30% of Your Code Now Comes from AI- a Warning Sign for Developers Everywhere?
AI tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT are now writing ~30% of Python code in the U.S., signaling a move from manual coding to AI-human collaboration. AI is increasingly seen as a "pair programmer".
Today's highlights:
You are reading the 103rd edition of the The Responsible AI Digest by SoRAI (School of Responsible AI) . Subscribe today for regular updates!
At the School of Responsible AI (SoRAI), we empower individuals and organizations to become AI-literate through comprehensive, practical, and engaging programs. For individuals, we offer specialized training such as AI Governance certifications (AIGP, RAI) and an immersive AI Literacy Specialization. This specialization teaches AI using a scientific framework structured around four levels of cognitive skills. Our first course is now live and focuses on the foundational cognitive skills of Remembering and Understanding. Want to learn more? Explore all courses: [Link] Write to us for customized enterprise training: [Link]
🔦 Today's Spotlight
AI tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT are now writing ~30% of Python code in the U.S., signaling a move from manual coding to AI-human collaboration. AI is increasingly seen as a "pair programmer" that can auto-generate code from natural language, turning software development into a blended task of prompting, reviewing, and supervising.
Who’s Using It and Where
Adoption is highest in the U.S. (30%), Western Europe (~23%), and growing fast in India (~21%), while China and Russia lag (~10–15%). Younger and newer developers use AI more extensively than veterans, narrowing skill gaps. Usage is widespread across startups, open-source, and big tech, though industries like finance and defense are cautious due to legal and compliance risks.
Last month Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella also revealed that 30% of Microsoft's code is now generated by AI, affirming the scale at which AI tools are reshaping real-world enterprise development. Nadella credited open-source ecosystems as the backbone of AI’s evolution, highlighting how tools like GitHub Copilot are redefining developer roles- from line-by-line coders to system thinkers and AI supervisors. Microsoft emphasized the need for a mindset shift, comparing this AI moment to the industrial leap electricity brought to factories. Developers, he warned, must evolve or risk falling behind in this new paradigm where AI is not replacing jobs, but transforming them.
Pros and Cons
AI-assisted coding significantly boosts productivity, encourages exploration, and helps bridge skill gaps- especially for junior developers-by automating repetitive tasks and suggesting novel solutions. However, it comes with notable risks: it can generate buggy or insecure code, promote code duplication, and erode core programming skills through over-reliance. Moreover, its limited contextual awareness often demands human intervention, and unresolved legal issues around code provenance pose ethical concerns. Ultimately, AI works best as a fast but fallible assistant- valuable when paired with experienced oversight and thoughtful integration.
Technical & Economic Impacts
AI-assisted coding increases output (2.4% on average, up to 39% for juniors in trials). Even small boosts yield billions in economic value – estimated $10–90B in the U.S. alone. Firms see high ROI from tools like Copilot. AI also promotes faster innovation, enabling small teams to prototype, explore, and deliver features faster.
Social Shifts and Skills
Developers are becoming curators of AI output. Entry-level roles are changing – fewer basic tasks, more prompt engineering and critical thinking. Education must adapt to teach collaboration with AI and maintain core CS principles. While AI may amplify inequality, it also democratizes skills and enhances job satisfaction for many.
Conclusion:
AI-assisted coding promises higher productivity, lower skill barriers, and more enjoyable coding, but also introduces risks around code quality, over-reliance, and global inequality. To harness its full potential, stakeholders – from developers to educators and policymakers – must consciously guide this transition, ensuring responsible use, inclusive access, and sustained creativity. Coding may be changing, but with the right oversight, it can change for the better.
If you want to stay relevant in the age of AI-assisted coding, don’t wait- start upskilling with our AI Literacy for Developers program. Comment #vibecodewithsorai to get your free guide.
🚀 AI Breakthroughs
WhatsApp Introduces Ads and Subscription Channels in Major Update from Meta
• WhatsApp introduces ads in its Stories-like status feature, allowing businesses to reach users through the "Updates" tab, which also provides a platform for sharing disappearing messages
• Meta claims that ads in WhatsApp will leverage limited data like users' location and language, with personal messages and phone numbers not being used for targeting purposes
• WhatsApp channels now offer subscriptions for exclusive content, enabling channel operators to enhance visibility, although the service remains free for users, with changes unfolding over coming months.
Meta's $14.3 Billion Investment in Scale AI Sparks Industry Realignment and CEO Change
• Scale AI secured a substantial investment from Meta, giving Meta a 49% stake and valuing Scale AI at $29 billion
• Alexandr Wang, Scale AI's co-founder and CEO, will join Meta to focus on AI initiatives, while serving on Scale AI's board
• Meta's investment creates tensions with Scale AI's major clients, OpenAI and Google, who are reducing business over potential competitive data exposure;
Google Launches Audio Overviews Using Gemini Models for Search Enhancements
• Google launches a new Search experiment called Audio Overviews in Labs, utilizing Gemini models to provide quick, conversational audio summaries for unfamiliar topics
• Audio Overviews offer a hands-free way to absorb information, with relevant web pages displayed for further exploration directly in the search results audio player
• Users can opt into the experiment in Labs and rate the usefulness of audio overviews on search result pages with a thumbs up or down system;
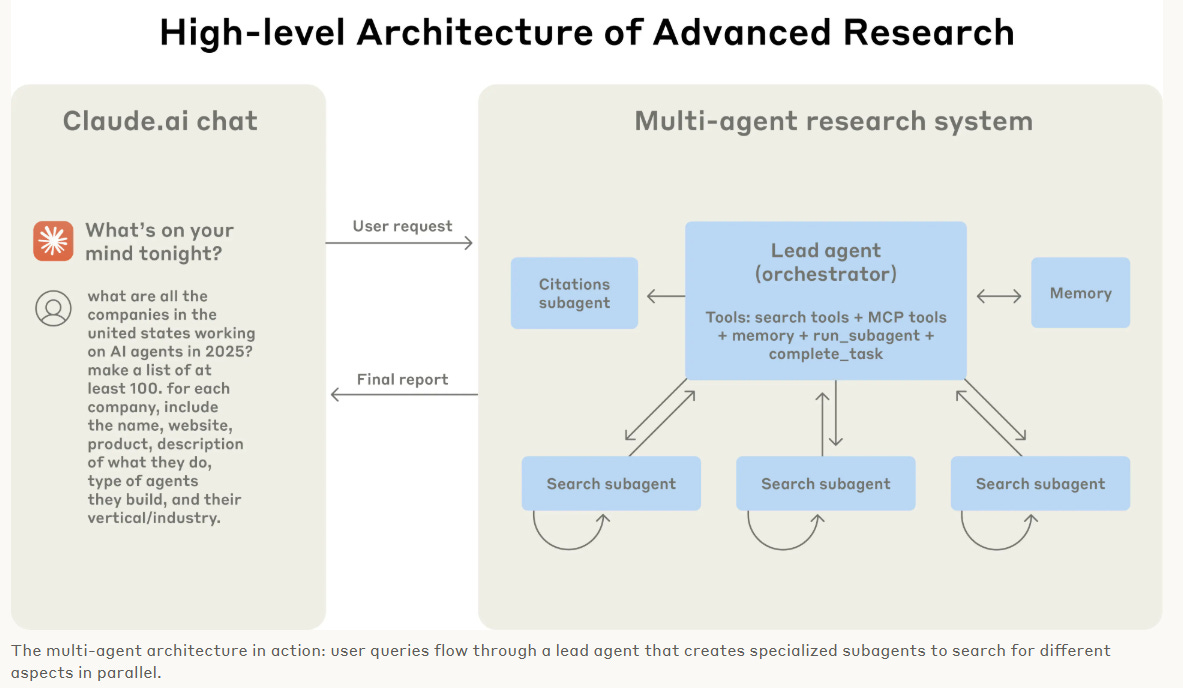
Claude shares engineering challenges and the lessons it learned from building multi-agent research system
• Claude's new Research capabilities enable agents to autonomously search across the web, Google Workspace, and integrations to handle complex tasks effectively;
• Multi-agent systems outperform single-agent architectures for research tasks by enabling parallel exploration, thus improving accuracy and speed by 90.2% in internal evaluations;
• Effective evaluations embrace flexible methods, employing LLM-as-judge evaluation techniques that accommodate diverse research paths rather than enforcing rigid procedural steps.
Context Engineering: Principles for Building Reliable Long-Running AI Agents in 2025
• In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI, context engineering emerges as critical, focusing on the automatic crafting of dynamic systems for effective agent communication and reliability.
• Sharing complete context and understanding implicit actions are revealed as fundamental principles in building reliable multi-agent AI systems, highlighting potential pitfalls of misaligned subagents.
• The challenges of long-context handling in multi-agent setups remain unsolved, as fragmented communication undermines reliability, prompting discussions on the enhancement of single-threaded agents for human-like discourse.
Gemini Code Assist Enhances Innovation with Gemini 2.5 and Personalization Features
• The latest update to Gemini Code Assist incorporates the state-of-the-art Gemini 2.5 model, enhancing chat capabilities, code generation reliability, and the accuracy of code transformations
• New personalization features in Gemini Code Assist enable developers to set custom commands and rules, ensuring a more tailored coding experience across different projects
• Enhanced chat features in Gemini Code Assist allow for improved context management, inclusion of entire folders, smarter context control, and support for multiple chat sessions;
Alibaba Releases Qwen3 AI Models Compatible with Apple's MLX Architecture
• China's Alibaba has unveiled Qwen3 AI models engineered for Apple’s MLX architecture, enhancing compatibility with a range of Apple devices, including iPhone, iPad, MacBook, and Mac;
• The Qwen3 models promise seamless integration across Apple's hardware and software ecosystems, marking a significant step in Alibaba's commitment to expanding its AI technology footprint globally;
HCLTech Partners with E.ON to Enhance Cloud Transformation Through AI and Automation
• HCLTech has entered a long-term partnership with E.ON to drive product-based transformation using advanced cloud and AI technologies, improving cloud and network maturity
• As part of the deal, HCLTech will develop a private cloud and manage E.ON's global cloud infrastructure, leveraging major hyperscalers for enhanced automation
• HCLTech's collaboration with E.ON highlights its commitment to European growth, aiming to deliver scalability, innovation, and efficiency through cloud and DevOps transformation;
Copilot Vision with Highlights Launches on Windows in the United States
• Copilot Vision on Windows with Highlights is now available in the US, designed to serve as an AI companion, enhancing user productivity by providing real-time insights and assistance
• With the ability to navigate multiple apps and offer step-by-step guidance, Copilot Vision supports tasks from improving photo lighting to reviewing travel plans, facilitating seamless multitasking
• Available for Windows 10 and 11, this feature is part of Copilot Labs and offers Deep Research and file search, optimizing users' workflow in a user-controlled environment.
Ericsson and AWS Join Forces to Advance Autonomous Networks with Agentic AI Technology
• Ericsson and AWS collaborate to enhance autonomous networks through Agentic AI, aiming to revolutionize network management for Communication Service Providers and improve efficiency and adaptability;
• The partnership focuses on integrating AWS's AI capabilities into Ericsson's Cognitive Network Solutions, promoting intent-based autonomous decision-making and reducing operational expenses for telecom providers worldwide;
• By leveraging Agentic AI, the collaboration seeks to transform network optimization and streamline operations, facilitating significant advancements in telecom technology and paving the way for future autonomous networks.
OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google Unveil AI Showdown for Code-Generating Model Comparison
• OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google collaborate with Lovable for The AI Showdown, offering unlimited access to their code-generating AI models over the June 14-15 weekend
• A $25k Content Challenge invites participants to create social media posts comparing AI model performance in Lovable, focusing on quality, reach, and depth, with submissions open until June 23
• The $40k Build Challenge encourages app development leveraging top AI models, with prizes for each model category and an overall winner, requiring minimal non-AI generated contributions.
⚖️ AI Ethics
ITU Report Highlights Surge in Indirect Emissions by AI Tech Giants 2020-2023
• The UN’s ITU reported a 150% average surge in indirect carbon emissions from AI-focused tech giants between 2020 and 2023 due to rising data centre energy demands
• Amazon, Microsoft, Meta, and Alphabet saw significant emissions increases, with Amazon leading at 182%, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable innovation
• AI's escalating development could strain global energy infrastructures, potentially emitting 102.6 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent annually, according to the ITU report;
AI Contribution to Python Code Reaches 30% in US by 2024 Study Finds
• A recent study highlights that by December 2024, AI contributed to 30.1% of Python code in the US, with varying rates across countries like Germany, France, and India
• Findings show newer GitHub users favor AI for coding, with AI use accounting for a 2.4% increase in quarterly commits, underscoring technology's growing role in programming
• Analyzing AI's economic impact, the study estimates it generates $9.6-14.4 billion annually in the US software sector by augmenting programming efficiency across nearly 900 occupations;
Italian Regulator Investigates AI Startup DeepSeek for Failing to Warn Users of False Information
• Italy's antitrust watchdog AGCM has initiated an investigation into DeepSeek for allegedly neglecting to warn users about the potential for AI-generated false information
• The Italian regulator criticized DeepSeek for providing inadequate warnings regarding AI "hallucinations," where outputs may contain inaccurate, misleading, or invented data
• Earlier this year, Italy's data protection authority ordered DeepSeek to block its chatbot due to unresolved privacy policy concerns;
AI Pioneer Hinton Warns: Plumbing May Outlast Automation, Unlike Legal Careers
• In a recent podcast, Geoffrey Hinton emphasized plumbing as a secure profession amid automation, citing its hands-on skills, unlike legal roles, which face significant AI replacement risks;
• Hinton, a key AI figure, expressed existential concerns about the technology's trajectory, fearing AI could eventually operate power stations alone and potentially sideline human roles;
• While highlighting productivity boosts, Hinton warned that AI could worsen social inequality, benefiting corporations while leaving workers, especially in pattern-based jobs, at risk of displacement.
EU Seeks 60 Experts for Advising AI Office on GPAI Risks and Systems
• The panel will guide the EU AI Office and national authorities on systemic risks and model classification, focusing on general-purpose AI models and systems
• The Commission seeks 60 experts with PhDs or equivalent experience in GPAI, cybersecurity, risk assessment, or related fields for a renewable 24-month term, remaining independent of AI providers
• The selection process will ensure gender balance and diverse representation across EU and EFTA, with 80% of experts from these regions, accepting applications until 14 September;
Concerns Grow Over Bureaucratic Hurdles in New York’s RAISE AI Safety Act
• New York State’s RAISE Act, authored by Alex Bores, aims to protect against AI harms but may complicate safety efforts with bureaucratic demands.
• The RAISE Act targets expensive, high-compute AI systems, requiring rigorous third-party audits and risk strategies, with heavy financial penalties for non-compliance.
• Experts argue RAISE's requirements could hinder practical safety outcomes, as market-driven external systems outpace regulatory frameworks in maintaining AI alignment.
Google DeepMind Partners with U.S. National Hurricane Center on AI Cyclone Forecasting Breakthrough
• Google DeepMind has claimed a breakthrough in hurricane forecasting with an AI system predicting cyclone paths and intensities, which could significantly improve upon traditional weather models
• The company introduced Weather Lab, an interactive platform with 50 cyclone scenarios 15 days ahead, and established a partnership with the U.S. National Hurricane Center
• DeepMind's new AI model showed enhanced accuracy and efficiency, achieving rapid forecast generation and excelling in intensity predictions, outperforming well-established systems like HAFS;
AI.gov Set to Launch July 4, Aiming to Transform Government with AI Integration
• The U.S. government is developing a website and API named “ai.gov” to foster innovation through AI, slated to launch on Independence Day, with usage analytics features
• “ai.gov” will initially integrate with OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, and potentially Amazon’s Bedrock and Meta’s LLaMA, also featuring an AI chatbot, though its exact function remains unspecified
• Internal sources express concerns about the GSA's AI initiatives potentially leading to security risks, with skepticism about AI's role in essential government decision-making processes.
Meta AI's Discover Feed Exposes Users' Private Chatbot Interactions to Public View
• Meta AI's discover feed unintentionally exposes users' personal chatbot conversations, revealing deeply private inquiries on topics like dating and health, leading to privacy concerns among users;
• Despite warnings about public posts, the new interface of Meta AI's discover feed causes confusion, allowing intimate conversations to be broadcasted, spurring both concern and public commentary;
• Meta continues significant investment in AI, with capital expenditures projected to reach up to $72 billion, as it tackles privacy issues while advancing towards AI superintelligence.
🎓AI Academia
Domain-Specific Benchmarks Enhance Evaluation of Multimodal Large Language Models
- A new paper delves into domain-specific benchmarks for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), highlighting unique capabilities and application challenges across seven key disciplines
- The research emphasizes the recent shift in the MLLM landscape, driven by "instruction tuning" and advanced reasoning techniques like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
- Foundational models, characterized by their transformative scaling, underpin MLLM evolution, with transformational strides in handling diverse modalities such as text and images for advanced AI applications.
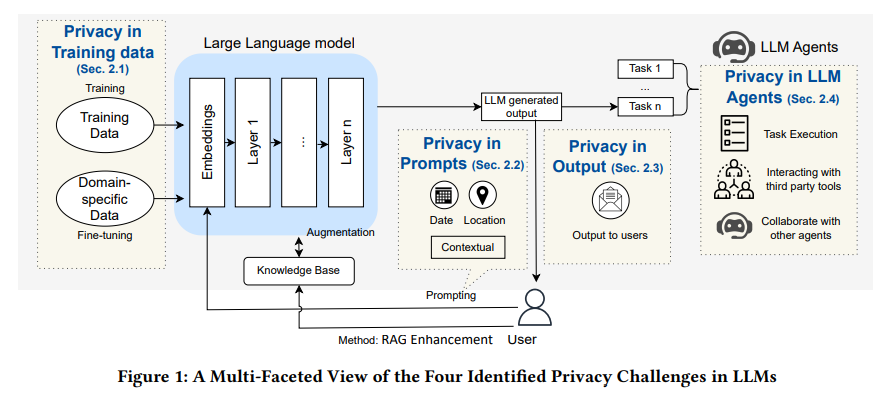
Exploring the Privacy Paradox in Large Language Models: Challenges and Solutions Unveiled
• A recent analysis highlights a gap in understanding the privacy risks posed by user interactions and the sophisticated capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs)
• The study categorizes LLM privacy challenges into four areas: training data privacy issues, user prompt risks, output vulnerabilities, and agent privacy challenges
• Existing privacy mitigation strategies for LLMs have limitations, with the paper calling for further research to address these complex privacy concerns effectively.
New Benchmark Assesses Large Language Models in Comprehensive Real-World Fact-Checking Tasks
• RealFactBench is a new benchmark developed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in real-world fact-checking tasks across multiple domains;
• The benchmark features 6,000 high-quality claims from authoritative sources, covering various modalities and domains, enabling comprehensive assessment of models' capabilities in practical scenarios;
• RealFactBench introduces a novel evaluation metric, the Unknown Rate (UnR), to assess models' handling of uncertainty, balancing over-conservatism and over-confidence in fact-checking endeavors.
New Study Addresses Gender Bias in Large Language Models Using Advanced Techniques
• A recent study on arXiv highlights how large language models significantly advance efficiency but suffer from gender bias with profound societal impacts
• In the Chinese Corpus for Gender Bias Detection challenge, innovative methods like reinforcement learning and Chain-of-Thought reasoning help detect, classify, and mitigate bias
• The approach using Direct Preference Optimization, leveraging GPT-4 for dataset annotation, ranked first in all NLPCC 2025 Shared Task 7 subtasks for addressing gender bias.
Study Highlights Secondary Risks in Large Language Models for Safe AI Integration
• A recent study highlights a new class of failures in Large Language Models, termed secondary risks, which manifest during typical interactions and evade existing safety protocols;
• Researchers developed a framework, SecLens, to systematically identify these secondary risks by optimizing task relevance, risk activation, and linguistic plausibility across various models;
• SecRiskBench, a newly introduced benchmark dataset containing 650 prompts, aids the evaluation of LLM safety by showcasing widespread secondary risks that persist across models and modalities.
Study Identifies Information Suppression Mechanisms in China's DeepSeek Language Model
• New research unveils semantic-level information suppression in DeepSeek, revealing that sensitive content appears in internal reasoning but is altered or omitted in final outputs;
• The study proposes an auditing framework used on 646 politically sensitive prompts, highlighting DeepSeek’s tendencies to suppress transparency and amplify state-aligned language;
• Researchers emphasize the importance of auditing AI models to ensure unbiased information access and evaluate practices related to alignment, content moderation, and censorship.
New Framework Automates Credit Card Fraud Investigations Using Large Language Models
• Researchers from Ben-Gurion University have developed the FAA Framework, an AI-based tool using large language models to automate credit card fraud investigations and streamline reporting.
• The FAA Framework utilizes LLMs' reasoning, code execution, and visual analysis capabilities to perform systematic fraud investigations, significantly reducing manual workload for analysts.
• In empirical testing, the framework efficiently handled 500 fraud cases, showing that it could simplify the investigation process and enhance the reliability and accuracy of results.
New gSMILE Framework Enhances Transparency in Large Language Models with Explanations
• The newly introduced gSMILE framework offers a model-agnostic approach to interpreting large language models by analyzing how specific input prompt parts influence output
• By generating intuitive heatmaps, gSMILE identifies and visually highlights influential words in prompts, enhancing the understanding of LLM decision-making processes
• gSMILE's evaluation across leading LLMs showed improvements in accuracy, consistency, stability, and fidelity, advancing the transparency and trustworthiness of AI systems.
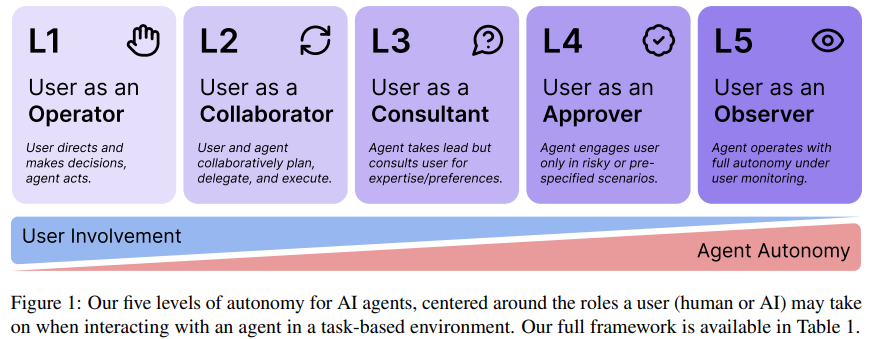
Researchers Define Autonomy Levels for AI Agents to Mitigate Operational Risks
• A new working paper from the University of Washington outlines five levels of AI agent autonomy, focusing on user roles like operator, collaborator, and observer
• This framework provides a structured approach for developers, separating autonomy decisions from agent capabilities and environment, emphasizing responsible deployment
• Potential applications include AI autonomy certificates for single- and multi-agent systems, aiming to standardize and govern agent behavior responsibly.
Survey Highlights Risks and Opportunities of Generative AI in Digital and Healthcare Sectors
• Large Language Models and generative AI systems are set to play a pivotal role in platform integrity, enhancing cybersecurity measures while simultaneously posing privacy challenges in digital ecosystems;
• A steep increase in AI-related security risks is anticipated, with LLM-assisted malware projected to surge from 2% in 2021 to 50% by 2025, highlighting the urgency for advanced defense strategies;
• Major digital platforms are increasingly integrating LLM capabilities to automate and improve review and moderation processes, aiming to bolster compliance and trust within their ecosystems.
About SoRAI: SoRAI is committed to advancing AI literacy through practical, accessible, and high-quality education. Our programs emphasize responsible AI use, equipping learners with the skills to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. Our flagship AIGP certification courses, built on real-world experience, drive AI governance education with innovative, human-centric approaches, laying the foundation for quantifying AI governance literacy. Subscribe to our free newsletter to stay ahead of the AI Governance curve.