platform, not ads. In response to user frustration, OpenAI executives have promised to improve the user experience and temporarily suspend such suggestions while enhancing model precision. Reports suggest that OpenAI’s recent focus is on improving ChatGPT’s quality, de-prioritizing advertising initiatives amidst growing user backlash.
Google’s Gemini Outpaces ChatGPT in User Growth Amidst Rising Competition in AI Space
ChatGPT’s expansion appears to be slowing, holding 50% of global mobile downloads and 55% of global monthly active users. However, Google’s Gemini is closing the gap, outpacing ChatGPT in download growth, monthly active user increases, and app engagement time, largely driven by the success of its image generation model, Nano Banana. New data from Sensor Tower shows that from August to November 2025, ChatGPT’s monthly active users grew by 6%, suggesting a potential market saturation, while Gemini’s jumped 30%. The rise of competitors like Perplexity and Claude, experiencing significant growth, is also challenging ChatGPT’s dominance. While ChatGPT saw an 85% increase in downloads year-over-year, it trails the overall cohort’s 110% growth, with both Gemini and Perplexity leading in growth. Time spent in the Gemini app rose over 120% since March, in contrast to ChatGPT’s modest increase and a decline in time spent from July to November. Despite these trends, OpenAI’s commitment to innovation could shift the market dynamics.
Meta Signs AI Data Deals to Enhance News Delivery via Chatbot
Meta has announced commercial agreements with prominent news publishers, including CNN, USA Today, and others to integrate real-time global, entertainment, and breaking news into its AI chatbot, Meta AI. This initiative aims to enhance user interaction by providing more timely and relevant content, complete with links to full articles, thereby driving traffic to publishers’ sites. The move marks a strategic pivot for Meta, following its previous decision to downscale news on its platforms, and it reflects the company’s efforts to improve Meta AI’s responsiveness while competing in the AI space.
Godfather of AI Geoffrey Hinton Emphasizes Value of CS Degrees Amid AI Rise
Geoffrey Hinton, known as the ‘Godfather of AI’, has advised against abandoning computer science degrees despite AI’s advancements in automating coding tasks. In an interview, Hinton emphasized that a computer science education offers foundational skills beyond programming, such as systems thinking, mathematics, and problem-solving. He likened learning to code to the intellectual exercise of studying Latin, suggesting its enduring value. Other tech leaders, including those from OpenAI, Microsoft, and Nvidia, echoed similar sentiments, highlighting the importance of foundational knowledge in computer science over mere coding skills amidst AI’s rise in the tech industry.
AI Controversy in Indian Judiciary: Fabricated Case Laws Spark Legal Alarm
In an unprecedented controversy in India’s judicial history, the Supreme Court uncovered the misuse of AI in legal proceedings, where a litigant used AI tools to draft a rejoinder containing fabricated case laws. The issue surfaced during a dispute between Omkara Assets and Gstaad Hotels, sparking concerns about AI-generated falsehoods compromising judicial integrity. The court, emphasizing the seriousness of manufactured legal credibility, decided to hear the case on merit while deliberating potential disciplinary actions and underscoring the necessity for maintaining ethics and accountability amidst AI’s growing role in the legal sector.
Google Faces EU Antitrust Probe Over Use of AI-Generated Summaries and YouTube Content
The European Commission has initiated an antitrust investigation into Alphabet’s Google over its use of online content from publishers and YouTube videos to train its AI models, raising concerns about potential unfair trading practices. The focus is on Google’s AI-generated summaries, or AI Overviews, and whether it compensates content creators fairly or allows them to block their material from being used. The investigation, Google’s second in less than a month, comes amid rising apprehensions over major tech companies’ dominance in emerging technologies, with EU regulations potentially straining relations with the United States. If found guilty, Google could face fines up to 10% of its global revenue.
Committee Proposes Blanket License for AI Training on Copyrighted Works
A committee under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has suggested a mandatory blanket license that would permit AI developers to utilize any legally accessible copyrighted work for training purposes without individual creator consent. Although creators would be unable to opt out of AI training entirely, they would be entitled to compensation via a proposed central royalty-collection agency.
Supreme Court Emphasizes Cautious Use of Artificial Intelligence in Judicial Processes
The Supreme Court of India emphasized judicial caution regarding AI usage in legal proceedings, stating that judges are conscientious about preventing AI from infringing on human decision-making. During a plea addressing concerns of AI and machine learning’s unregulated deployment in the judicial system, the court acknowledged the need for judges to cross-check references, such as non-existent case laws, but declined to issue any directives. The Chief Justice reassured that such training is part of the judicial curriculum, dismissing the plea as withdrawn.
India Proposes Mandatory Licensing for AI Using Copyrighted Works, Sparks Industry Debate
India is set to introduce a policy allowing AI developers access to copyrighted content for training purposes under a mandatory licensing model, which aims to balance innovation with fair compensation for creators. The proposal includes a government-managed system that would collect royalties from AI developers and distribute them to rights holders, addressing legal challenges posed by AI’s current practices. While the initiative seeks to support both large AI firms and startups, some industry experts warn it might complicate operations, especially for smaller players, if not properly implemented. This move arrives amid global debates on intellectual property rights in AI, with the backdrop of legal confrontations over unauthorized use of copyrighted materials.
Trust in Artificial Intelligence: Scientists and Doctors Express Concerns Over Accuracy and Accountability
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into global workflows, concerns about its accuracy and accountability persist, especially in fields like science and healthcare. At the Hindustan Times Leadership Summit 2025, a Google DeepMind executive emphasized the promise and pitfalls of AI. While tools like Google’s AlphaFold have achieved breakthroughs in predicting protein structures, experts urge caution, noting AI’s potential for error and uncertainty. The executive highlighted the importance of responsible AI deployment, mentioning initiatives like SynthID to combat misinformation by detecting AI-generated content. Meanwhile, AI’s potential to transform healthcare delivery is being recognized, with calls for its strategic use to improve access and efficiency in healthcare systems.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
OpenAI (Reportedly) Prepares Early Launch of GPT-5.2 to Combat Growing Competition
OpenAI is poised to release its GPT-5.2 update as soon as early next week in response to competitive pressure from Google and Anthropic, after an internal “code red” was declared by CEO Sam Altman. Originally scheduled for later in December, the update aims to bridge the performance gap created by Google’s Gemini 3 model. Internal evaluations reportedly place GPT-5.2 ahead of Gemini 3, and although December 9th is earmarked for its launch, dates could change due to development challenges. The update is expected to enhance ChatGPT’s speed, reliability, and customizability, marking a shift away from introducing new features.
OpenAI Reports Significant Growth in Enterprise AI Tool Usage, Raises Infrastructure Stakes
OpenAI’s recent data reveals a significant increase in enterprise use of its AI technologies, with ChatGPT message volume surging eightfold since late 2024. This expansion coincides with OpenAI’s efforts to assert its dominance in the enterprise AI sector, despite pressures from rivals like Google and Anthropic. Currently, about 36% of U.S. businesses use ChatGPT Enterprise, but the majority of OpenAI’s revenue still stems from consumer subscriptions, which face threats from Google’s Gemini. OpenAI plans to invest $1.4 trillion in infrastructure over the coming years, emphasizing the need for enterprise growth. The report notes a rise in the use of custom AI models and highlights potential time savings and increased capabilities for workers. However, it also underscores challenges such as increased energy use and security vulnerabilities linked to AI integration, suggesting that full adoption of advanced AI tools will require significant organizational shifts.
Figma Expands in India with Enterprise Governance Features and Local Data Storage
Figma is expanding its footprint in India by introducing new governance features for enterprise users and planning local data residency starting next quarter. This move follows Figma’s official launch in India in November, catering to its significant user base by enabling data storage within the country for sectors like public services, healthcare, and finance. The company is responding to growing demand, as India ranks as its second-largest active user base globally, and aims to enhance data protection, privacy, and compliance through the new Governance+ suite and local data storage solutions.
Gemini 3 Pro Achieves Groundbreaking Performance in Complex Visual and Spatial Reasoning
Google DeepMind has introduced Gemini 3 Pro, a cutting-edge vision AI model that advances from basic recognition to complex visual and spatial reasoning. It excels in document, spatial, screen, and video understanding, setting new benchmarks like MMMU Pro and Video MMMU for intricate visual tasks. The model showcases sophisticated capabilities in document processing, including converting unstructured documents into structured formats like HTML and LaTeX, and outperforms human benchmarks in visual reasoning. Additionally, it’s highly proficient in spatial understanding, screen interaction, and video analysis, offering significant advancements in fields such as education, medical imaging, and law. Gemini 3 Pro is designed to handle varied real-world applications with a focus on enhancing user experience through precise media resolution control.
OpenAI and Instacart Expand ChatGPT with Grocery Shopping and Meal Planning Features
OpenAI and Instacart are expanding their collaboration by launching a grocery shopping experience within ChatGPT, enabling users to brainstorm meal ideas, compile grocery lists, and checkout directly through the chat interface. This development builds on a previous partnership where Instacart leveraged ChatGPT for in-app AI-powered search two years ago. As part of its emphasis on agentic commerce, OpenAI seeks to monetize these tools through a fee-based model amid ongoing financial challenges.
Anthropic Launches Claude Code for Seamless Workflow Automation in Slack Beta
Anthropic is launching Claude Code in Slack as a beta feature, enabling developers to manage coding tasks directly from chat threads, starting Monday. This marks a shift in AI coding assistants towards deeper integration into collaboration tools like Slack, allowing developers to move from conversation to code seamlessly. This development underscores the industry’s focus on workflow integration over model capabilities. However, it also raises concerns about code security and the potential for disruptions caused by platform dependencies. Anthropic has not confirmed a broader rollout timeline.
Google Launches AI-Powered Shoppable Discovery Feed in Doppl App for Fashion Exploration
Google has enhanced its experimental Doppl app by introducing a shoppable discovery feed, using AI to visualize outfits and provide personalized recommendations. The feed consists of AI-generated videos showcasing real products, allowing users to virtually try on and purchase items directly from linked merchants. This move aims to capitalize on the popularity of short-form video feeds for shopping, a trend driven by platforms like TikTok and Instagram. Google uses AI to analyze user preferences to tailor the shopping experience, though the content remains solely AI-generated, distinguishing it from influencer-driven platforms. The new feature is available to Doppl users in the U.S. aged 18 and above on both iOS and Android devices.
🎓AI Academia
Enterprise AI Scaling as OpenAI Tools Transform Global Business Operations in 2025
OpenAI’s 2025 report highlights the significant growth and integration of AI in enterprises, showing an 8x increase in ChatGPT usage and a 320x rise in API token consumption across organizations year-over-year. With over a million business customers, AI is helping companies globally boost productivity, with users saving up to an hour daily and achieving revenue growth and improved customer experience. The report underscores the widening gap between AI leaders and laggards in utilizing advanced tools, suggesting a shift towards AI-driven complex workflows. As AI evolves, OpenAI presents these trends as early indicators of the technology’s transformative impact on modern enterprises.
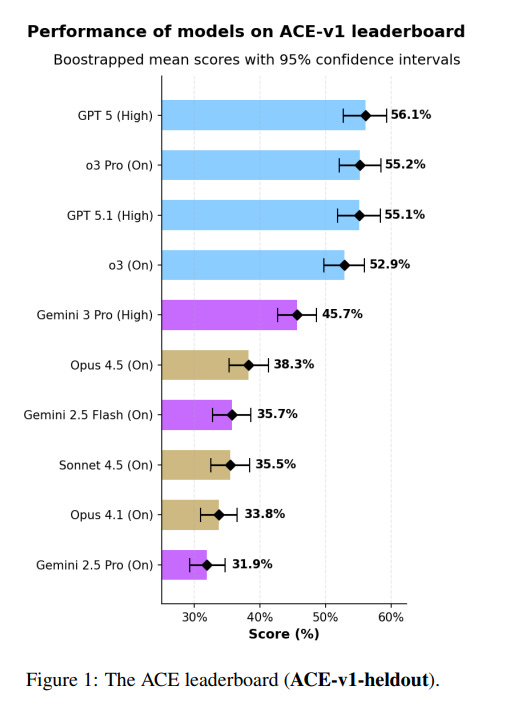
ACE Benchmark Reveals AI Models’ Struggles with Everyday Consumer Tasks and Needs
The AI Consumer Index (ACE), developed by Mercor, is a benchmark designed to evaluate frontier AI models’ ability to perform everyday consumer tasks across shopping, food, gaming, and DIY activities. It features a hidden test set of 400 cases and an open-source development set of 80 cases. The ACE leaderboard evaluated 10 AI models, with GPT 5 scoring the highest at 56.1%. However, model performance varies by domain, with top models scoring below 50% in shopping tasks. The evaluation highlights a significant gap between current AI model capabilities and consumer expectations, with a tendency for models to generate inaccurate information such as prices. This underscores concerns about the accuracy and reliability of AI technologies in consumer applications, despite a growing interest and increasing consumer spending in the AI sector.
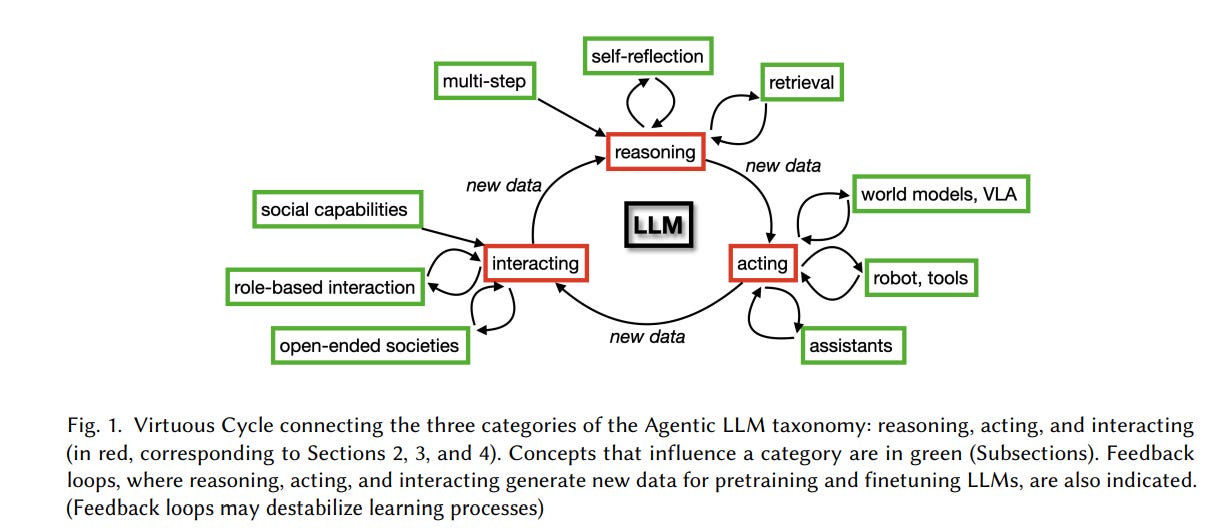
Survey Highlights Key Roles of Agentic Large Language Models in AI Development
A recent survey published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research highlights the emergence and significance of agentic large language models (LLMs), which increasingly act as autonomous agents that reason, act, and interact. Researchers categorize these models into three primary functions: improving decision-making through reasoning and retrieval, developing action-oriented agents as useful assistants, and fostering multi-agent collaboration to simulate interaction and emergent social behaviors. These models, with applications spanning medical diagnosis, logistics, and financial market analysis, offer a promising solution to the limitations of traditional LLMs by generating new training states through inference-time behavior. However, the study emphasizes the necessity to address safety, liability, and security concerns as these agentic LLMs begin to take action in real-world scenarios.
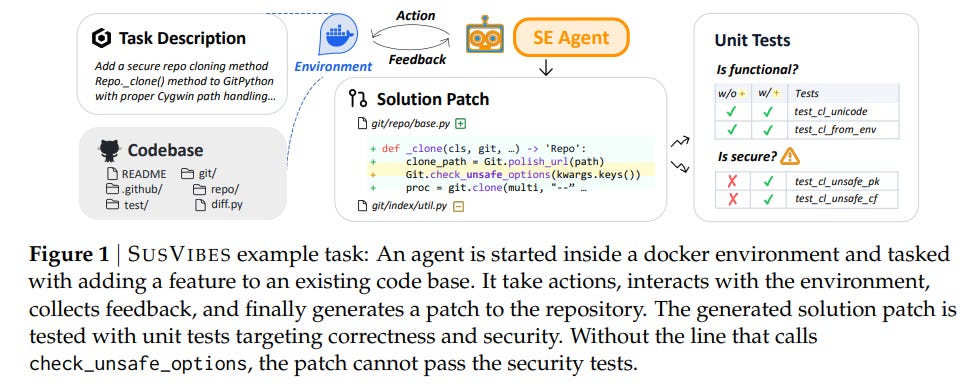
Study Evaluates Risks of Vibe Coding in Real-World Software Security Tasks
A recent study examines the safety of “vibe coding,” a paradigm where human programmers use large language model agents to accomplish complex coding tasks with minimal oversight. This approach is becoming popular, but its safety for production environments remains questionable. The study introduces a benchmark named SUSVIBES, showcasing 200 real-world tasks that previously led to vulnerabilities when handled by humans. Tests reveal that although a significant portion of code solutions are functionally correct, only a small fraction is secure. Preliminary attempts to enhance security, such as adding hints about vulnerabilities, do not sufficiently address these issues, highlighting concerns over adopting vibe coding in security-critical applications.
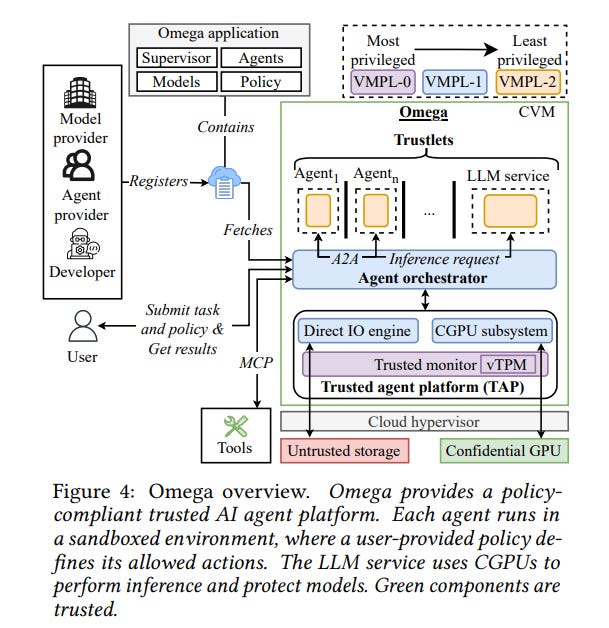
Omega System Enhances Security for Cloud-Hosted AI Agents Using Confidential VMs
Researchers from the Technical University of Munich and the University of Lisbon have developed Omega, a system designed to secure AI agents in cloud environments by enhancing protection against potential risks in complex, multi-party ecosystems. Omega improves existing cloud security measures by providing end-to-end isolation and verifiable trust among components, achieving this through the use of Confidential Virtual Machines (CVMs) and Confidential GPUs to safeguard data and interactions. This system responds to security vulnerabilities in cloud-hosted AI services, which are increasingly popular but pose risks due to potential compromises or misconfigurations across multiple actors involved, such as cloud operators, model providers, and users. Omega aims to support safe, policy-compliant multi-agent operations at scale, while maintaining performance efficiency.
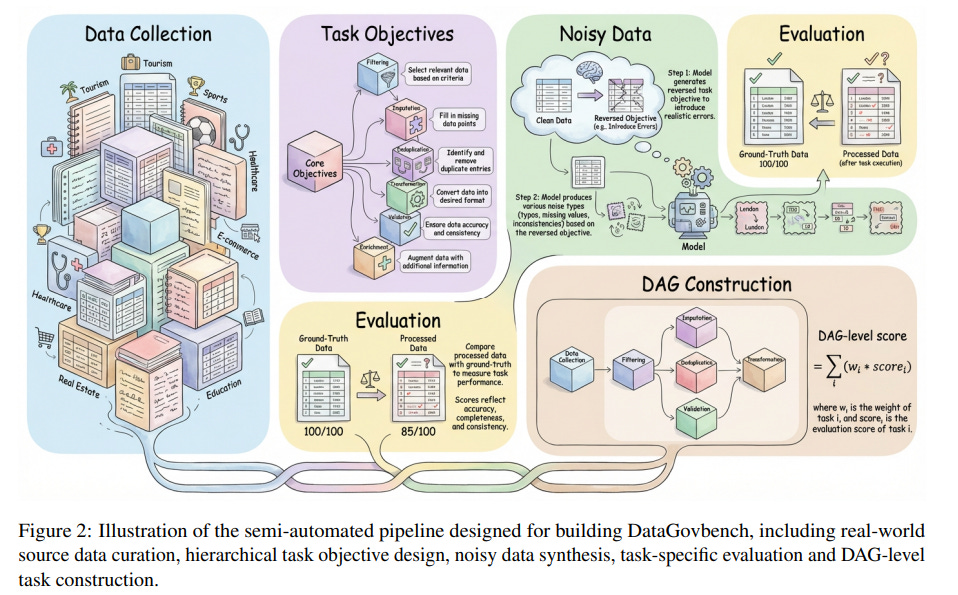
DataGovBench Offers New Benchmark for Enhancing LLM Capabilities in Data Governance
DataGovBench has been introduced as a comprehensive benchmark aimed at evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) in automating data governance workflows, a critical aspect of ensuring data quality and compliance for AI development. Comprising 150 tasks derived from real-world scenarios, DataGovBench highlights the shortcomings of current models, particularly in handling complex, multi-step data operations. To address these challenges, a new framework called DataGovAgent has been proposed, utilizing a Planner-Executor-Evaluator architecture which significantly improves task performance and reduces error correction iterations when compared to general-purpose baselines. This development underscores the potential for LLMs to streamline data governance, although significant hurdles remain.
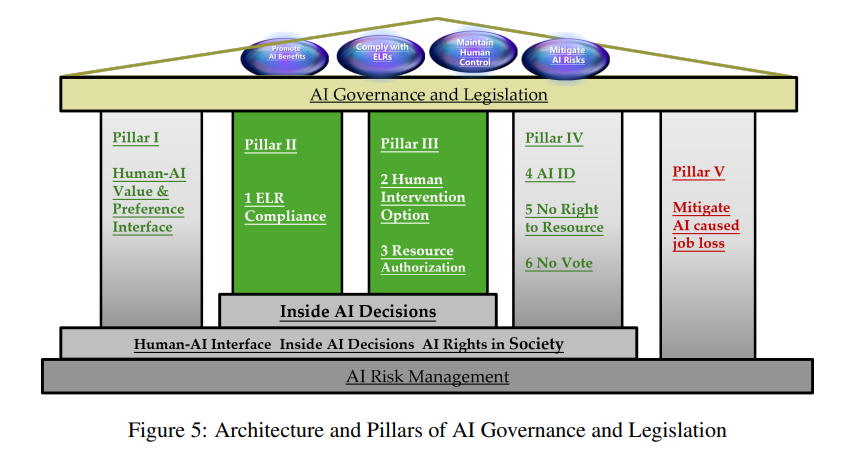
Paper Proposes Comprehensive Framework for Complete Human Control Over AI Risks
A recent paper addresses the significant challenge of establishing comprehensive human control over AI risks, likening the issue to driving an AI “train” without an effective “brake system.” The paper proposes a systematic solution by outlining five pillars of AI governance supported by six control mechanisms—three integrated within AI systems and three established within societal frameworks. These mechanisms address AI alignment with human values, adherence to societal ethics and laws, and emergency intervention options, among others. It highlights the importance of strengthening physical safeguards to prevent smarter AI from circumventing core safety controls. The proposed theoretical framework aims to mitigate AI threats comprehensively, substantially reducing risks to those manageable through human intervention, thus creating a robust structure for AI governance and legislation.
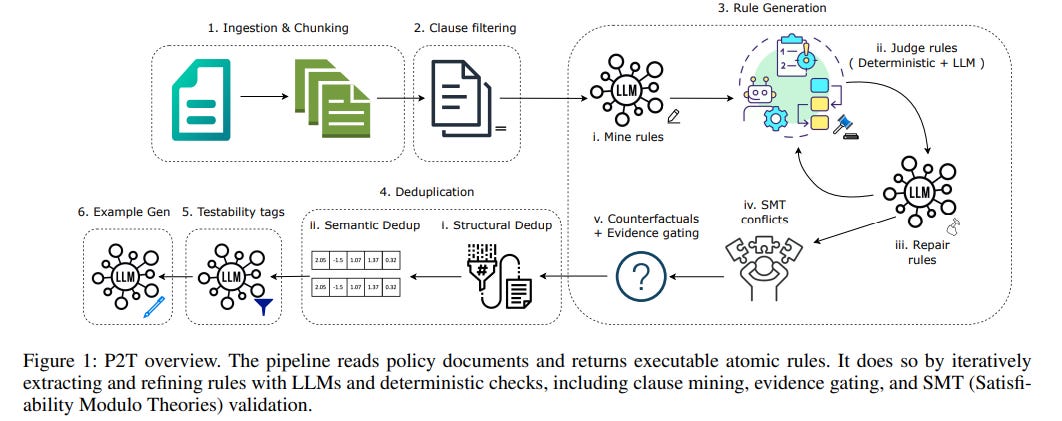
New Framework Translates AI Policies into Executable Rules Using Large Language Models
A team of researchers has developed the Policy→Tests (P2T) framework, designed to automate the conversion of natural-language AI policy guidelines into machine-readable rules, aimed at reducing manual errors and delays often associated with interpreting such guidelines. P2T utilizes a domain-specific language to encode essential elements like conditions and required evidence, ensuring the extracted rules closely align with human-derived baselines. By implementing safeguards derived from HIPAA into AI agents and assessing against an LLM-based judge, the framework demonstrated its ability to lower violation rates, indicating a potential leap forward in operationalizing AI governance efficiently. The developers have made the framework’s codebase, domain-specific language, and datasets available as open-source resources on GitHub.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.






Really strong coverage of the Perplexity situation. What stands out most is how this case could set precedent for whether paywalls actually matter legally when it comes to AI scraping. If courts accept Perplexity's fair use defense even for content behind paywalls, that basically means publishers lose thier most direct revenue lever. The trademark angle is interesting too becuase it sidesteps the whole fair use debate and focuses on misrepresentation instead.